



Miscellaneous
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo





Transcript
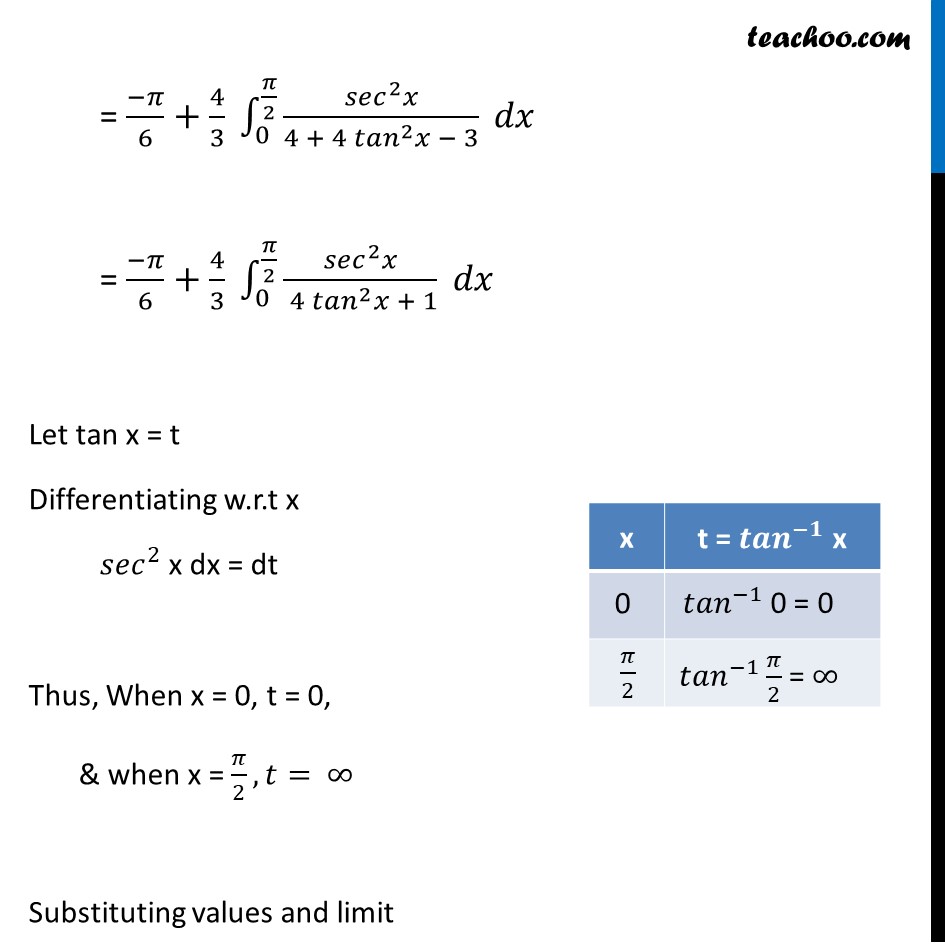
Misc 26 Evaluate the definite integral ∫_0^(𝜋/2)▒〖(cos^2𝑥 𝑑𝑥)/(cos^2𝑥 + 4 sin^2𝑥 ) 〗 Let I = ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒(〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥)/(〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥 + 4〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^2 𝑥) 𝑑𝑥 = ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒(〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥)/(〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥 + 4(〖1 − 𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥) 𝑑𝑥) = ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒(〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥)/(4 − 3 〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥) 𝑑𝑥 = (−1)/3 ∫1_0^(𝜋/4)▒〖 (−3 〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥 )/(4 − 3 〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥) 〗 𝑑𝑥 = (−1)/3 ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒(〖− 3 𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥 + 4 − 4)/(4 − 3 〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥) 𝑑𝑥 = (−1)/3 ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒(〖4 − 3 𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥 − 4)/(4 − 3 〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥) 𝑑𝑥 = (−1)/3 ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒〖1−4/(4 − 3 〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥)〗 𝑑𝑥 Dividing numerator and denominator by 〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥 = (−1)/3 (𝜋/2)+4/3 ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒(𝑑𝑥/(〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥))/((4 − 3 〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥 )/(〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥)) 𝑑𝑥 = (−1)/3 (𝜋/2)+4/3 ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒(〖𝑠𝑒𝑐〗^2 𝑥)/(4 〖𝑠𝑒𝑐〗^2 𝑥 − 3) 𝑑𝑥 = (−𝜋)/6+4/3 ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒(〖𝑠𝑒𝑐〗^2 𝑥)/(4 (1 + 〖𝑡𝑎𝑛〗^2 𝑥) − 3) 𝑑𝑥 = (−𝜋)/6+4/3 ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒(〖𝑠𝑒𝑐〗^2 𝑥)/(4 + 4 〖𝑡𝑎𝑛〗^2 𝑥 − 3) 𝑑𝑥 = (−𝜋)/6+4/3 ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒(〖𝑠𝑒𝑐〗^2 𝑥)/( 4 〖𝑡𝑎𝑛〗^2 𝑥 + 1) 𝑑𝑥 Let tan x = t Differentiating w.r.t x 〖𝑠𝑒𝑐〗^2 x dx = dt Thus, When x = 0, t = 0, & when x = 𝜋/2, 𝑡= ∞ Substituting values and limit I = (−𝜋)/6+4/3 ∫1_0^(𝜋/2)▒(〖𝑠𝑒𝑐〗^2 𝑥)/( 4 〖𝑡𝑎𝑛〗^2 𝑥 + 1) 𝑑𝑥 ∴ I =(−𝜋)/6+4/3 ∫1_0^∞▒𝑑𝑡/(〖4𝑡〗^2+1) = (−𝜋)/6+4/3 ∙1/4 ∫1_0^∞▒𝑑𝑡/(〖 𝑡〗^2+1/4) =(−𝜋)/6+4/3∙1/4 × 1/((1/2) ) [〖𝑡𝑎𝑛〗^(−1) 𝑡/(1/2)]_0^∞ = (−𝜋)/6+2/3∙ [〖𝑡𝑎𝑛〗^(−1) 2𝑡]_0^∞ =(−𝜋)/6+2/3∙〖[𝑡𝑎𝑛〗^(−1) ∞−〖𝑡𝑎𝑛〗^(−1) 0] = −𝜋/6+2/3∙[𝜋/2−0] =−𝜋/6+𝜋/3 =𝝅/𝟔