![Ex 6.3, 12 - Find max and min of x + sin 2x on [0, 2pi] - Ex 6.3 - Ex 6.3](https://cdn.teachoo.com/1e231181-e8a1-4bf2-8869-cbcfab2b6055/slide36.jpg)






Ex 6.3
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo
![Ex 6.3, 12 - Find max and min of x + sin 2x on [0, 2pi] - Ex 6.3 - Ex 6.3](https://cdn.teachoo.com/1e231181-e8a1-4bf2-8869-cbcfab2b6055/slide36.jpg)








Transcript
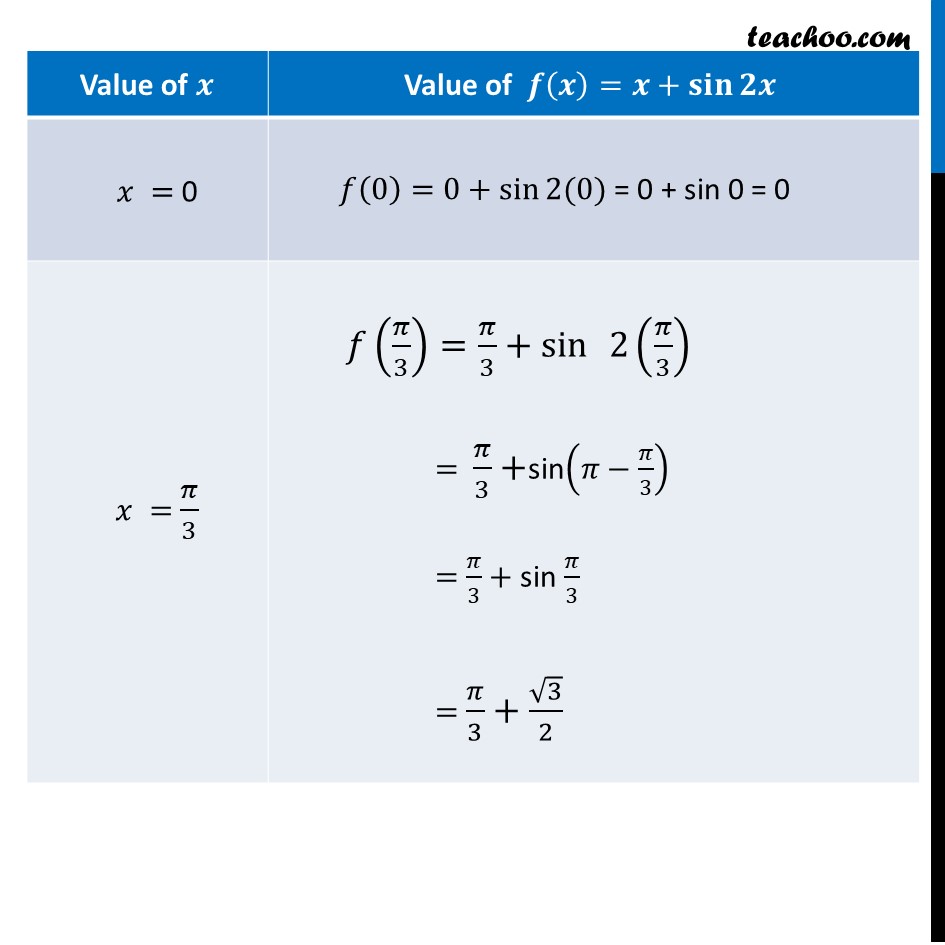
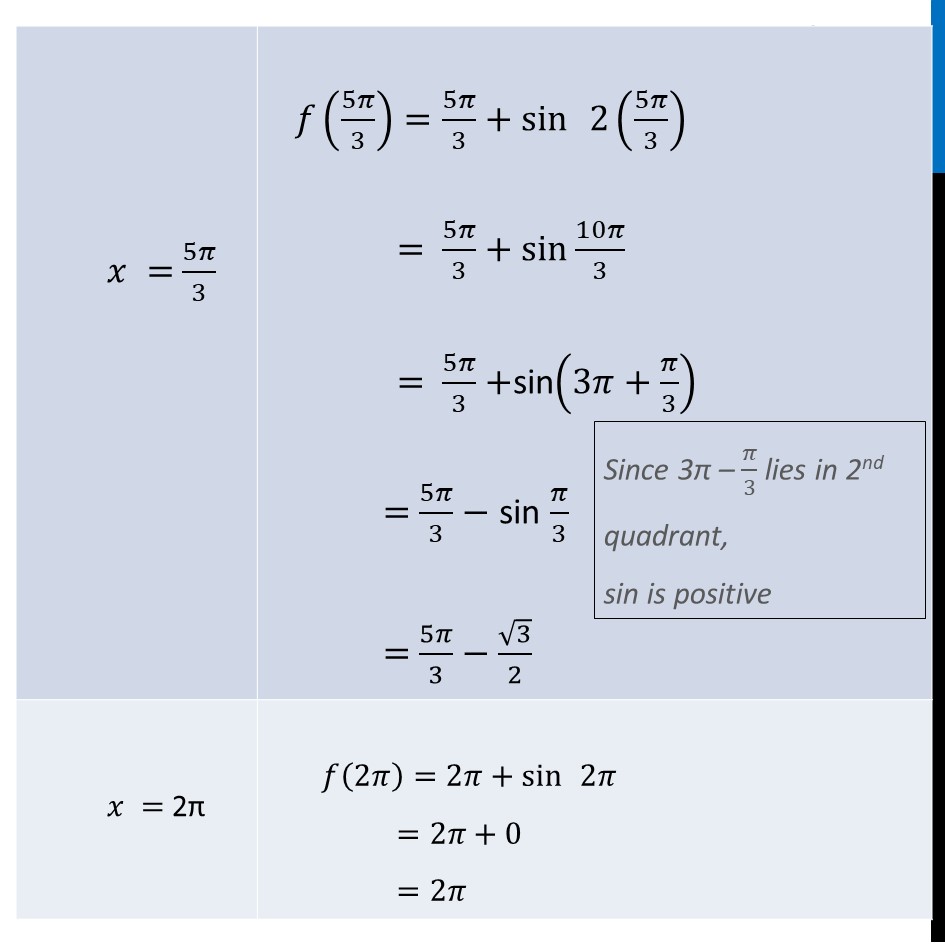
Ex 6.3, 12 Find the maximum and minimum values of 𝑥 + sin 2𝑥 on [0, 2π ] Let f(𝑥)=𝑥 + sin 2𝑥 Finding f’(𝒙) 𝑓’(𝑥)=𝑑(𝑥 + sin 2𝑥)/𝑑𝑥 =1+2 cos2𝑥 Putting f’(𝒙)=𝟎 1 + 2 cos 2𝑥=0 2 cos 2𝑥=−1 cos 2𝑥=(−1)/2 cos 2𝑥=cos〖2𝜋/3〗 General solution for cos 2𝑥 is 2𝑥=2𝑛𝜋±2𝜋/3 𝑥=(2𝑛𝜋 ± 2𝜋/3)/2 𝑥= nπ ± 𝜋/3 Putting 𝑛=0 𝑥=0(𝜋)±𝜋/3 =±𝜋/3 " " We know that 𝑐𝑜𝑠 60°=1/2 And cos is negative in 2nd & 3rd quadrant 𝜃 = 180 − 60 = 120 = 120 × 𝜋/180 = 2𝜋/3 So, 𝑥=(−𝜋)/3,𝜋/3 Since Given 𝑥 ∈[0 , 2𝜋] ∴ 𝑥=𝜋/3 only Putting 𝑛=1 𝑥=(1)𝜋±𝜋/3 =𝜋±𝜋/3 =(3𝜋 + 𝜋)/3 , (3𝜋 − 𝜋)/3 =4𝜋/3 , 2𝜋/3 Putting 𝑛=2 𝑥=2(𝜋)±𝜋/3 𝑥=2𝜋−𝜋/3 & 2𝜋+𝜋/3 𝑥=(6𝜋 − 𝜋)/3 & (6𝜋 + 𝜋)/3 𝑥=5𝜋/3 & 7𝜋/3 So, 𝑥=5𝜋/3 only Also, We are given interval 𝑥 ∈[0 , 2𝜋] Hence , calculating f(𝑥) at 𝑥=0 , 𝜋/3 , 2𝜋/3 , 4𝜋/3 , 5𝜋/3 , 2𝜋 Hence, f(𝑥) is Maximum at 𝑥=2𝜋 Maximum value of f(𝒙)=𝟐𝝅 & f(𝑥) is Minimum at 𝑥=0 Minimum value of f(𝒙)=𝟎