





Ex 7.5
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo








Transcript
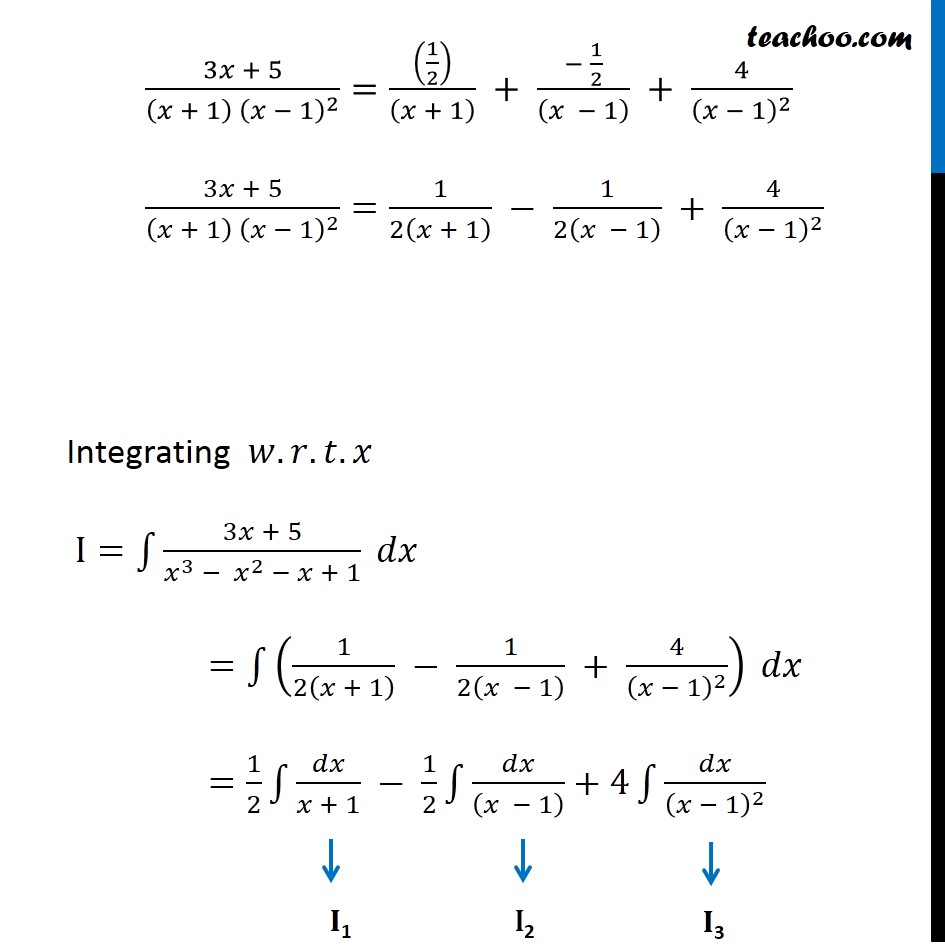
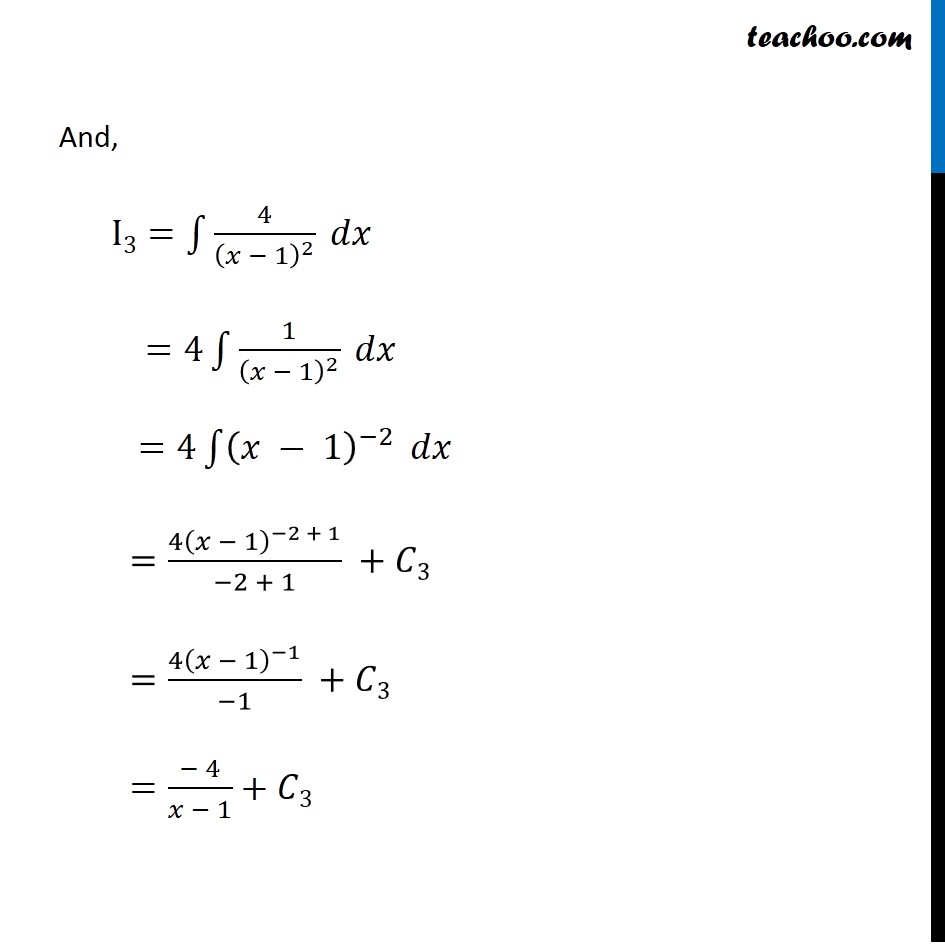
Ex 7.5, 9 Integrate the function (3𝑥 + 5)/(𝑥^3 − 𝑥^2 − 𝑥 + 1) Let I=∫1▒(3𝑥 + 5)/(𝑥^3 − 𝑥^2 − 𝑥 + 1) 𝑑𝑥 We can write integrand as (3𝑥 + 5)/(𝑥^3 − 𝑥^2 − 𝑥 + 1)=(3𝑥 + 5)/(𝑥 − 1)(𝑥^2 − 1) =(3𝑥 + 5)/(𝑥 − 1)(𝑥^2 − 1^2 ) =(3𝑥 + 5)/((𝑥 − 1) (𝑥 − 1) (𝑥 + 1) ) =(3𝑥 + 5)/〖(𝑥 + 1) (𝑥 − 1)〗^2 Rough 𝑥^3−𝑥^2−𝑥+1 Put 𝑥=1 1^3−1^2−1+1 =1−1−1+1 =0 So, 𝑥−1 is a factor of 𝑥^3−𝑥^2−𝑥+1 We can write it as (3𝑥 + 5)/〖(𝑥 + 1) (𝑥 − 1)〗^2 =𝐴/((𝑥 + 1) ) + 𝐵/((𝑥 − 1) ) + 𝐶/(𝑥 − 1)^2 (3𝑥 + 5)/〖(𝑥 + 1) (𝑥 − 1)〗^2 =(𝐴(𝑥 − 1)^2 + 𝐵(𝑥 + 1)(𝑥 − 1) + 𝐶(𝑥 + 1))/(𝑥 + 1)(𝑥 − 1)(𝑥 − 1) (3𝑥 + 5)/〖(𝑥 + 1) (𝑥 − 1)〗^2 =(𝐴(𝑥 − 1)^2 + 𝐵(𝑥^2 − 1) + 𝐶(𝑥 + 1))/((𝑥 + 1) (𝑥 − 1)^2 ) By Cancelling denominator 3𝑥+5=𝐴(𝑥−1)^2+𝐵(𝑥^2−1)+𝐶(𝑥+1) Put 𝑥=1 in (1) 3×1+5=𝐴(1−1)^2+𝐵(1^2−1)+𝐶(1+1) 8=𝐴×0+ 𝐵×0+𝐶×2 …(1) 8=2𝐶 𝐶=4 Putting 𝑥=−1 in (1) 3𝑥+5=𝐴(𝑥−1)^2+𝐵(𝑥^2−1)+𝐶(𝑥+1) 3(−1)+5=𝐴(−1−1)^2+𝐵((−1)^2−1)+𝐶(−1+1) −3+5=𝐴(−2)^2+𝐵(1−1)+𝐶(0) 2=4𝐴+𝐵×0+𝐶×0 2=4𝐴 𝐴=1/2 Putting x = 0 in (1) 3𝑥+5=𝐴(𝑥−1)^2+𝐵(𝑥^2−1)+𝐶(𝑥+1) 3(0)+5=𝐴(0−1)^2+𝐵(0−1)+𝐶(0+1) 5=𝐴−𝐵+𝐶 5= 1/2 −𝐵+4 5= −𝐵+9/2 𝐵=9/2 −5 𝐵=(−1)/2 Hence, we can our equation as write (3𝑥 + 5)/〖(𝑥 + 1) (𝑥 − 1)〗^2 =𝐴/((𝑥 + 1) ) + 𝐵/((𝑥 − 1) ) + 𝐶/(𝑥 − 1)^2 (3𝑥 + 5)/〖(𝑥 + 1) (𝑥 − 1)〗^2 =((1/2))/((𝑥 + 1) ) + (− 1/2)/((𝑥 − 1) ) + 4/(𝑥 − 1)^2 (3𝑥 + 5)/〖(𝑥 + 1) (𝑥 − 1)〗^2 =1/2(𝑥 + 1) − 1/2(𝑥 − 1) + 4/(𝑥 − 1)^2 Integrating 𝑤.𝑟.𝑡.𝑥 I=∫1▒(3𝑥 + 5)/(𝑥^3 − 𝑥^2 − 𝑥 + 1) 𝑑𝑥 =∫1▒(1/2(𝑥 + 1) − 1/2(𝑥 − 1) + 4/(𝑥 − 1)^2 ) 𝑑𝑥 =1/2 ∫1▒𝑑𝑥/(𝑥 + 1) − 1/2 ∫1▒𝑑𝑥/((𝑥 − 1) )+4∫1▒𝑑𝑥/(𝑥 − 1)^2 Hence I=I1−I2+I3 Now, I1=1/2 ∫1▒1/(𝑥 + 1) 𝑑𝑥 =1/2 log|𝑥+1|+𝐶1 Also, I2 =1/2 ∫1▒1/(𝑥 − 1) 𝑑𝑥 = 1/2 log|𝑥−1|+𝐶2 And, I3=∫1▒4/(𝑥 − 1)^2 𝑑𝑥 =4∫1▒1/(𝑥 − 1)^2 𝑑𝑥 =4∫1▒(𝑥 − 1)^(−2) 𝑑𝑥 =(4(𝑥 − 1)^(−2 + 1))/(−2 + 1) +𝐶3 =(4(𝑥 − 1)^(−1))/(−1) +𝐶3 =(− 4)/(𝑥 − 1)+𝐶3 Therefore I=I1−I2+I3 I=1/2 log|𝑥+1|+𝐶1− 1/2 log|𝑥−1|−𝐶2+(− 4)/(𝑥 − 1)+𝐶3 =1/2 log|𝑥+1|+− 1/2 log|𝑥−1|−4/(𝑥 − 1) +𝐶1−𝐶2+𝐶3 =1/2 [log|𝑥+1|−log|𝑥−1| ]−4/(𝑥 − 1) +𝐶 =𝟏/𝟐 𝒍𝒐𝒈|(𝒙 + 𝟏)/(𝒙 − 𝟏)|− 𝟒/(𝒙 − 𝟏) +𝑪