
Ex 5.1
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo


Transcript
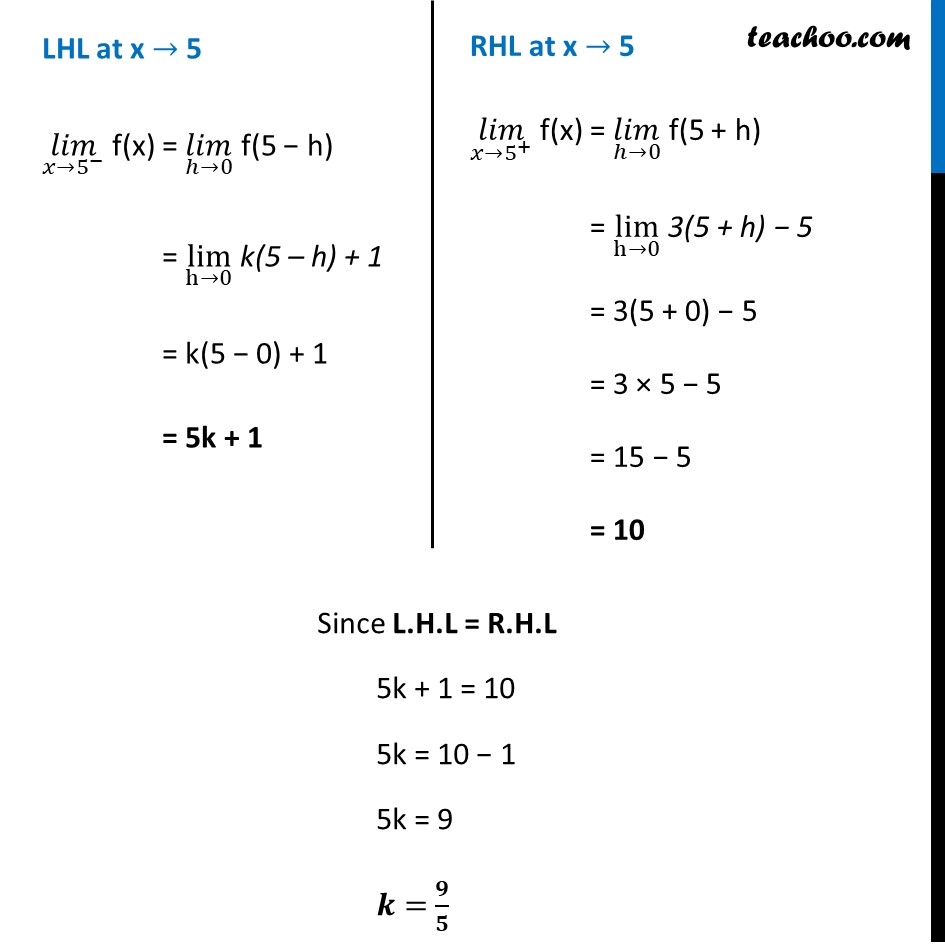
Ex 5.1, 29 Find the values of k so that the function f is continuous at the indicated point 𝑓(𝑥)={█(𝑘𝑥+1, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥≤5@3𝑥−5, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥>5)┤ at x = 5 Given that function is continuous at 𝑥 =5 𝑓 is continuous at 𝑥 =5 if L.H.L = R.H.L = 𝑓(5) i.e. lim┬(x→5^− ) 𝑓(𝑥)=lim┬(x→5^+ ) " " 𝑓(𝑥)= 𝑓(5) LHL at x → 5 (𝑙𝑖𝑚)┬(𝑥→5^− ) f(x) = (𝑙𝑖𝑚)┬(ℎ→0) f(5 − h) = lim┬(h→0) k(5 – h) + 1 = k(5 − 0) + 1 = 5k + 1 RHL at x → 5 (𝑙𝑖𝑚)┬(𝑥→5^+ ) f(x) = (𝑙𝑖𝑚)┬(ℎ→0) f(5 + h) = lim┬(h→0) 3(5 + h) − 5 = 3(5 + 0) − 5 = 3 × 5 − 5 = 15 − 5 = 10 Since L.H.L = R.H.L 5k + 1 = 10 5k = 10 − 1 5k = 9 𝒌= 𝟗/𝟓