





Ex 7.7
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo








Transcript
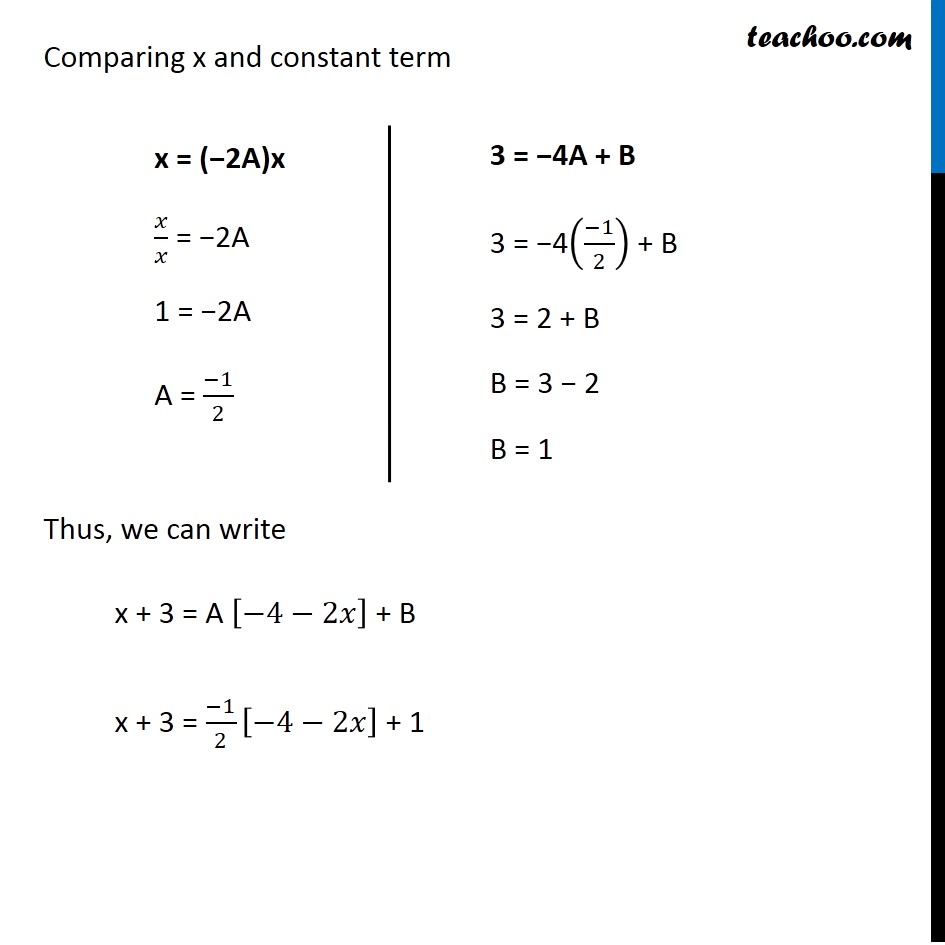
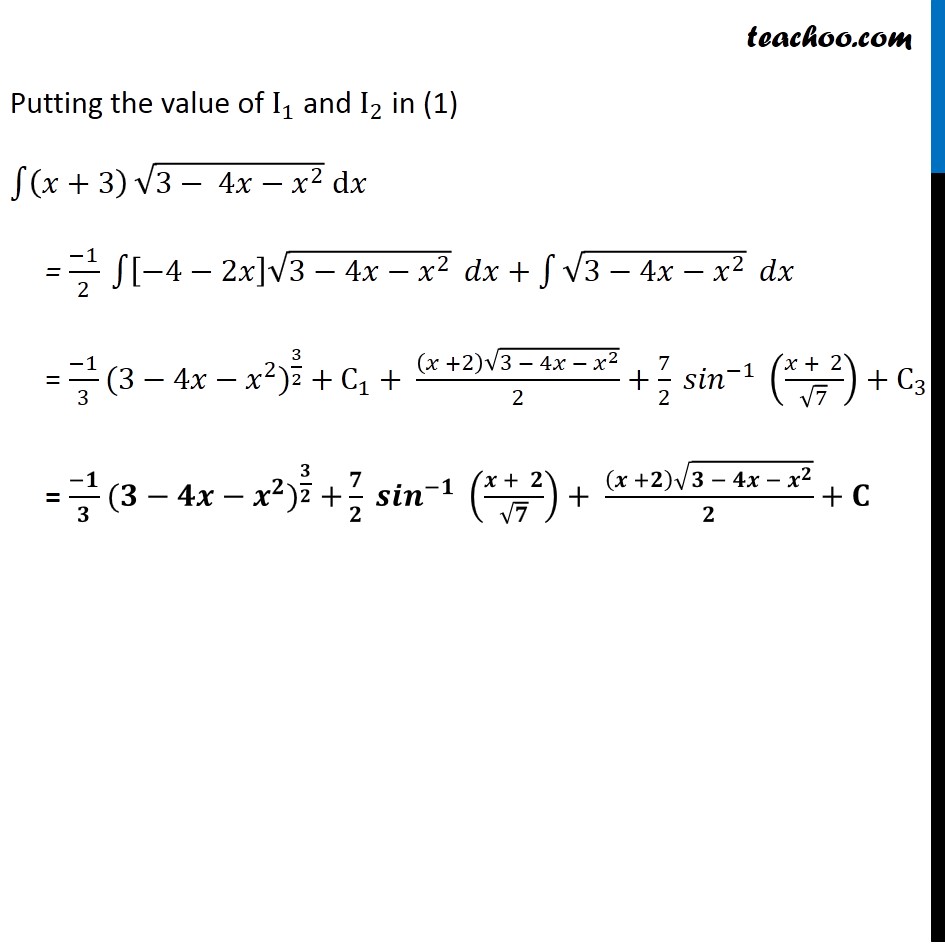
Ex 7.7, 14 (Supplementary NCERT) (𝑥+3) √(3−4𝑥〖−𝑥〗^2 ) (𝑥+3) √(3−4𝑥〖−𝑥〗^2 ) We can write it as:- x + 3 = A [𝑑/𝑑𝑥 (3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 )]+ B x + 3 = A [0−4−2𝑥]+ B x + 3 = A [−4−2𝑥]+ B x + 3 = −4"A"−2"A" 𝑥+ B x + 3 = −2"A" 𝑥+(−4"A"+𝐵) Comparing x and constant term Thus, we can write x + 3 = A [−4−2𝑥] + B x + 3 = (−1)/2 [−4−2𝑥] + 1 x = (−2A)x 𝑥/𝑥 = −2A 1 = −2A A = (−1)/2 3 = −4A + B 3 = −4((−1)/2) + B 3 = 2 + B B = 3 − 2 B = 1 Integrating the function w.r.t.x ∫1▒〖(𝑥+3) √(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 ) 〗 𝑑𝑥 = ∫1▒〖[−1/2 [−4 −2𝑥]+1] 〗 √(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥 = ∫1▒〖[−1/2 [−4 −2𝑥] √(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 )+1√(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 )] 〗 𝑑𝑥 = ∫1▒〖−1/2 [−4 −2𝑥] √(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥+〗 ∫1▒√(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥 = −1/2 ∫1▒〖[−4 −2𝑥] √(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥+〗 ∫1▒√(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥 Solving 𝑰_𝟏 I_1 = (−1)/2 ∫1▒〖[−4−2𝑥] √(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 )〗 𝑑𝑥 Let 3 − 4𝑥 − 𝑥^2 = t Diff. both sides w.r.t.x 0 − 4 −2x = 𝑑𝑡/𝑑𝑥 − 4 − 2x = 𝑑𝑡/𝑑𝑥 dx = 𝑑𝑡/(−4 − 2𝑥) Thus, our equation becomes I_1 = (−1)/2 ∫1▒〖[−4−2𝑥] √(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 )〗 𝑑𝑥 Putting the value if (3−4𝑥−𝑥^2) and dx, we get I_1 = (−1)/2 ∫1▒〖[−4−2𝑥] √𝑡〗. 𝑑𝑥 I_1 = (−1)/2 ∫1▒〖[−4−2𝑥] √𝑡〗. 𝑑𝑡/[−4−2𝑥] ("Using t = " 3−4𝑥 −𝑥^2 ) Solving 𝑰_𝟐 I_2 = ∫1▒√(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥 I_2 = ∫1▒√(3−(4𝑥+𝑥^2)) 𝑑𝑥 I_2 = ∫1▒√(3−(𝑥^2+4𝑥)) 𝑑𝑥 I_2 = ∫1▒〖√(3−[𝑥^2+2(2) (𝑥))] 〗 𝑑𝑥 I_2 = ∫1▒〖√(3−[𝑥^2+2(2)+(2)^2 −〖(2)〗^2 )] 〗 𝑑𝑥 I_2 = ∫1▒〖√(3−[(〖𝑥+2)〗^2− 〖(2)〗^2 )] 〗 𝑑𝑥 I_2 = ∫1▒〖√(3−(𝑥+2)^2+ 〖(2)〗^2 ) 〗 𝑑𝑥 I_2 = ∫1▒〖√(3−(𝑥+2)^2+4) 〗 𝑑𝑥 I_2 = ∫1▒〖√(7−(𝑥+2)^2 ) 〗 𝑑𝑥 I_2 = ∫1▒〖√(〖(√7)〗^2−(𝑥+2)^2 ) 〗 𝑑𝑥 I_2 = (𝑥 + 2)/2 √((√7)^2−(𝑥+2)^2 )+〖(7)〗^2/2 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1) ((𝑥 + 2)/√7)+ C_2 I_2 = (𝑥 + 2)/2 √(7−〖(𝑥〗^2 + 4𝑥 +4)) +7/2 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1) ((𝑥 + 2)/√7)+ C_2 I_2 = (𝑥 + 2)/2 √(7−𝑥^2 + 4𝑥 +4) +7/2 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1) ((𝑥 + 2)/√7)+ C_2 I_2 = (𝑥 + 2)/2 √(3− 4𝑥−𝑥^2 ) +7/2 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1) ((𝑥 + 2)/√7)+ C_2 It is of form √(𝑎^2−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥=1/2 𝑥√(𝑎^2−𝑥^2 )+𝑎^2/2 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1) (𝑥/𝑎)+ 𝐶_2 Replacing x by (x + 2) a by √7 , we get Putting the value of I_1 and I_2 in (1) ∫1▒(𝑥+3) √(3− 4𝑥−𝑥^2 ) d𝑥 = (−1)/2 ∫1▒〖[−4−2𝑥] √(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 )〗 𝑑𝑥+∫1▒√(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥 = (−1)/3 〖(3−4𝑥−𝑥^2)〗^(3/2) + C_1+ ((𝑥 +2) √(3 − 4𝑥 − 𝑥^2 ))/2+7/2 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1) ((𝑥 + 2)/√7)+ C_3 = (−𝟏)/𝟑 〖(𝟑−𝟒𝒙−𝒙^𝟐)〗^(𝟑/𝟐) +𝟕/𝟐 〖𝒔𝒊𝒏〗^(−𝟏) ((𝒙 + 𝟐)/√𝟕)+ ((𝒙 +𝟐) √(𝟑 − 𝟒𝒙 − 𝒙^𝟐 ))/𝟐+ 𝐂