


Examples
Last updated at December 16, 2024 by Teachoo




Transcript
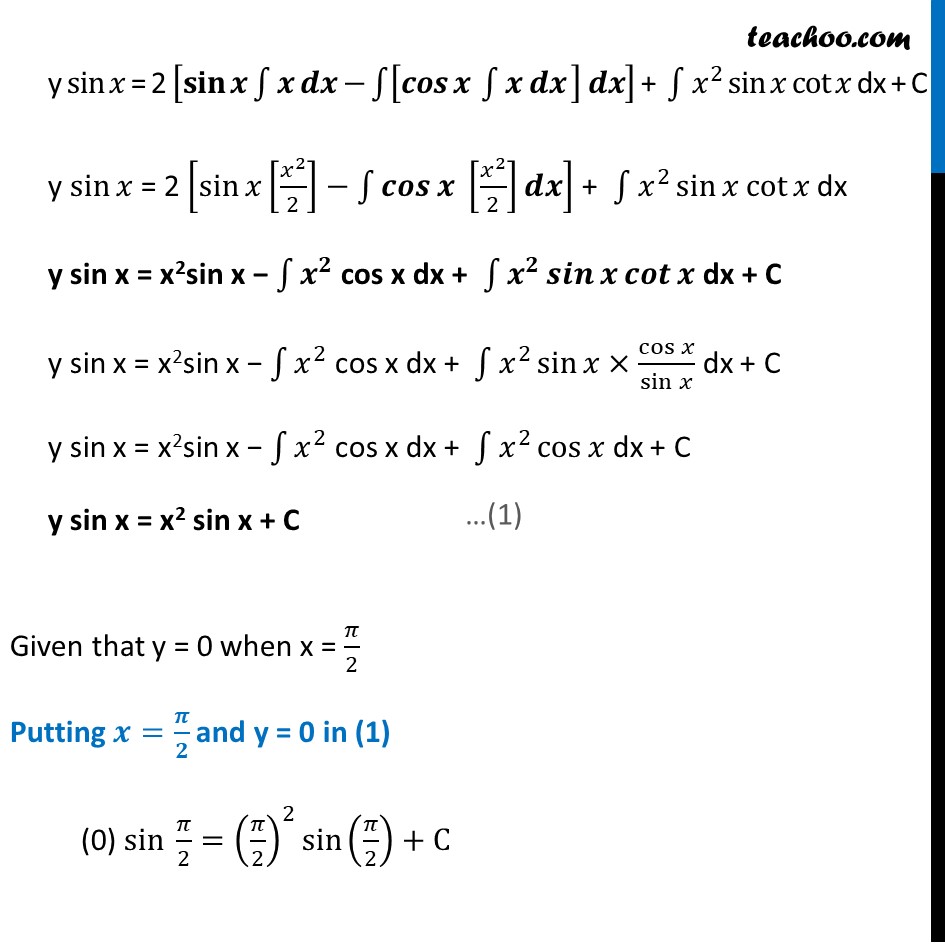
Example 17 Find the particular solution of the differential equation 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥+𝑦 cot〖𝑥=2𝑥+𝑥^2 cot𝑥(𝑥≠0) 〗 given that 𝑦=0 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑥=𝜋/2 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥+𝑦 cot〖𝑥=2𝑥+𝑥^2 cot𝑥 〗 Differential equation is of the form 𝒅𝒚/𝒅𝒙+𝑷𝒚=𝑸 where P = cot x & Q = 2x + x2 cot x IF = 𝑒^∫1▒〖𝑝 𝑑𝑥〗 IF = 𝒆^∫1▒〖𝐜𝐨𝐭𝒙 𝒅𝒙〗 IF = 〖𝑒^logsin𝑥 〗^" " IF = sin x Solution is y (IF) =∫1▒〖(𝑄×𝐼𝐹) 𝑑𝑥+𝑐〗 y sin x = ∫1▒〖𝐬𝐢𝐧𝒙×(𝟐𝒙+𝒙^(𝟐 ) 𝐜𝐨𝐭𝒙 ) 𝒅𝒙〗 + C y sin x = ∫1▒〖(2𝑥 sin𝑥+𝑥^(2 ) sin〖𝑥 cot𝑥 〗 ) 𝑑𝑥〗 + C y sin𝑥 = ∫1▒〖2𝑥 sin𝑥 𝑑𝑥+〗 ∫1▒〖𝑥^2 sin𝑥 cot𝑥 𝑑𝑥+〗 𝐶 y sin𝑥 = 2∫1▒〖𝐬𝐢𝐧𝒙 (𝒙) 𝒅𝒙〗+∫1▒〖𝑥^2 sin𝑥 cot𝑥 𝑑𝑥+〗 𝐶 Integrating by parts with ∫1▒〖𝑓(𝑥) 𝑔(𝑥) 𝑑𝑥=𝑓(𝑥) ∫1▒〖𝑔(𝑥) 𝑑𝑥 −∫1▒〖[𝑓^′ (𝑥) ∫1▒〖𝑔(𝑥) 𝑑𝑥] 𝑑𝑥〗〗〗〗 Take f (x) = sin x & g (x) = 𝑥 y sin𝑥 = 2 [𝐬𝐢𝐧𝒙 ∫1▒〖𝒙 𝒅𝒙−〗 ∫1▒〖[𝒄𝒐𝒔〖𝒙 ∫1▒〖𝒙 𝒅𝒙〗 〗 ] 𝒅𝒙〗] + ∫1▒〖𝑥^2 sin𝑥 〗 cot𝑥 dx + C y sin𝑥 = 2 [sin𝑥 [𝑥^2/2]−∫1▒〖𝒄𝒐𝒔〖𝒙 〗 [𝑥^2/2]𝒅𝒙〗] + ∫1▒〖𝑥^2 sin𝑥 〗 cot𝑥 dx y sin x = x2sin x − ∫1▒𝒙^𝟐 cos x dx + ∫1▒〖𝒙^𝟐 𝒔𝒊𝒏𝒙 〗 𝒄𝒐𝒕𝒙 dx + C y sin x = x2sin x − ∫1▒𝑥^2 cos x dx + ∫1▒〖𝑥^2 sin𝑥 〗×cos𝑥/sin𝑥 dx + C y sin x = x2sin x − ∫1▒𝑥^2 cos x dx + ∫1▒〖𝑥^2 cos𝑥 〗 dx + C y sin x = x2 sin x + C Given that y = 0 when x = 𝜋/2 Putting 𝒙=𝝅/𝟐 and y = 0 in (1) (0) sin 𝜋/2=(𝜋/2)^2 sin〖(𝜋/2)+C〗 0 =𝜋^2/4 (1)+C 〖−𝝅〗^𝟐/𝟒=𝐂 Putting value in C in (1) y sin x = x2 sin x + C y sin x = 𝒙^𝟐 𝒔𝒊𝒏〖𝒙 −〗 𝝅^𝟐/𝟒 Dividing both sides by sin x (𝑦 sin𝑥)/sin𝑥 =(𝑥^2 sin𝑥)/sin𝑥 −𝜋^2/(4 sin𝑥 ) 𝒚=𝒙^𝟐−𝝅^𝟐/〖𝟒 𝐬𝐢𝐧〗𝒙 where sin〖𝑥≠0〗 y sin𝑥 = 2 [𝐬𝐢𝐧𝒙 ∫1▒〖𝒙 𝒅𝒙−〗 ∫1▒〖[𝒄𝒐𝒔〖𝒙 ∫1▒〖𝒙 𝒅𝒙〗 〗 ] 𝒅𝒙〗] + ∫1▒〖𝑥^2 sin𝑥 〗 cot𝑥 dx + C