




Examples
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo






Transcript
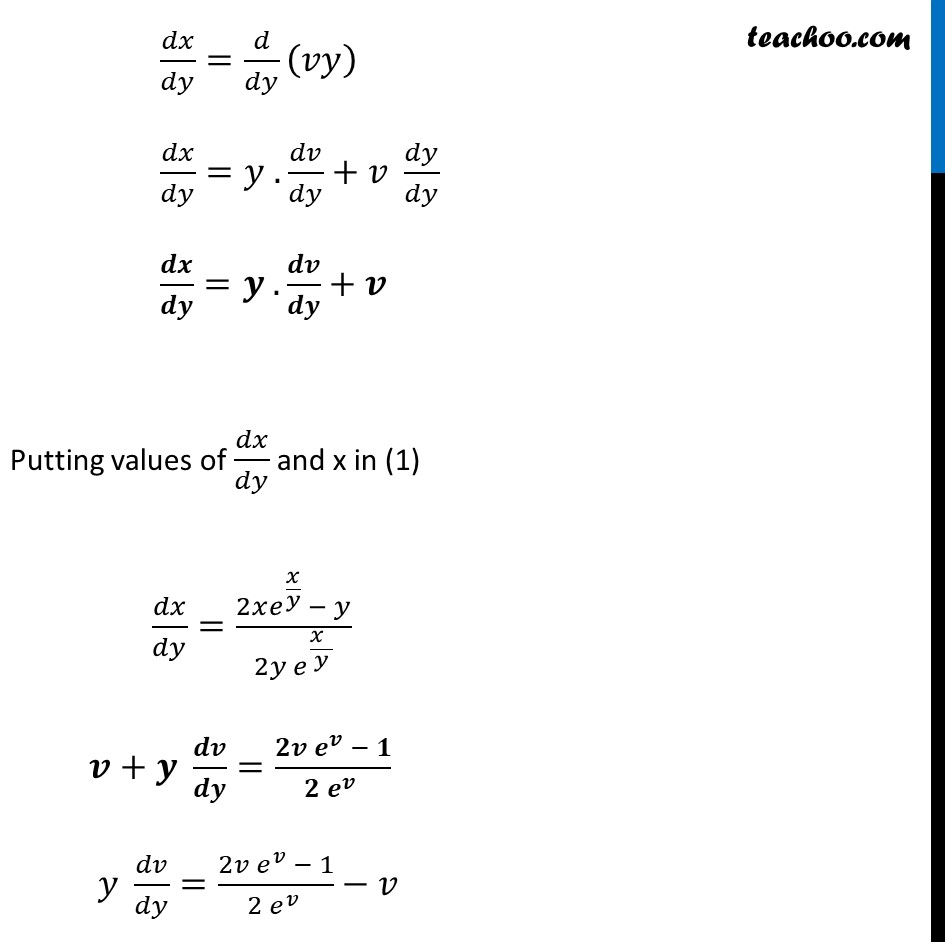
Example 12 Show that the differential equation 2𝑦𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) 𝑑𝑥+(𝑦−2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) )𝑑𝑦=0 is homogeneous and find its particular solution , given that, 𝑥=0 when 𝑦=1 2𝑦𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) 𝑑𝑥+(𝑦−2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) )𝑑𝑦 = 0 Step 1: Finding 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 2𝑦𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) 𝑑𝑥+(𝑦−2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) )𝑑𝑦=0 2𝑦𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) 𝑑𝑥=−(𝑦−2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) )𝑑𝑦 2𝑦𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) 𝑑𝑥=(2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦)−𝑦)𝑑𝑦 Since the equation is in the form 𝑥/𝑦 , we will take 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 Instead of 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 𝒅𝒙/𝒅𝒚=((𝟐𝒙𝒆^(𝒙/𝒚) − 𝒚))/(𝟐𝒚𝒆^(𝒙/𝒚) ) Step 2: Put F(𝑥 , 𝑦)=𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 and find F(𝜆𝑥 ,𝜆𝑦) F(𝑥 , 𝑦)= (2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) − 𝑦)/(2𝑦𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) ) Finding F(𝝀𝒙 ,𝝀𝒚) F(𝜆𝑥 ,𝜆𝑦)=(2 (𝜆𝑥) 〖 𝑒〗^(𝜆𝑥/𝜆𝑦 −𝜆𝑦))/(2𝜆𝑦 〖 𝑒〗^(𝜆𝑥/𝜆𝑦 ) )=𝜆(2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) − 𝑦)/(𝜆 . 2𝑦 𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) ) =(2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) − 𝑦)/(2𝑦 𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) ) = F (𝒙 , 𝒚) So, F(𝜆𝑥 ,𝜆𝑦)= F(𝑥 , 𝑦) = 𝜆° F(𝑥 , 𝑦) Thus , F(𝑥 ,𝑦) is a homogeneous function of degree zero Therefore given differential equation is homogeneous differential equation Step 3: Solving 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 by Putting 𝑥=𝑣𝑦 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦=(2𝑥 𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) − 𝑦)/(2𝑦 𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) ) Put 𝒙=𝒗𝒚 Diff. w.r.t. 𝑦 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦=𝑑/𝑑𝑦 (𝑣𝑦) 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦=𝑦 . 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑦+𝑣 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑦 𝒅𝒙/𝒅𝒚=𝒚 . 𝒅𝒗/𝒅𝒚+𝒗 Putting values of 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 and x in (1) 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦=(2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) − 𝑦)/(2𝑦 𝑒^(𝑥" " /𝑦) ) 𝒗+𝒚 𝒅𝒗/𝒅𝒚=(𝟐𝒗 𝒆^𝒗 − 𝟏)/(𝟐〖 𝒆〗^𝒗 ) 𝑦 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑦=(2𝑣 𝑒^𝑣 − 1)/(2〖 𝑒〗^𝑣 )−𝑣 (𝑦 𝑑𝑣)/𝑑𝑦=(2𝑣𝑒^𝑣 − 1 − 2𝑣𝑒^𝑣)/(2〖 𝑒〗^𝑣 ) 𝑦 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑦=(−1)/(2〖 𝑒〗^𝑣 ) 𝟐〖 𝒆〗^𝒗 𝒅𝒗=(−𝒅𝒚)/( 𝒚) Integrating Both Sides ∫1▒〖2〖 𝑒〗^𝑣 𝑑𝑣〗=∫1▒(−𝑑𝑦)/( 𝑦) 𝟐〖 𝒆〗^𝒗=−𝐥𝐨𝐠|𝒚|+𝒄 Putting back 𝑣=𝑥/𝑦 2𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦)=−𝑙𝑜𝑔|𝑦|+𝑐 2𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦)+𝑙𝑜𝑔|𝑦|=𝑐 Given that at 𝒙=𝟎 , 𝒚=𝟏 Putting 𝑥=0 and 𝑦=1 in (2) 2𝑒^(0/1)−𝑙𝑜𝑔|1|=𝑐 2 ×1+0=𝑐 𝒄=𝟐 Put Value of 𝑐 in (2) i.e., 2𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦)+𝑙𝑜𝑔|𝑦|=𝐶 𝟐𝒆^(𝒙/𝒚)+𝒍𝒐𝒈|𝒚|=𝟐" " is the particular solution of given differential equation