


Examples
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo





Transcript
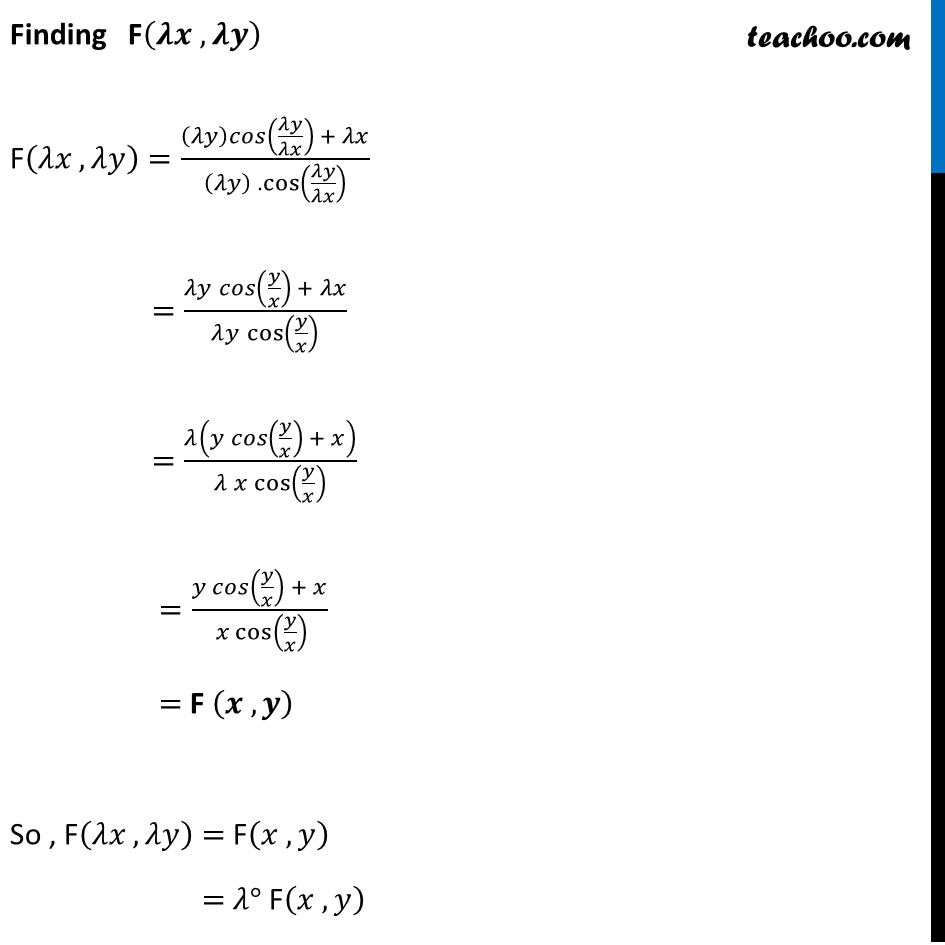
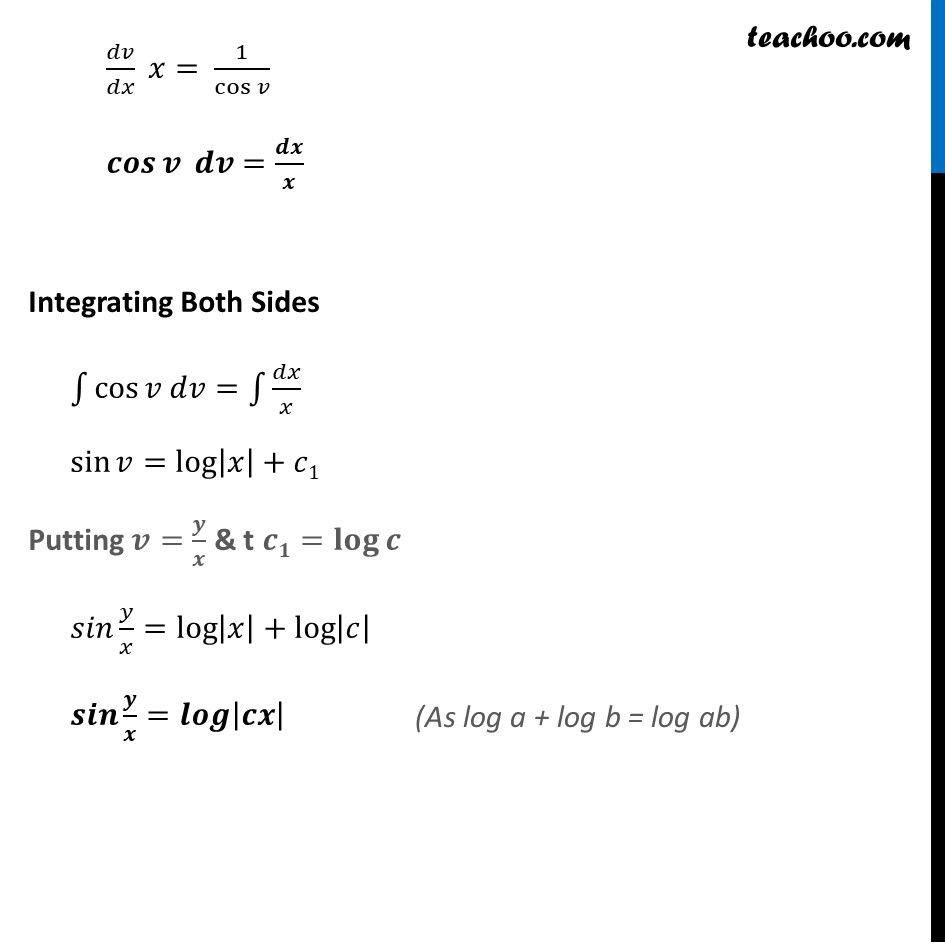
Example 11 Show that the differential equation 𝑥−𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑦/𝑥)=𝑦 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑦/𝑥)+𝑥 is homogeneous and solve it.Step 1: Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 𝑥 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑦/𝑥) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=𝑦 cos(𝑦/𝑥)+𝑥 𝒅𝒚/𝒅𝒙=(𝒚 𝐜𝐨𝐬 (𝒚/𝒙) + 𝒙)/(𝒙 𝐜𝐨𝐬(𝒚/𝒙) ) Step 2: Put F(𝑥 ,𝑦)=𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 & find F(𝜆𝑥 ,𝜆𝑦) F(𝑥 ,𝑦)=(𝑦 cos (𝑦/𝑥) + 𝑥)/(𝑥 cos(𝑦/𝑥) ) Finding F(𝝀𝒙 ,𝝀𝒚) F(𝜆𝑥 ,𝜆𝑦)=((𝜆𝑦)𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝜆𝑦/𝜆𝑥) + 𝜆𝑥)/((𝜆𝑦) . cos(𝜆𝑦/𝜆𝑥) ) =(𝜆𝑦 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑦/𝑥) + 𝜆𝑥)/(𝜆𝑦 cos(𝑦/𝑥) ) =𝜆(𝑦 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑦/𝑥) + 𝑥)/(𝜆 𝑥 cos(𝑦/𝑥) ) =(𝑦 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑦/𝑥) + 𝑥)/( 𝑥 cos(𝑦/𝑥) ) = F (𝒙 , 𝒚) So , F(𝜆𝑥 ,𝜆𝑦)= F(𝑥 , 𝑦) = 𝜆° F(𝑥 , 𝑦) Thus , F(𝑥 , 𝑦) is a homogeneous function of degree zero. Therefore, the given differential equation is homogeneous differential equation Step 3: Solving 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 by Putting 𝑦=𝑣𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=(𝑦 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑦/𝑥) + 𝑥)/(𝑥 cos(𝑦/𝑥) ) Put 𝒚=𝒗𝒙 So, 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=𝑑(𝑣𝑥) =𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 . 𝑥+𝑣 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑥 =𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 𝑥+𝑣 Putting values of 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 and y = vx in (1) i.e. 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑦 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑦/𝑥)+𝑥)/(𝑥 cos(𝑦/𝑥) ) 𝒅𝒗/𝒅𝒙 𝒙+𝒗=((𝒗𝒙) 𝒄𝒐𝒔(𝒗𝒙/𝒙) + 𝒙)/(𝒙 𝐜𝐨𝐬(𝒗𝒙/𝒙) ) 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 𝑥+𝑣=(𝑣𝑥 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑣) + 𝑥)/(𝑥 cos𝑣 ) 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 𝑥+𝑣=𝑥(𝑣 cos〖𝑣 +1〗 )/(𝑥 cos𝑣 ) 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 𝑥+𝑣=(𝑣 cos〖𝑣 +1〗)/cos𝑣 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 𝑥=(𝑣 cos〖𝑣 + 1〗)/cos𝑣 −𝑣 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 𝑥=(𝑣 cos〖𝑣 + 1〗 −𝑣 cos𝑣)/cos𝑣 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 𝑥= 1/cos𝑣 𝒄𝒐𝒔𝒗 𝒅𝒗=𝒅𝒙/𝒙 Integrating Both Sides ∫1▒cos〖𝑣 𝑑𝑣=∫1▒𝑑𝑥/𝑥〗 sin〖𝑣=log|𝑥|+𝑐1〗 Putting 𝒗=𝒚/𝒙 & t 𝒄𝟏=𝐥𝐨𝐠𝒄 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑦/𝑥=log〖|𝑥|+log|𝑐| 〗 𝒔𝒊𝒏 𝒚/𝒙=𝒍𝒐𝒈|𝒄𝒙|