






Miscellaneous
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo










Transcript
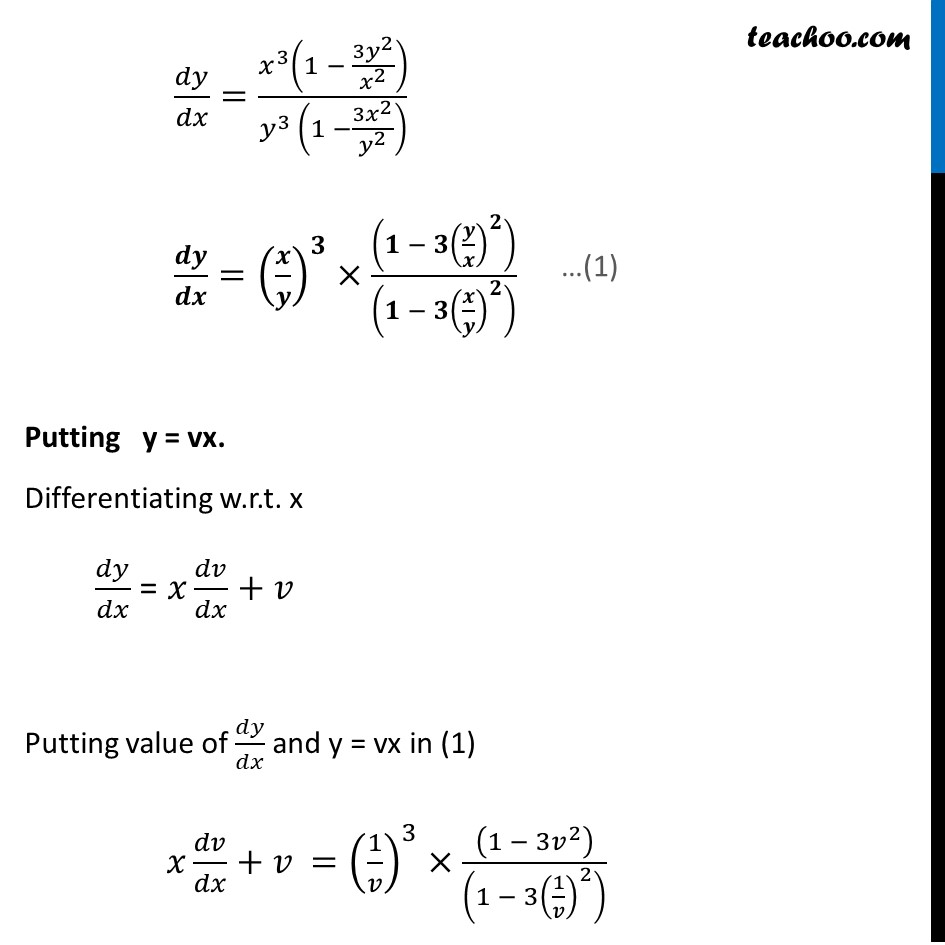
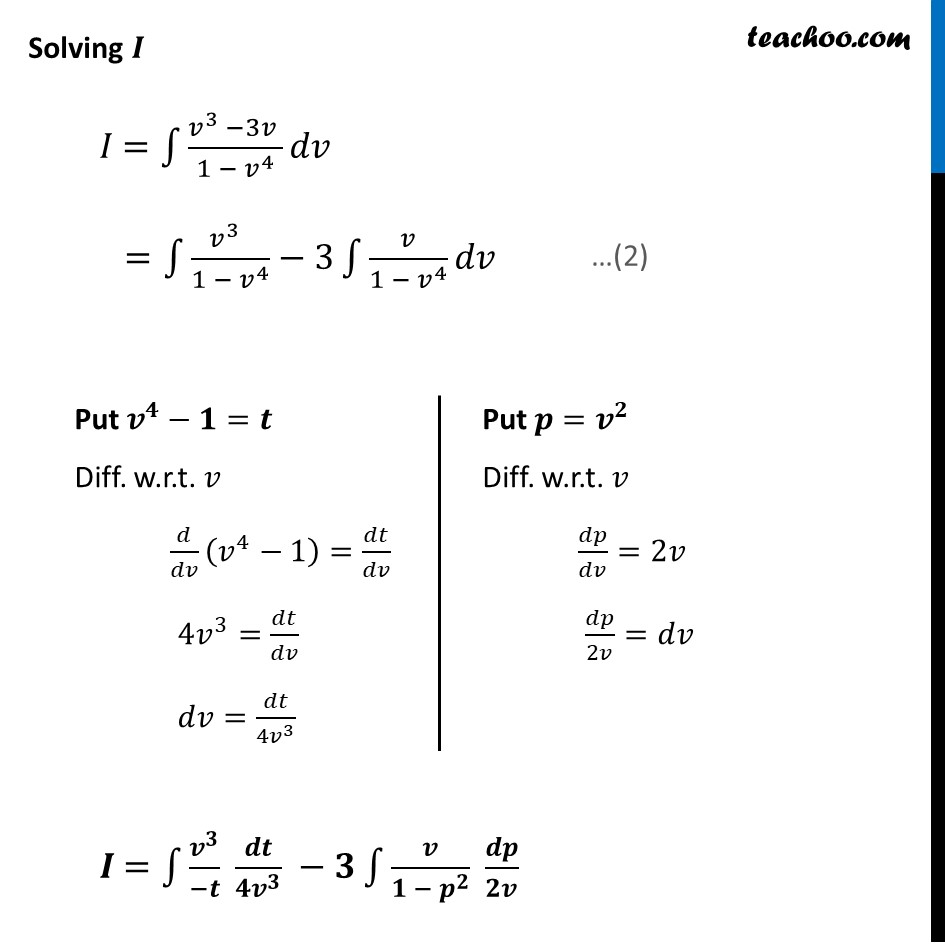
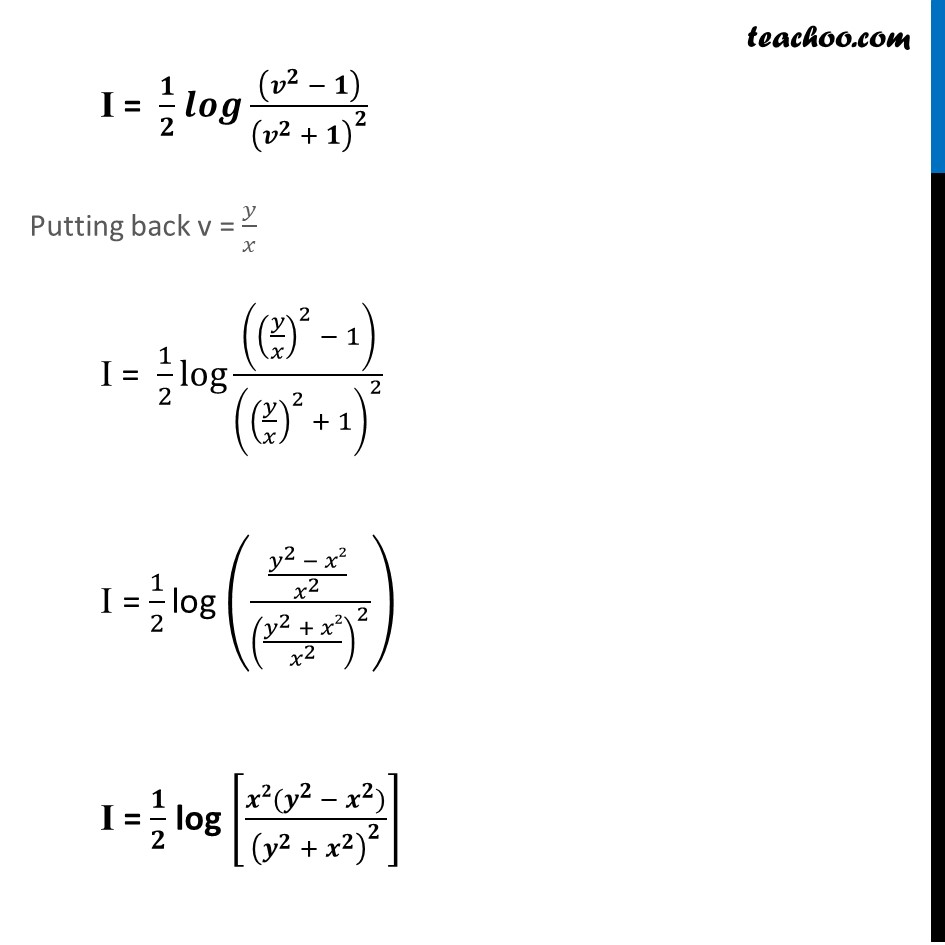
Misc 3 Prove that 𝑥^2−𝑦^2=𝑐(𝑥^2+𝑦^2 )^2 is the general solution of differential equation (𝑥^3−3𝑥𝑦^2 )𝑑𝑥=(𝑦^3−3𝑥^2 𝑦)𝑑𝑦, where 𝑐 is a parameter .Given differential equation (𝑥^3−3𝑥𝑦^2 )𝑑𝑥=(𝑦^3−3𝑥^2 𝑦)𝑑𝑦 (𝑥^3 − 3𝑥𝑦^2)/(𝑦^3 − 3𝑥^2 𝑦)=𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=(𝑥^3 − 3𝑥𝑦^2)/(𝑦^(3 )− 3𝑥^2 𝑦) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=(𝑥^3 (1 − (3𝑥𝑦^2)/𝑥^3 ))/(𝑦^(3 ) (1 −(3𝑥^2 𝑦)/𝑦^3 ) ) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=(𝑥^3 (1 − (3𝑦^2)/𝑥^2 ))/(𝑦^(3 ) (1 −(3𝑥^2)/𝑦^2 ) ) 𝒅𝒚/𝒅𝒙=(𝒙/𝒚)^𝟑×((𝟏 − 𝟑(𝒚/𝒙)^𝟐 ))/((𝟏 − 𝟑(𝒙/𝒚)^𝟐 ) ) Putting y = vx. Differentiating w.r.t. x 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = 𝑥 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 + 𝑣 Putting value of 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 and y = vx in (1) 𝑥 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥+𝑣 =(1/𝑣)^3×((1 − 3𝑣^2 ))/((1 − 3(1/𝑣)^2 ) ) 𝑥 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥+𝑣 =1/𝑣^3 ×((1 − 3𝑣^2 ))/(((𝑣^2 − 3)/𝑣^2 ) ) 𝒙 𝒅𝒗/𝒅𝒙+𝒗 =𝟏/𝒗×((𝟏 − 𝟑𝒗^𝟐 ))/((𝒗^𝟐 − 𝟑) ) 𝑥 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥=1/𝑣×((1 − 3𝑣^2 ))/((𝑣^2 − 3) )−𝑣 𝑥 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥=1/𝑣×((1 − 3𝑣^2 ) − 𝑣 × 𝑣 (𝑣^2 − 3))/((𝑣^2 − 3) ) 𝑥 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥=1/𝑣×(1 − 3𝑣^2 − 𝑣^4 + 3𝑣^2)/((𝑣^2 − 3) ) 𝑥 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥=1/𝑣×(1 − 𝑣^4)/((𝑣^2 − 3) ) 𝒙 𝒅𝒗/𝒅𝒙=(𝟏 − 𝒗^𝟒)/((𝒗^𝟑 − 𝟑𝒗) ) (𝒗^𝟑 −𝟑𝒗)𝒅𝒗/((𝟏 −𝒗^𝟒 ) )=𝒅𝒙/𝒙 Integrating Both Sides ∫1▒〖(𝑣^3 −3𝑣 )/(1 − 𝑣^4 ) 𝑑𝑣〗=∫1▒𝑑𝑥/𝑥 ∫1▒〖(𝒗^𝟑 −𝟑𝒗 )/(𝟏 − 𝒗^𝟒 ) 𝒅𝒗〗=𝐥𝐨𝐠〖|𝒙|〗+𝑪 Let I = ∫1▒(𝒗^𝟑 − 𝟑𝒗)/(𝟏 − 𝒗^𝟒 ) 𝒅𝒗 Therefore, 𝐼 =log〖|𝑥|+𝑐〗 Solving 𝑰 𝐼 =∫1▒〖(𝑣^3 −3𝑣 )/(1 − 𝑣^4 ) 𝑑𝑣〗 =∫1▒〖(𝑣^3 )/(1 − 𝑣^4 )−3∫1▒〖𝑣/(1 −〖 𝑣〗^4 ) 𝑑𝑣〗〗 Put 𝒗^𝟒−𝟏=𝒕 Diff. w.r.t. 𝑣 𝑑/𝑑𝑣 (𝑣^4−1)=𝑑𝑡/𝑑𝑣 4𝑣^3=𝑑𝑡/𝑑𝑣 𝑑𝑣=𝑑𝑡/(4𝑣^3 ) Put 𝒑=𝒗^𝟐 Diff. w.r.t. 𝑣 𝑑𝑝/𝑑𝑣=2𝑣 𝑑𝑝/2𝑣=𝑑𝑣 𝑰 =∫1▒〖𝒗^𝟑/(−𝒕) 𝒅𝒕/(𝟒𝒗^𝟑 ) −𝟑∫1▒〖𝒗/(𝟏 − 𝒑^𝟐 ) 𝒅𝒑/𝟐𝒗〗〗 𝐼 =−1/4 ∫1▒〖 𝑑𝑡/𝑡−3/2 ∫1▒〖 𝑑𝑝/(1 − 𝑝^2 )〗〗 𝐼 =−1/4 ∫1▒〖 𝑑𝑡/𝑡+3/2 ∫1▒〖 𝑑𝑝/((𝑝^2 − 1^2 ) )〗〗 𝑰 = (−𝟏)/( 𝟒) 𝐥𝐨𝐠𝒕+𝟑/𝟐 × 𝟏/(𝟐(𝟏)) 𝒍𝒐𝒈((𝒑 − 𝟏)/(𝒑 + 𝟏)) Putting t = 𝑣^4 − 1 and p = v2 I = (−𝟏)/𝟒 𝐥𝐨𝐠〖(𝒗^𝟒−𝟏) 〗+𝟑/𝟒 𝐥𝐨𝐠〖((𝒗^𝟐 − 𝟏))/((𝒗^𝟐 + 𝟏))〗 I = 1/4 [−log〖(𝑣^4−1)+3 𝑙𝑜𝑔 ((𝑣^2 − 1))/((𝑣^2 + 1))〗 ] I = 1/4 [−𝒍𝐨𝐠〖(𝒗^𝟒−𝟏)+ 𝑙𝑜𝑔 (𝑣^2 − 1)^3/(𝑣^2 + 1)^3 〗 ] I = 1/4 [𝑙𝑜𝑔 (𝑣^2 − 1)^3/(𝑣^2 + 1)^3 × 1/((𝑣^4 − 1))] I = 1/4 [𝒍𝒐𝒈〖𝟏/((𝒗^𝟒−𝟏) )+ 𝑙𝑜𝑔 (𝑣^2 − 1)^3/(𝑣^2 + 1)^3 〗 ] I = 1/4 𝒍𝒐𝒈 𝟏/((𝒗^𝟒 − 𝟏))×(𝒗^𝟐 − 𝟏)^𝟑/(𝒗^𝟐 + 𝟏)^𝟑 I = 1/4 𝑙𝑜𝑔 1/((𝑣^2 − 1)(𝑣^2 + 1))×(𝑣^2 − 1)^3/(𝑣^2 + 1)^3 I = 1/4 𝑙𝑜𝑔 (𝑣^2 − 1)^2/(𝑣^2 + 1)^4 I = 𝟏/𝟒 𝐥𝐨𝐠〖(((𝒗^𝟐 − 𝟏))/(𝒗^𝟐 + 𝟏)^𝟐 )^𝟐 〗 I = 1/4 × 2 log〖((𝑣^2 − 1))/(𝑣^2 + 1)^2 〗 I = 𝟏/𝟐 𝒍𝒐𝒈〖((𝒗^𝟐 − 𝟏))/(𝒗^𝟐 + 𝟏)^𝟐 〗 Putting back v = 𝑦/𝑥 I = 1/2 log〖(((𝑦/𝑥)^2 − 1))/((𝑦/𝑥)^2 + 1)^2 〗 I = 1/2 log (((𝑦^2 − 𝑥2)/𝑥^2 )/((𝑦^2 + 𝑥2)/𝑥^2 )^2 ) I = 𝟏/𝟐 log [(𝒙𝟐(𝒚^𝟐 − 𝒙^𝟐))/(𝒚^𝟐 + 𝒙^𝟐 )^𝟐 ] Substituting value of I in (2) I = log |x| + c 𝟏/𝟐 log ⌈(𝒙𝟐(𝒚𝟐 − 𝒙𝟐))/((𝒚𝟐 + 𝒙𝟐))⌉ = log |x| + c log ⌈(𝑥2(𝑦2 − 𝑥2))/((𝑥2 + 𝑦2))⌉ = 2 log |x| + 2c log ⌈(𝑥2(𝑦2 − 𝑥2))/((𝑥2 + 𝑦2))⌉ = log |x|2 + log c1 log ⌈(𝑥2(𝑦2 − 𝑥2))/((𝑥2 + 𝑦2))⌉ = log |x|2 + log c1 log ⌈(𝑥2(𝑦2 − 𝑥2))/(𝑥2 + 𝑦2)^2 ⌉ = log c1|x|2 Cancelling log (𝒙𝟐(𝒚𝟐 − 𝒙𝟐))/(𝒙𝟐 + 𝒚𝟐)^𝟐 = c1 x2 x2 (y2 − x2) = c1 x2 (x2 + y2)2 Cancelling x2 from both sides y2 − x2 = c1 (x2 + y2)2 x2 − y2 = c2 (x2 + y2)2 Hence proved