





Ex 10.3
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo







Transcript
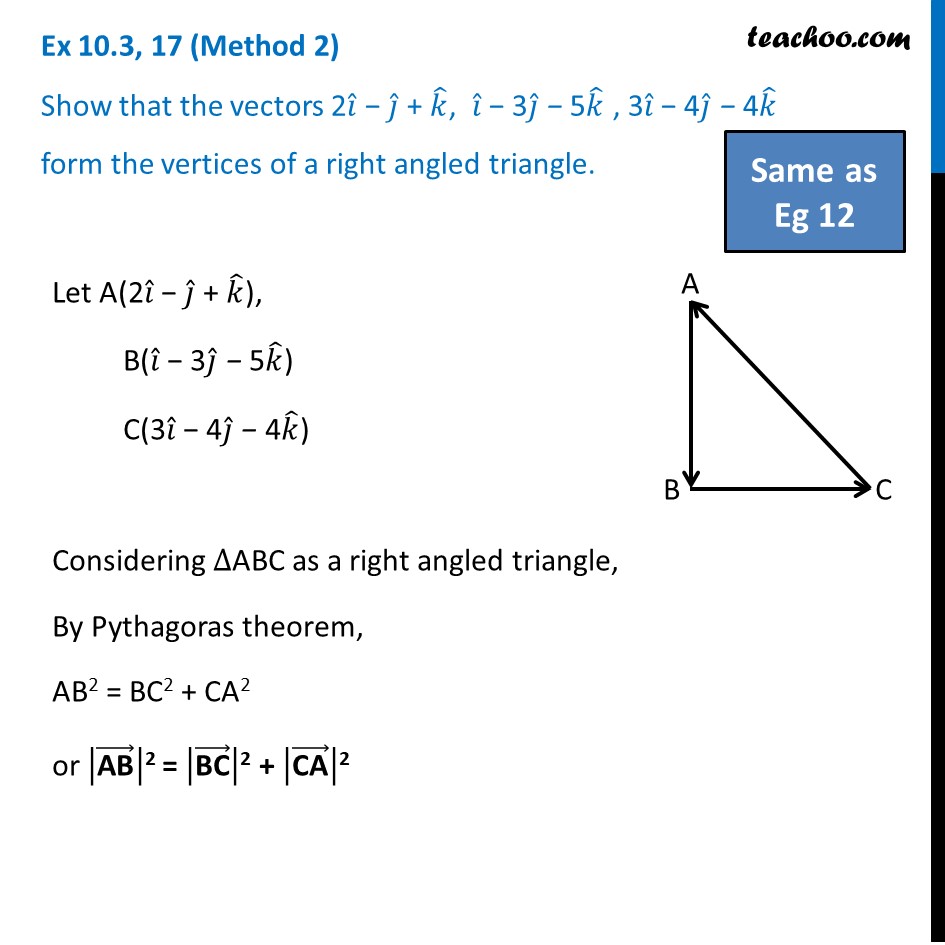
Ex 10.3, 17 (Method 1) Show that the vectors 2𝑖 ̂ − 𝑗 ̂ + 𝑘 ̂, 𝑖 ̂ − 3𝑗 ̂ − 5𝑘 ̂ , 3𝑖 ̂ − 4𝑗 ̂ − 4𝑘 ̂ form the vertices of a right angled triangle. Let A(2𝑖 ̂ − 𝑗 ̂ + 𝑘 ̂), B(𝑖 ̂ − 3𝑗 ̂ − 5𝑘 ̂) C(3𝑖 ̂ − 4𝑗 ̂ − 4𝑘 ̂) We know that two vectors are perpendicular to each other, i.e have an angle of 90° between them , if their scalar product is zero. (𝐴𝐵) ⃗ = (𝑖 ̂ − 3𝑗 ̂ − 5𝑘 ̂) − (2𝑖 ̂ − 𝑗 ̂ + 𝑘 ̂) = 1𝑖 ̂ − 3𝑗 ̂ − 5𝑘 ̂ − 2𝑖 ̂ + 1𝑗 ̂ − 1𝑘 ̂ = (1 − 2) 𝑖 ̂ + (−3 + 1) 𝑗 ̂ + (−5 −1) 𝑘 ̂ = −1𝑖 ̂ − 2𝑗 ̂ − 6𝑘 ̂ (𝐵𝐶) ⃗ = (3𝑖 ̂ − 4𝑗 ̂ − 4𝑘 ̂) − (𝑖 ̂ − 3𝑗 ̂ − 5𝑘 ̂) = 3𝑖 ̂ − 4𝑗 ̂ − 4𝑘 ̂ − 1𝑖 ̂ + 3𝑗 ̂ + 5𝑘 ̂ = (3 − 1) 𝑖 ̂ + (−4 + 3) 𝑗 ̂ + (−4 + 5) 𝑘 ̂ = 2𝑖 ̂ − 1𝑗 ̂ + 1𝑘 ̂ (𝐶𝐴) ⃗ = (2𝑖 ̂ − 𝑗 ̂ + 𝑘 ̂) − (3𝑖 ̂ − 4𝑗 ̂ − 4𝑘 ̂) = 2𝑖 ̂ − 1𝑗 ̂ + 1𝑘 ̂ − 3𝑖 ̂ + 4𝑗 ̂ + 4𝑘 ̂ = (2 − 3) 𝑖 ̂ + (−1 + 4) 𝑗 ̂ + (1 + 4) 𝑘 ̂ = −1𝑖 ̂ + 3𝑗 ̂ + 5𝑘 ̂ Now, (𝐵𝐶) ⃗. (𝐶𝐴) ⃗ = (2𝑖 ̂ − 1𝑗 ̂ + 1𝑘 ̂) . (-1𝑖 ̂ + 3𝑗 ̂ + 5𝑘 ̂) = (2 × –1) + (−1 × 3) + (1 × 5) = (−2) + (−3) + 5 = −5 + 5 = 0 Since, (𝑩𝑪) ⃗. (𝑪𝑨) ⃗ = 0 Therefore, (𝐵𝐶) ⃗ is perpendicular to (𝐶𝐴) ⃗ . Hence Δ ABC is a right angled triangle Ex 10.3, 17 (Method 2) Show that the vectors 2𝑖 ̂ − 𝑗 ̂ + 𝑘 ̂, 𝑖 ̂ − 3𝑗 ̂ − 5𝑘 ̂ , 3𝑖 ̂ − 4𝑗 ̂ − 4𝑘 ̂ form the vertices of a right angled triangle. Let A(2𝑖 ̂ − 𝑗 ̂ + 𝑘 ̂), B(𝑖 ̂ − 3𝑗 ̂ − 5𝑘 ̂) C(3𝑖 ̂ − 4𝑗 ̂ − 4𝑘 ̂) Considering ∆ABC as a right angled triangle, By Pythagoras theorem, AB2 = BC2 + CA2 or |("AB" ) ⃗ |"2" = |("BC" ) ⃗ |"2" + |("CA" ) ⃗ |"2" (𝐴𝐵) ⃗ = (𝑖 ̂ − 3𝑗 ̂ − 5𝑘 ̂) − (2𝑖 ̂ − 𝑗 ̂ + 𝑘 ̂) = 1𝑖 ̂ − 3𝑗 ̂ − 5𝑘 ̂ − 2𝑖 ̂ + 1𝑗 ̂ − 1𝑘 ̂ = (1 − 2) 𝑖 ̂ + (−3 + 1) 𝑗 ̂ + (−5 −1) 𝑘 ̂ = −1𝑖 ̂ − 2𝑗 ̂ − 6𝑘 ̂ (𝐵𝐶) ⃗ = (3𝑖 ̂ − 4𝑗 ̂ − 4𝑘 ̂) − (𝑖 ̂ − 3𝑗 ̂ − 5𝑘 ̂) = 3𝑖 ̂ − 4𝑗 ̂ − 4𝑘 ̂ − 1𝑖 ̂ + 3𝑗 ̂ + 5𝑘 ̂ = (3 − 1) 𝑖 ̂ + (−4 + 3) 𝑗 ̂ + (−4 + 5) 𝑘 ̂ = 2𝑖 ̂ − 1𝑗 ̂ + 1𝑘 ̂ (𝐶𝐴) ⃗ = (2𝑖 ̂ − 𝑗 ̂ + 𝑘 ̂) − (3𝑖 ̂ − 4𝑗 ̂ − 4𝑘 ̂) = 2𝑖 ̂ − 1𝑗 ̂ + 1𝑘 ̂ − 3𝑖 ̂ + 4𝑗 ̂ + 4𝑘 ̂ = (2 − 3) 𝑖 ̂ + (−1 + 4) 𝑗 ̂ + (1 + 4) 𝑘 ̂ = −1𝑖 ̂ + 3𝑗 ̂ + 5𝑘 ̂ Now, "Magnitude of " (𝐴𝐵) ⃗" = " √((−1)2+(−2)2+(−6)2) " " |(𝐴𝐵) ⃗ |" = " √(1+4+36) " = " √41 Magnitude of (𝐵𝐶) ⃗ = √(22+(−1)2+1) |(𝐵𝐶) ⃗ | = √(4+1+1) = √6 Magnitude of (𝐶𝐴) ⃗ = √((−1)2+32+52) |(𝐶𝐴) ⃗ | = √(1+9+25) = √35 Now, |(𝐵𝐶) ⃗ |2 + |(𝐶𝐴) ⃗ |2 = (√6)2 + (√35)2 = 6 + 35 = 41 = (√41)2 = |(𝐴𝐵) ⃗ |2 Thus, |(𝐴𝐵) ⃗ |^2 = |(𝐵𝐶) ⃗ |^2 + |(𝐶𝐴) ⃗ |^2 So, ABC is a right angled triangle.