





Miscellaneous
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo








Transcript
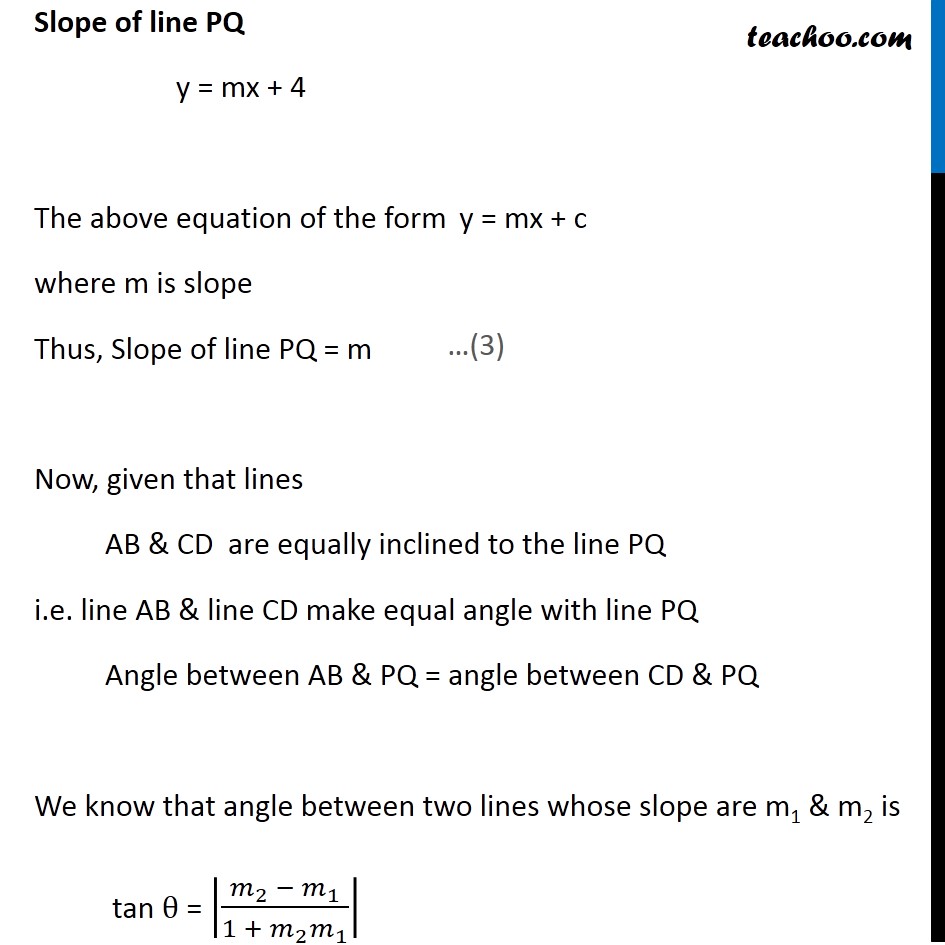
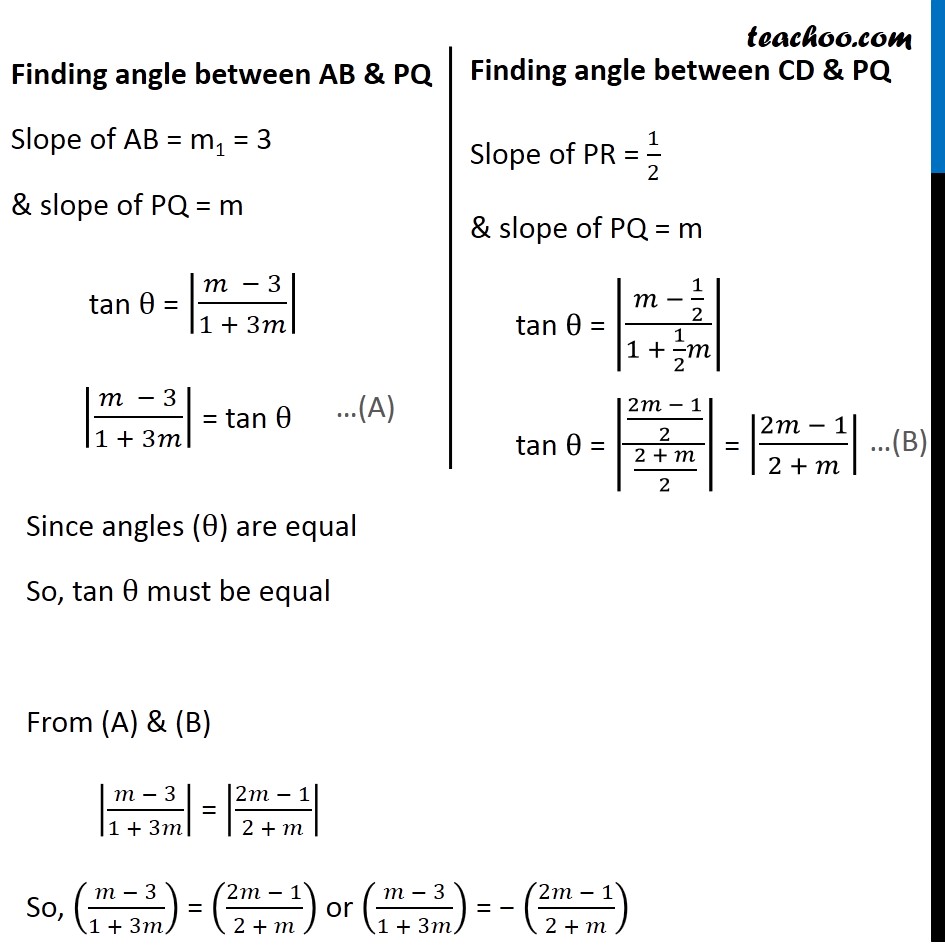
Misc 18 If the lines y = 3x + 1 and 2y = x + 3 are equally inclined to the line y = mx + 4, find the value of m. Let line AB be y = 3x + 1 ,line CD be 2y = x + 3 & line PQ be y = mx + 4 Lines AB & CD are equally inclined to the line PQ First we find slopes of lines Slope of line AB y = 3x + 1 The above equation is of the form y = m1x + c1 where slope of line AB = m1 ∴ Slope of line AB = m1 = 3 Slope of line CD 2y = x + 3 y = (𝑥 + 3)/2 y = (1/2)x + 3/2 The above equation of the form y = m2x + c2 where slope of line CD = m2 ∴ Slope of CD = m2 = 1/2 Slope of line PQ y = mx + 4 The above equation of the form y = mx + c where m is slope Thus, Slope of line PQ = m Now, given that lines AB & CD are equally inclined to the line PQ i.e. line AB & line CD make equal angle with line PQ Angle between AB & PQ = angle between CD & PQ We know that angle between two lines whose slope are m1 & m2 is tan θ = |(𝑚_2 − 𝑚_1)/(1 + 𝑚_2 𝑚_1 )| Finding angle between AB & PQ Slope of AB = m1 = 3 & slope of PQ = m tan θ = |(𝑚 − 3)/(1 + 3𝑚)| |(𝑚 − 3)/(1 + 3𝑚)| = tan θ Finding angle between CD & PQ Slope of PR = 1/2 & slope of PQ = m tan θ = |(𝑚 − 1/2)/(1 + 1/2 𝑚)| tan θ = |((2𝑚 − 1)/2)/((2 + 𝑚)/2)| = |(2𝑚 − 1)/(2 + 𝑚)| Since angles (θ) are equal So, tan θ must be equal From (A) & (B) |(𝑚 − 3)/(1 + 3𝑚)| = |(2𝑚 − 1)/(2 + 𝑚)| So, ((𝑚 − 3)/(1 + 3𝑚)) = ((2𝑚 − 1)/(2 + 𝑚)) or ((𝑚 − 3)/(1 + 3𝑚)) = − ((2𝑚 − 1)/(2 + 𝑚)) Solving ((𝒎 − 𝟑)/(𝟏 + 𝟑𝒎))= ((𝟐𝒎 − 𝟏)/(𝟐 + 𝒎)) (𝑚 − 3)/(1 + 3𝑚) = (2𝑚 − 1)/(2 + 𝑚) (m − 3)(2 + m) = (2m − 1) (1 + 3m) m (2 + m) − 3(2 + m) = 2m + 6m2 − 1 + 3m 5m + m2 − 6 = 5m + 6m2 − 1 5m − 5m + m2 − 6m2 − 6 + 1 = 0 0 − 5m2 − 5 = 0 − 5m2 = 5 m2 = 5/( − 5) m2 = − 1 This is not possible as square of a number cannot be negative Solving (𝒎 − 𝟑)/(𝟏 + 𝟑𝒎) = − ((𝟐𝒎 − 𝟏)/(𝟐 + 𝒎)) (𝑚 − 3)/(1 + 3𝑚) = (1 − 2𝑚)/(2 + 𝑚) (m − 3) (2 + m) = (1 − 2m)(1 + 3m) m(2 + m) − 3(2 + m) = 1(1 + 3m) − 2m(1 + 3m) 2m + m2 − 6 − 3m = 1 + 3m − 2m − 6m2 m2 − 6 − m = − 6m2 + m + 1 m2 + 6m2 − m − m − 6 − 1 = 0 7m2 − 2m − 7 = 0 The above equation is of the form ax2 + 3x + c = 0 Where solution is x = ( − 𝑏 ± √(𝑏^2 − 4𝑎𝑐))/2𝑎 Here a = 7, b = − 2,c = –7 & x = m So, m = ( −(−2) ± √(〖(−2)〗^2 − 4(7)(−7)))/(2(7)) m = (2 ± √(4 (1 + (7) × (−7)))/14 m = (2 ± 2 √((1 + 49)))/14 m = (2(1 ± √50 ))/14 m = (2(1± √(5 × 5 × 2)))/14 m = 1/7(1 ± 5√2) m = (1 ± 5√2)/7 Thus, the required value of m is (𝟏 + 𝟓√𝟐)/𝟕 & (𝟏 − 𝟓√𝟐)/𝟕