






Miscellaneous
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo












Transcript
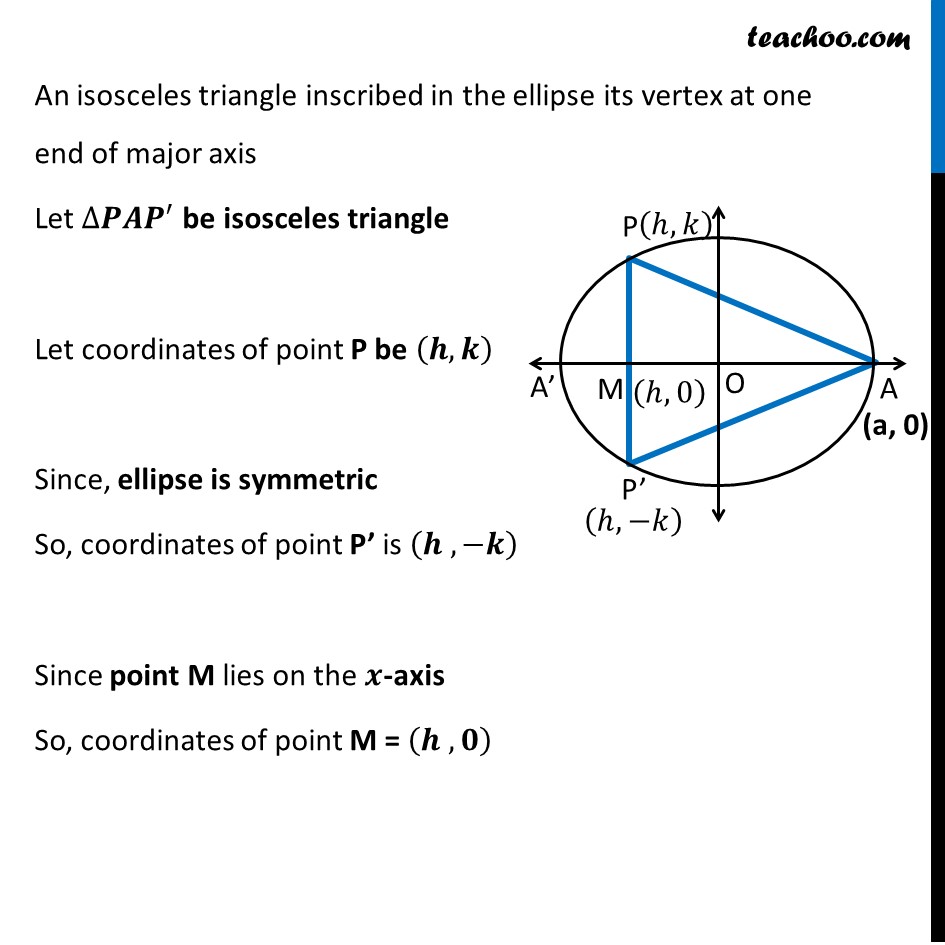
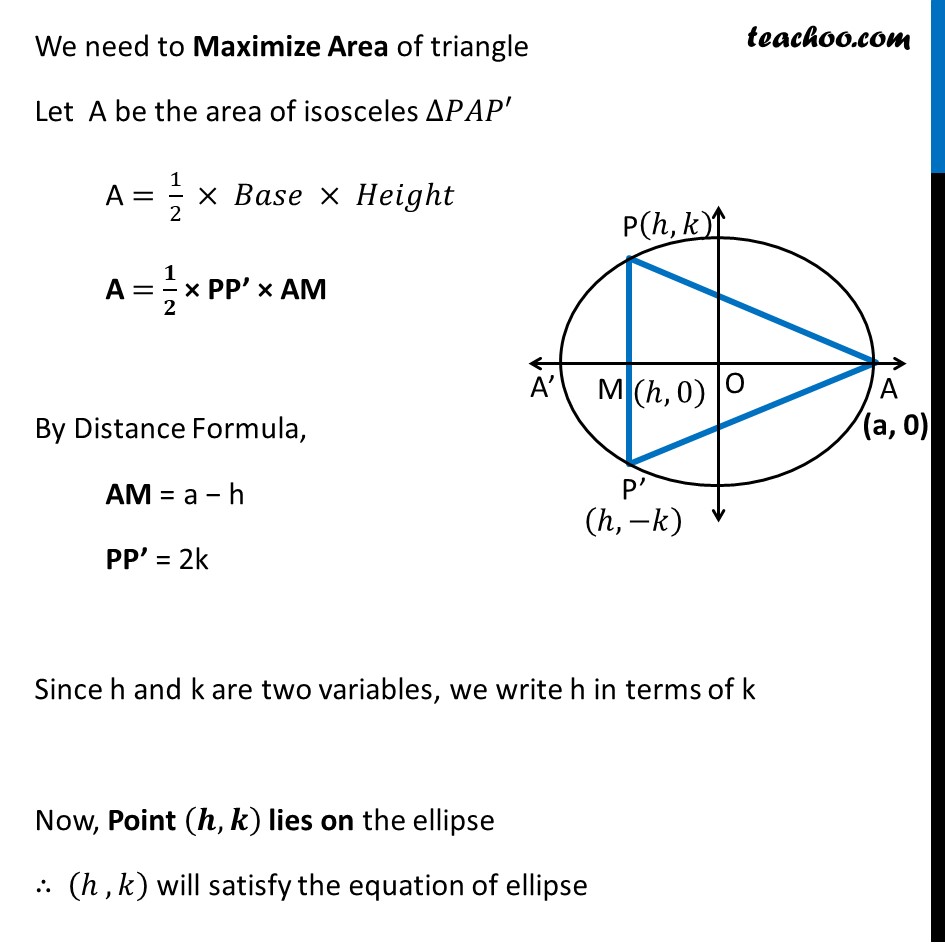
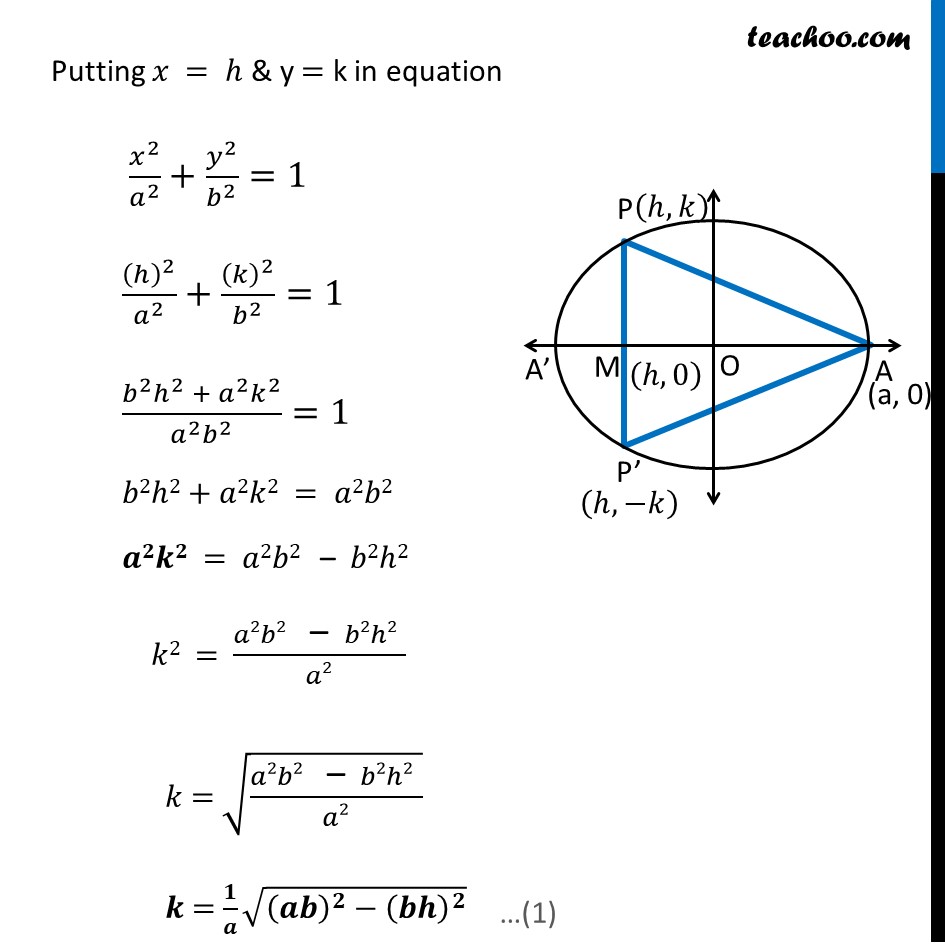
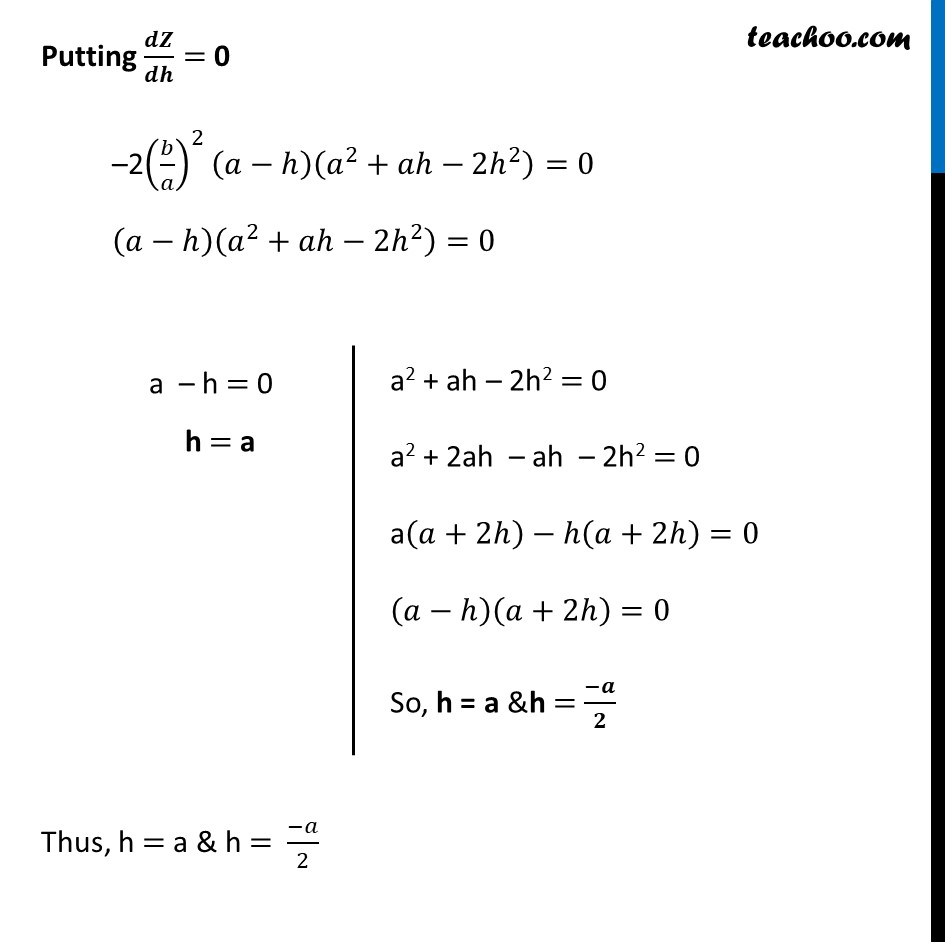
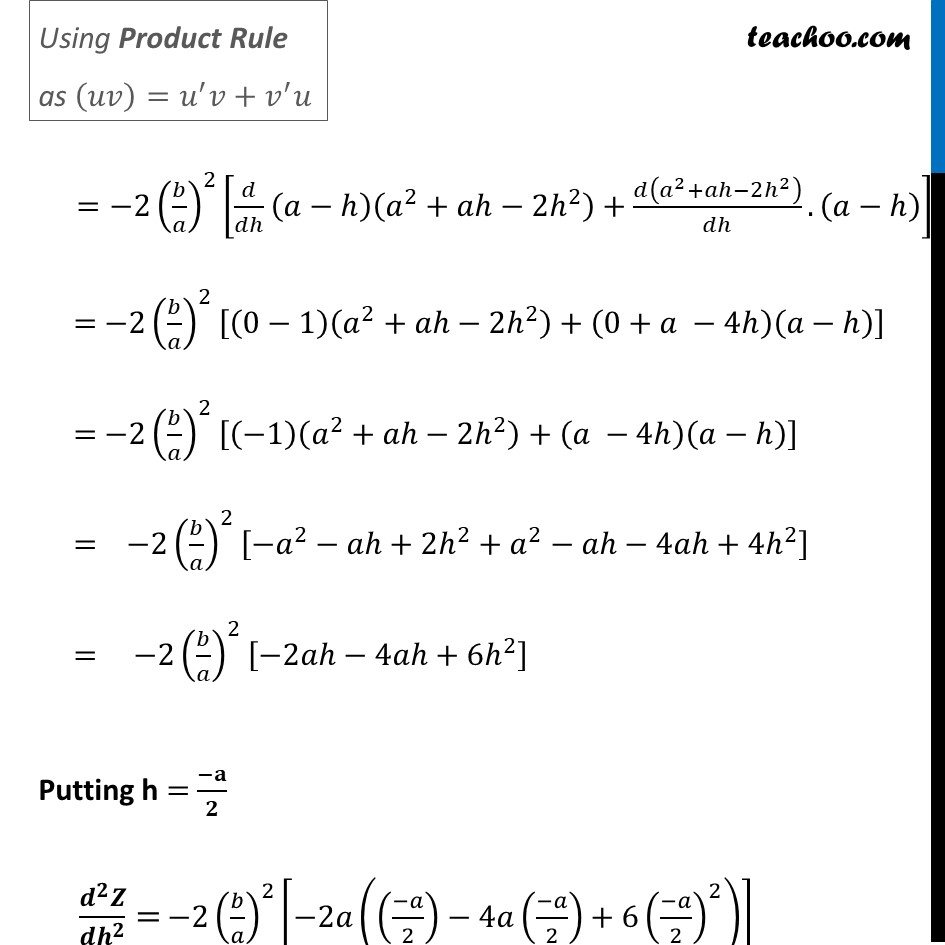
Misc 5 Find the maximum area of an isosceles triangle inscribed in the ellipse 𝑥^2/𝑎^2 + 𝑦^2/𝑏^2 = 1 with its vertex at one end of the major axis.Given equation of ellipse is 𝑥^2/𝑎^2 +𝑦^2/𝑏^2 =1 where Major axis of ellipse is along x-axis Here, Coordinate of A = (a, 0) Coordinate of A’ = (−a, 0) An isosceles triangle inscribed in the ellipse its vertex at one end of major axis Let ∆𝑷𝑨𝑷^′ be isosceles triangle Let coordinates of point P be (𝒉, 𝒌) Since, ellipse is symmetric So, coordinates of point P’ is (𝒉 , −𝒌) Since point M lies on the 𝒙-axis So, coordinates of point M = (𝒉 , 𝟎) We need to Maximize Area of triangle Let A be the area of isosceles ∆𝑃𝐴𝑃′ A = 1/2 × 𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒 × 𝐻𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 A = 𝟏/𝟐 × PP’ × AM By Distance Formula, AM = a − h PP’ = 2k Since h and k are two variables, we write h in terms of k Now, Point (𝒉, 𝒌) lies on the ellipse ∴ (ℎ , 𝑘) will satisfy the equation of ellipse Putting 𝑥 = ℎ & y = k in equation 𝑥^2/𝑎^2 +𝑦^2/𝑏^2 =1 (ℎ)^2/𝑎^2 +(𝑘)^2/𝑏^2 =1 (𝑏^2 ℎ^2 + 𝑎^2 𝑘^2)/(𝑎^2 𝑏^2 )=1 𝑏2ℎ2+𝑎2𝑘2 = 𝑎2𝑏2 𝒂𝟐𝒌𝟐 = 𝑎2𝑏2 – 𝑏2ℎ2 𝑘2 = (𝑎2𝑏2" – " 𝑏2ℎ2" " )/𝑎2 𝑘 = √((𝑎2𝑏2" – " 𝑏2ℎ2" " )/𝑎2) 𝒌 = 𝟏/𝒂 √((𝒂𝒃)^𝟐−(𝒃𝒉)^𝟐 ) Thus, Area of Triangle A = 1/2 × AM × PP’ A = 1/2 × (𝑎−ℎ) ×2𝑘 A = (𝒂−𝒉) ×𝟏/𝒂 √((𝒂𝒃)^𝟐−𝒃^𝟐 𝒉^𝟐 ) We need to maximise A, but A has a square root Which will be difficult to differentiate Let Z = A2 Z = ((𝑎−ℎ) × 1/𝑎 √((𝑎𝑏)^2−(𝑏 ℎ)^2 ))^2 Z = (𝑎−ℎ)^2 × 1/𝑎^2 ((𝑎𝑏)^2−(𝑏^2 ℎ^2 )) Z = (𝑎−ℎ)^2 × 1/𝑎^2 × 𝑏^2 (𝑎^2−ℎ^2 ) Z = (𝒂−𝒉)^𝟐 × (𝒃/𝒂)^𝟐 (𝒂^𝟐−𝒉^𝟐 ) Z = (𝑏/𝑎)^2 (𝑎−ℎ)^2 (𝑎^2−ℎ^2 ) Since A is positive, A is maximum if A2 is maximum So, we maximise Z = A2 Differentiating w.r.t h 𝑑𝑍/𝑑ℎ= 𝑑((𝑏/𝑎)^2 (𝑎 − ℎ)^2 (𝑎^2 − ℎ^2 ))/𝑑ℎ 𝑑𝑍/𝑑ℎ=(𝑏/𝑎)^2. [(𝑑(𝑎−ℎ)^2)/𝑑ℎ.(𝑎^2−ℎ^2 )+𝑑(𝑎^2− ℎ^2 )/𝑑ℎ . (𝑎−ℎ)^2 ] 𝑑𝑍/𝑑ℎ=(𝑏/𝑎)^2 [2(𝑎−ℎ). 𝑑(−ℎ)/𝑑ℎ (𝑎^2−ℎ^2 )+(0−2ℎ) (𝑎−ℎ)^2 ] 𝑑𝑍/𝑑ℎ= (𝑏/𝑎)^2 [−2(𝑎−ℎ)(𝑎^2−ℎ^2 )−2ℎ(𝑎−ℎ)^2 ] 𝑑𝑍/𝑑ℎ= (𝑏/𝑎)^2 (−2)[(𝑎−ℎ)(𝑎^2−ℎ^2 )+ℎ(𝑎−ℎ)^2 ] 𝑑𝑍/𝑑ℎ= 〖−2(𝑏/𝑎)〗^2 [(𝑎−ℎ)(𝑎^2−ℎ^2+ℎ(𝑎−ℎ))] 𝑑𝑍/𝑑ℎ= 〖−2(𝑏/𝑎)〗^2 (𝑎−ℎ)[𝑎^2−ℎ^2+ℎ𝑎−ℎ^2 ] 𝑑𝑍/𝑑ℎ= 〖−2(𝑏/𝑎)〗^2 (𝑎−ℎ)[𝑎^2+ℎ𝑎−2ℎ^2 ] Putting 𝒅𝒁/𝒅𝒉= 0 –2(𝑏/𝑎)^2 (𝑎−ℎ)(𝑎^2+𝑎ℎ−2ℎ^2 )=0 (𝑎−ℎ)(𝑎^2+𝑎ℎ−2ℎ^2 )=0 Thus, h = a & h = (−𝑎)/2 a2 + ah – 2h2 = 0 a2 + 2ah – ah – 2h2 = 0 a(𝑎+2ℎ)−ℎ(𝑎+2ℎ)=0 (𝑎−ℎ)(𝑎+2ℎ)=0 So, h = a &h = (−𝒂)/𝟐 If h = a then k = 1/𝑎 √((𝑎𝑏)^2−(𝑏ℎ)^2 )= 1/𝑎 √((𝑎𝑏)^2−(𝑏𝑎)^2 )= 0 Which is not possible Hence, h = (−𝒂)/𝟐 only Finding (𝒅^𝟐 𝒁)/(𝒅𝒉^𝟐 ) 𝑑𝑍/𝑑ℎ=−2(𝑏/𝑎)^2 ((𝑎−ℎ)(𝑎^2+𝑎ℎ−2ℎ^2 )) Differentiating w.r.t ℎ (𝑑^2 𝑍)/(𝑑ℎ^2 ) = −2(𝑏/𝑎)^2. 𝑑((𝑎−ℎ)(𝑎^2+𝑎ℎ−2ℎ^2 ))/𝑑ℎ =−2(𝑏/𝑎)^2 [𝑑/𝑑ℎ (𝑎−ℎ)(𝑎^2+𝑎ℎ−2ℎ^2 )+𝑑(𝑎^2+𝑎ℎ−2ℎ^2 )/𝑑ℎ.(𝑎−ℎ)] = −2(𝑏/𝑎)^2 [(0−1)(𝑎^2+𝑎ℎ−2ℎ^2 )+(0+𝑎 −4ℎ)(𝑎−ℎ)] = −2(𝑏/𝑎)^2 [(−1)(𝑎^2+𝑎ℎ−2ℎ^2 )+(𝑎 −4ℎ)(𝑎−ℎ)] = −2(𝑏/𝑎)^2 [−𝑎^2−𝑎ℎ+2ℎ^2+𝑎^2−𝑎ℎ−4𝑎ℎ+4ℎ^2 ] = −2(𝑏/𝑎)^2 [−2𝑎ℎ−4𝑎ℎ+6ℎ^2 ] Putting h = (−𝐚)/𝟐 " " (𝒅^𝟐 𝒁)/(𝒅𝒉^𝟐 )= −2(𝑏/𝑎)^2 [−2𝑎(((−𝑎)/2)−4𝑎((−𝑎)/2)+6((−𝑎)/2)^2 )] = −2(𝑏/𝑎)^2 [𝑎^2+2𝑎^2+6/4 𝑎^2 ] = –2 (𝑏/𝑎)^2 [3𝑎^2+3/2 𝑎^2 ] = –2((𝑏^2 )/𝑎^2 )((9𝑎^2)/2) = −9b^2 < 0 Since 𝐙^′′ < 0 for h = (−𝑎)/2 ∴ Z is maximum when h = (−𝑎)/2 Thus, A is maximum at h = (−𝒂)/𝟐 Maximum value of Area A = (𝒂−𝒉) ×𝟏/𝒂 √((𝒂𝒃)^𝟐−𝒃^𝟐 𝒉^𝟐 ) = (𝑎−((−𝑎)/2)) ×1/𝑎 √((𝑎𝑏)^2−𝑏^2 ((−𝑎)/2)^2 ) = 3a/2 ×1/𝑎 √(𝑎^2 𝑏^2−(𝑎^2 𝑏^2)/4) = 3a/2 ×1/𝑎 √((3𝑎^2 𝑏^2)/4) = 3a/2 ×1/𝑎 × (√3 𝑎𝑏)/2 = (3√3 𝑎𝑏)/4 Hence, maximum area is (𝟑√𝟑 𝒂𝒃)/𝟒 square units