


Examples
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo





Transcript
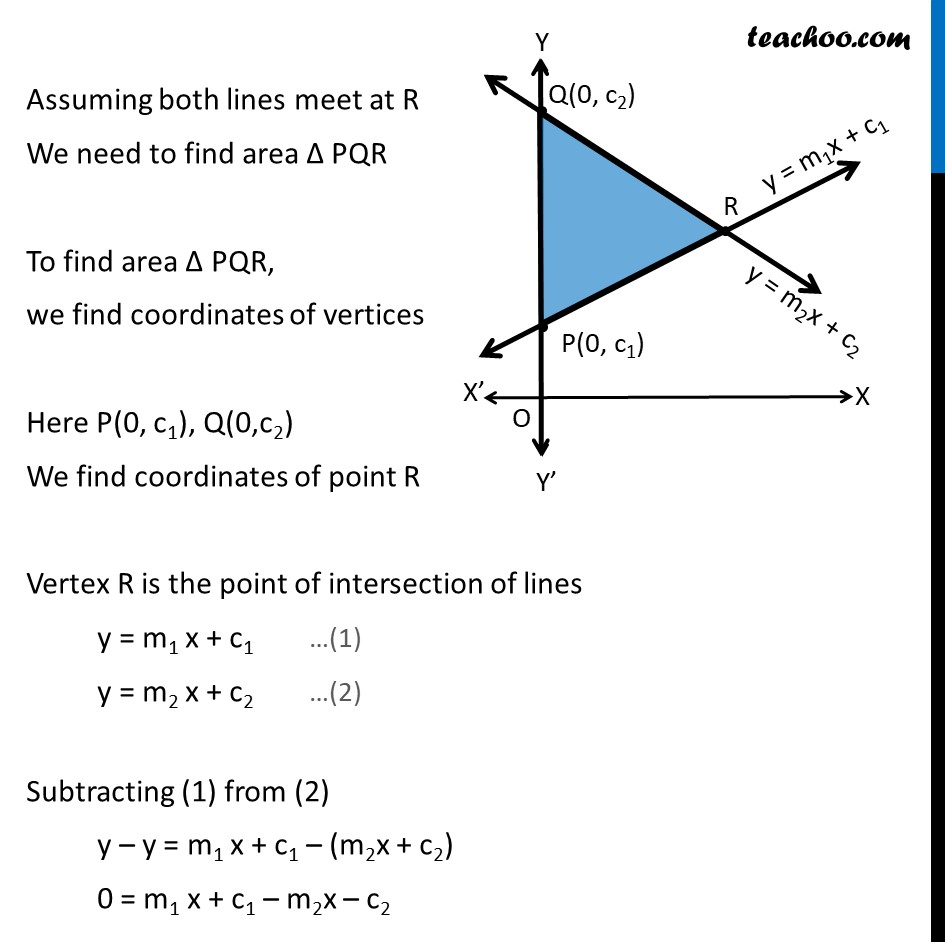
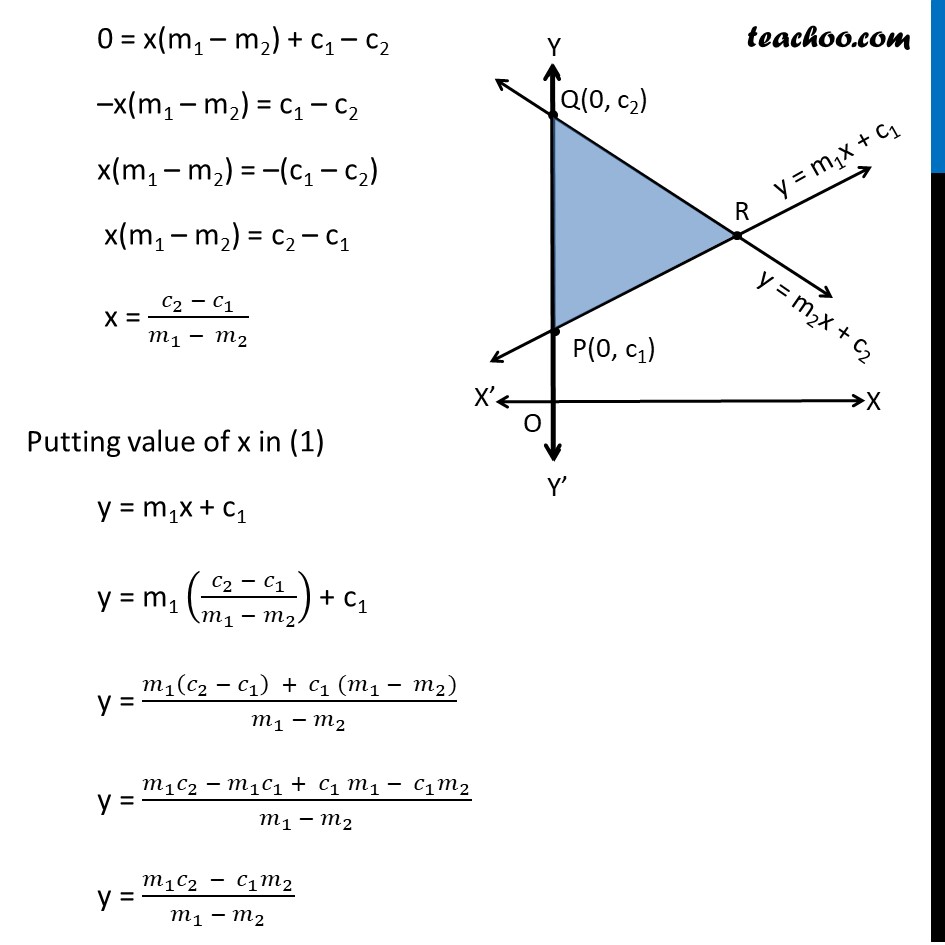
Example 14 Show that the area of the triangle formed by the lines y = m1 x + c1 , y = m2x + c2 and x = 0 is (𝑐_2 − 𝑐_1 )^2/2|𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 | . There are three lines given in the graph x = 0 This line will lie be y-axis y = m1 x + c1 Putting x = 0 y = 0 + c1 = c1 Hence point is P(0, c1) y = m2 x + c2 Putting x = 0 y = 0 + c2 = c2 Hence point is Q(0, c2) Assuming both lines meet at R We need to find area Δ PQR To find area Δ PQR, we find coordinates of vertices Here P(0, c1), Q(0,c2) We find coordinates of point R Vertex R is the point of intersection of lines y = m1 x + c1 …(1) y = m2 x + c2 …(2) Subtracting (1) from (2) y – y = m1 x + c1 – (m2x + c2) 0 = m1 x + c1 – m2x – c2 0 = x(m1 – m2) + c1 – c2 –x(m1 – m2) = c1 – c2 x(m1 – m2) = –(c1 – c2) x(m1 – m2) = c2 – c1 x = (𝑐_2 − 𝑐_1)/(𝑚_1 − 〖 𝑚〗_2 ) Putting value of x in (1) y = m1x + c1 y = m1 ((𝑐_2 − 𝑐_1)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 )) + c1 y = (𝑚_1 (𝑐_2 − 𝑐_1 ) + 〖 𝑐〗_1 (𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2))/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 ) y = (𝑚_1 𝑐_2 − 𝑚_1 𝑐_1 + 〖 𝑐〗_1 𝑚_1 − 〖 𝑐〗_1 𝑚_2)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 ) y = (𝑚_1 𝑐_(2 ) − 〖 𝑐〗_1 𝑚_2)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 ) ∴ Vertex R is ((𝑐_2 − 𝑐_1)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 ) ", " (𝑚_1 𝑐_(2 ) − 𝑚_2 〖 𝑐〗_1)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 )) The vertices of ∆ PRQ is P(0, c1), R((𝑐_2 − 𝑐_1)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 ) ", " (𝑚_1 𝑐_(2 ) − 𝑚_2 〖 𝑐〗_1)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 )) & Q(0, c2) We know that Area of triangle whose vertices are (x1, y1) (x2, y2) (x3, y3) is 1/2 |"x1" ("y2 – y3" ) + 𝑥2 (𝑦3 − 𝑦1) + 𝑥3(𝑦1 − 𝑦2)| For ∆ PRQ, (x1, y1) = P(0, c1) (x2,y2) = R ((𝑐_2 − 𝑐_1)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 ) ", " (𝑚_1 𝑐_(2 ) − 𝑚_2 〖 𝑐〗_1)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 )) (x3,y3) = Q (0, c2) Area ∆ PRQ = ■8(1/2 " " |0((𝑚_1 𝑐_(2 ) − 𝑚_2 〖 𝑐〗_1)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 ) −𝑐2) + (𝑐_2 − 𝑐_1)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 ) (𝑐2 −𝑐1) + 0(𝑐1 − (𝑚_1 𝑐_(2 ) − 𝑚_2 〖 𝑐〗_1)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 ))| ) = ■8(1/2 " " |█(0 + (𝑐2 − 𝑐1)2/(𝑚1 − 𝑚2) + 0)| ) = ■8(1/2 " " |(〖(𝑐〗_2 − 𝑐_1)2)/(𝑚_1 − 𝑚_2 )| ) = 1/2 (𝑐2 − 𝑐1)2/|𝑚1 − 𝑚2| ∴ Area required = 1/2 (𝑐2 − 𝑐1)2/|𝑚1 − 𝑚2| Hence proved