





Minima/ maxima (statement questions) - Geometry questions
Minima/ maxima (statement questions) - Geometry questions
Last updated at December 16, 2024 by Teachoo








Transcript
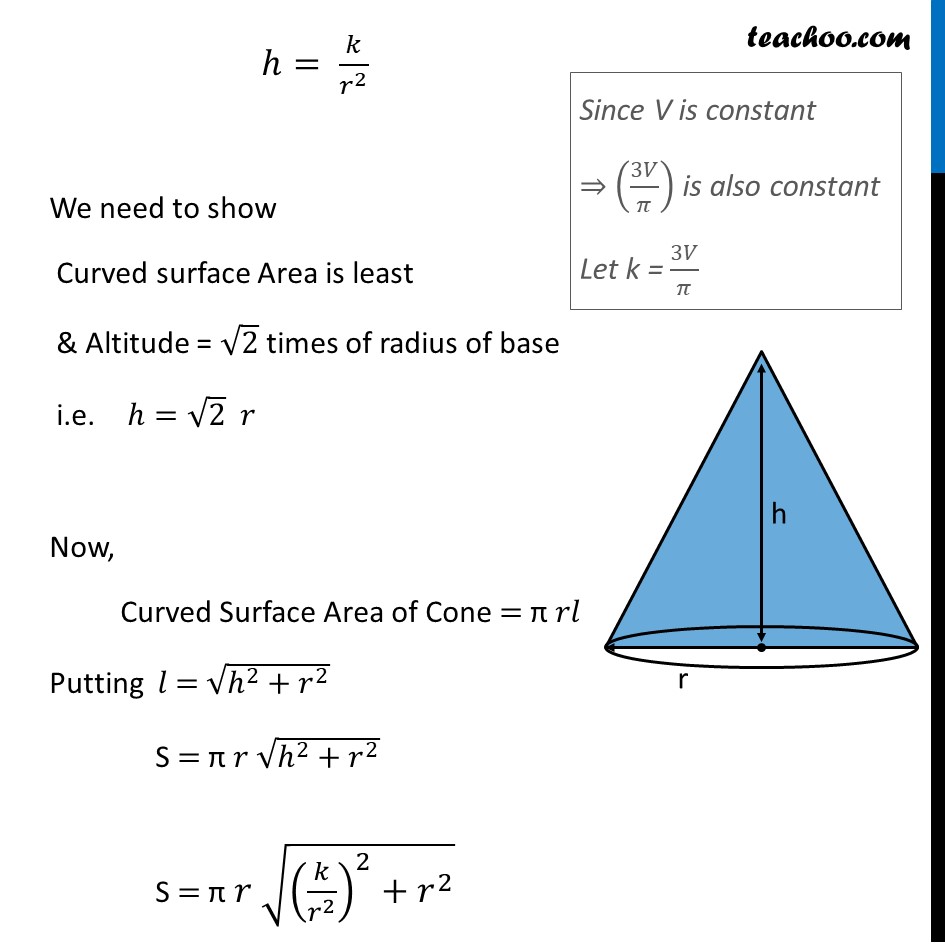
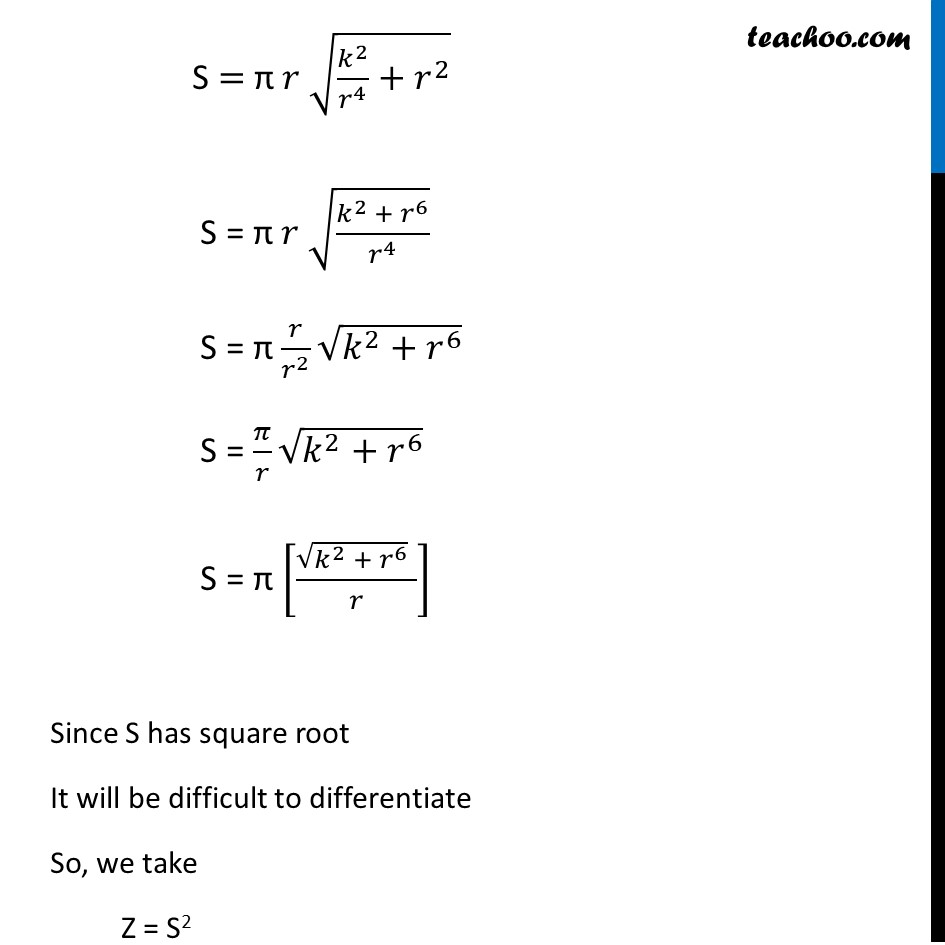
Ex 6.3, 24 Show that the right circular cone of least curved surface and given volume has an altitude equal to √2 time the radius of the baseLet r & h be the radius & height of a cone respectively And V & S be the volume & curved surface area of cone respectively Given volume of cone is constant Volume of cone = 1/3 𝜋(𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠)^2 (ℎ𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡) V = 1/3 𝜋(𝑟)^2 ℎ 3𝑉/𝜋=𝑟^2 ℎ h = (3𝑉/𝜋) 1/𝑟^2 ℎ= 𝑘/𝑟^2 We need to show Curved surface Area is least & Altitude = √2 times of radius of base i.e. ℎ=√2 𝑟 Now, Curved Surface Area of Cone = π 𝑟𝑙 Putting 𝑙 = √(ℎ^2+𝑟^2 ) S = π 𝑟 √(ℎ^2+𝑟^2 ) S = π 𝑟 √((𝑘/𝑟^2 )^2+𝑟^2 ) S = π 𝑟 √(𝑘^2/𝑟^4 +𝑟^2 ) S = π 𝑟 √((𝑘^2 + 𝑟^6)/𝑟^4 ) S = π 𝑟/𝑟^2 √(𝑘^2+𝑟^6 ) S = 𝜋/𝑟 √(𝑘^2+𝑟^6 ) S = π [(√(𝑘^2 + 𝑟^6 ) " " )/𝑟] Since S has square root It will be difficult to differentiate So, we take Z = S2 Z = 𝜋^2 [(𝑘^2 + 𝑟^6 " " )/𝑟^2 ] Z = 𝜋^2 [(𝑘^2 " " )/𝑟^2 +𝑟^4 ] Z = 𝜋^2 [𝑘^2 𝑟^(−2)+𝑟^4 ] Since S is positive, S is minimum if A2 is minium So, we minimize Z = A2 Diff. Z w.r.t 𝑟 𝑑Z/𝑑𝑟=𝑑(𝜋^2 [𝑘^2 𝑟^(−2)+𝑟^4 ])/𝑑𝑟 𝑑Z/𝑑𝑟=𝜋^2 [𝑘^2 (−2𝑟^(−2−1))+4𝑟^3 ] 𝑑Z/𝑑𝑟=𝜋^2 [−2𝑘^2 𝑟^(−3)+4𝑟^3 ] Putting 𝒅𝒁/𝒅𝒓 = 0 𝜋^2 [−2𝑘^2 𝑟^(−3)+4𝑟^3 ] = 0 −2𝑘^2 𝑟^(−3)+4𝑟^3= 0 4𝑟^3 = 2𝑘^2 𝑟^(−3) 4𝑟^3 = (2𝑘^2)/𝑟^3 4𝑟^3 × 𝑟^3 = 2𝑘^2 4𝑟^6 = 2𝑘^2 𝑟^6 = 𝑘^2/2 Finding (𝒅^𝟐 𝐙)/(𝐝𝒙^𝟐 ) 𝑑Z/𝑑𝑟=𝜋^2 [−2𝑘^2 𝑟^(−3)+4𝑟^3 ] Diff w.r.t 𝑥 (𝑑^2 Z)/(𝑑𝑟^2 ) = 𝑑/𝑑𝑟 [𝜋^2 [−2𝑘^2 𝑟^(−3)+4𝑟^3 ]] (𝑑^2 Z)/(𝑑𝑥^2 ) = 𝜋^2 [−2𝑘^2 (−3𝑟^(−4))+4(3𝑟^2)] (𝑑^2 Z)/(𝑑𝑥^2 ) = 𝜋^2 [6𝑘^2 𝑟^(−4)+12𝑟^2 ] Since everything is positive, (𝑑^2 Z)/(𝑑𝑥^2 ) > 0 for 𝑟^6 = 𝑘^2/2 Thus, Surface area is minimum when 𝑟^6 = 𝑘^2/2 Now, ℎ=𝑘/𝑟^2 ℎ𝑟^2=𝑘 (ℎ𝑟^2 )^2=𝑘^2 ℎ^2 𝑟^4=𝑘^2 Putting value of 𝑘^2=2𝑟^6 ℎ^2 𝑟^4=2𝑟^6 ℎ^2=(2𝑟^6)/𝑟^4 ℎ^2=2𝑟^2 ℎ=√(2𝑟^2 ) 𝒉=𝒓√𝟐 Hence altitude equal to √2 times the radius of the base Hence proved