


Ex 6.2
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo




Transcript
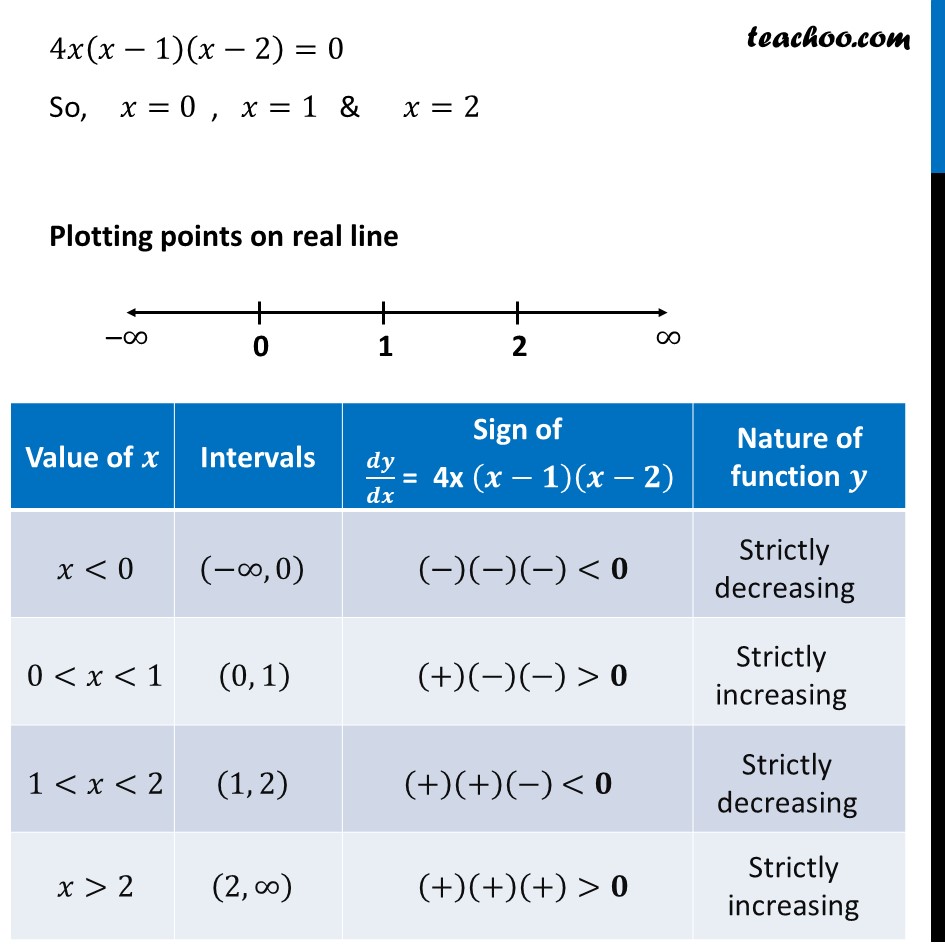
Ex 6.2, 8 Find the values of 𝑥 for which y = [𝑥(𝑥 – 2)]2 is an increasing function 𝑦 = [𝑥(𝑥−2)]^2 Finding 𝒅𝒚/𝒅𝒙 𝑦 = [𝑥(𝑥−2)]^2 𝑦 = [𝑥^2−2𝑥]^2 𝑦 = (𝑥)^4+(2𝑥)^2−2(𝑥^2 )(2𝑥) 𝒚 = 𝒙^𝟒+𝟒𝒙^𝟐−𝟒𝒙^𝟑 Differentiating w.r.t 𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=𝑑(𝑥^4 + 4𝑥^2 − 4𝑥^3 )/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=4𝑥^3+8𝑥−12𝑥^2 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=4𝑥(𝑥^2+2−3𝑥) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=4𝑥(𝑥^2−3𝑥+2) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=4𝑥(𝑥^2−2𝑥−𝑥+2) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=4𝑥(𝑥(𝑥−2)−1(𝑥−2)) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=4𝑥((𝑥−1)(𝑥−2)) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=4𝑥(𝑥−1)(𝑥−2) Putting 𝒅𝒚/𝒅𝒙=𝟎 4𝑥(𝑥−1)(𝑥−2)=0 So, 𝑥=0 , 𝑥=1 & 𝑥=2 Plotting points on real line Thus, the function is strictly increasing for 0 <𝒙<𝟏 and 𝒙>𝟐