



Chapter 13 Class 12 Probability
Chapter 13 Class 12 Probability
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo





Transcript
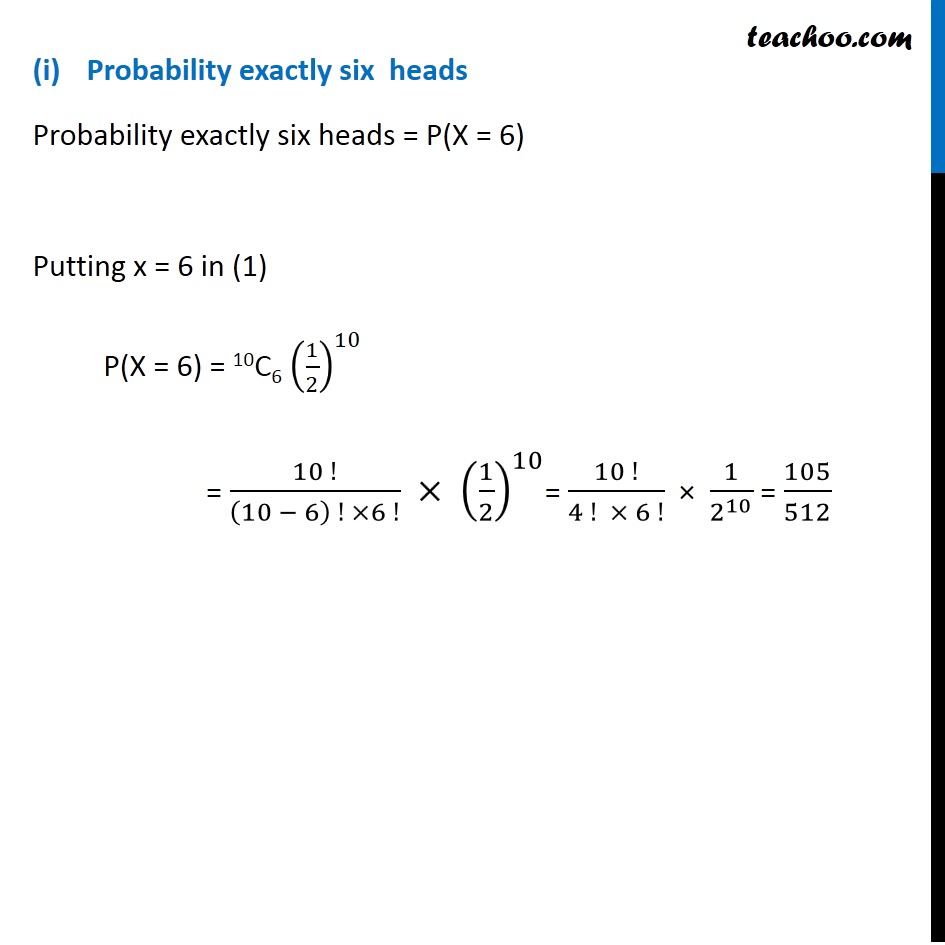
Question 10 If a fair coin is tossed 10 times, find the probability of (i) exactly six heads (ii) at least six heads (iii) at most six headsIf a trial is Bernoulli, then There is finite number of trials They are independent Trial has 2 outcomes i.e. Probability success = P then Probability failure = q = 1 – P (4) Probability of success (P) is same for all trials Let X : Number of heads appearing Coin toss is a Bernoulli trial So, X has a binomial distribution P(X = x) = nCx 𝒒^(𝒏−𝒙) 𝒑^𝒙 n = number of coins tosses = 10 p = Probability of head = 1/2 q = 1 – p = 1 – 1/2 = 1/2 Hence, P(X = x) = 10Cx (1/2)^𝑥 (1/2)^(10−𝑥) P(X = x) = 10Cx (1/2)^(10 − 𝑥 + 𝑥) P(X = x) = 10Cx (𝟏/𝟐)^𝟏𝟎 Probability exactly six heads Probability exactly six heads = P(X = 6) Putting x = 6 in (1) P(X = 6) = 10C6 (1/2)^10 = (10 !)/((10 − 6) ! ×6 !) × (1/2)^10= (10 !)/(4 ! × 6 !) × 1/2^10 = 105/512 (ii) Probability appearing at least six heads i.e. P(X ≥ 6) P(X ≥ 6) = P(X = 6) + P(X = 7) + P(X = 8) + P(X = 9) + P(X = 10) = 10C6 (1/2)^10 + 10C7 (1/2)^10 + 10C8 (1/2)^10 + 10C9 (1/2)^10 + 10C10 (1/2)^10 = (1/2)^10(10C6 + 10C7 + 10C8 + 10C9 + 10C10) = (1/2)^10(210 + 120 + 45 + 10 + 1) = (1/2)^10(386) = 𝟏𝟗𝟑/𝟓𝟏𝟐 (iii) Probability appearing at most six heads i.e. P(X ≤ 6) P(X ≤ 6) = P(X = 6) + P(X = 5) + P(X = 4) + P(X = 3) + P(X = 2) + P(X = 1) + P(X = 0) = 10C6 (1/2)^10 + 10C5 (1/2)^10 + 10C4 (1/2)^10 + 10C3 (1/2)^10 + 10C2 (1/2)^10 + 10C1 (1/2)^10+ 10C0 (1/2)^10 = (1/2)^10(10C6 + 10C5 + 10C4 + 10C3 + 10C2 + 10C1 + 10C0) = (1/2)^10(210 + 252 + 210 + 120 + 45 + 10 + 1) = (1/2)^10(848) = 𝟓𝟑/𝟔𝟒