

Examples
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo



Transcript
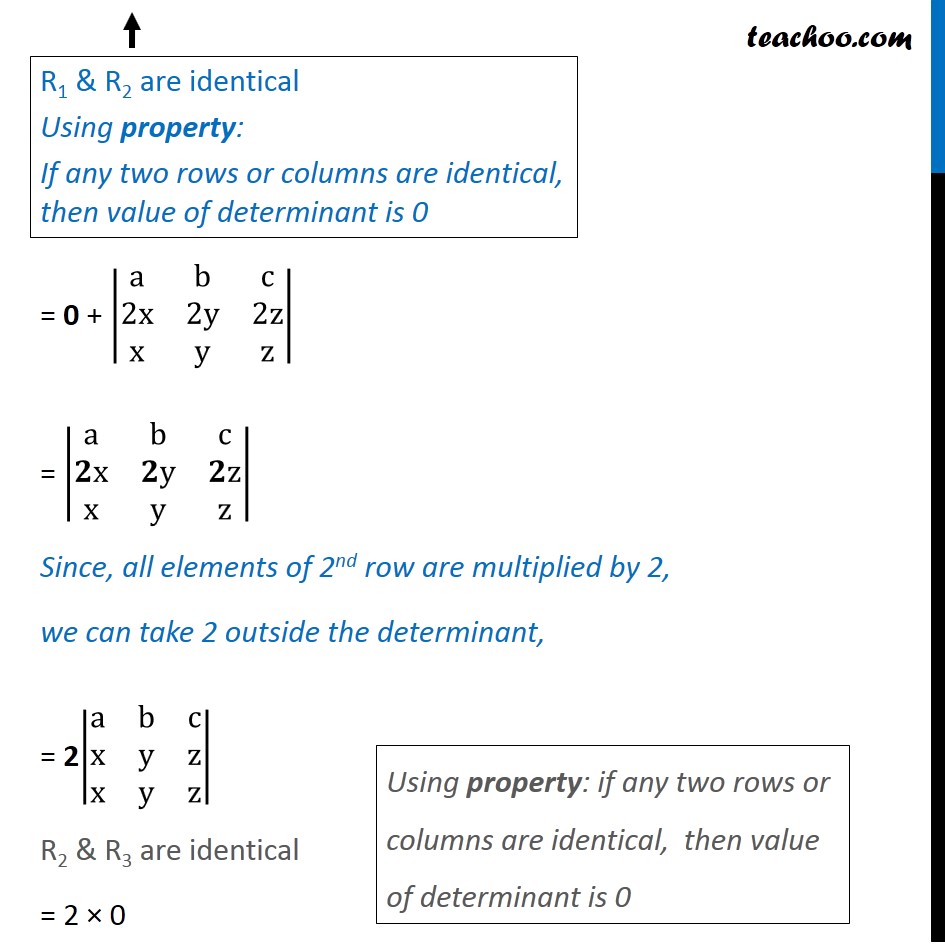
Question 5 Show that |■8(a&b&c@a+2x&b+2y&c+2z@x&y&z)| = 0 Solving L.H.S |■8(a&b&c@a+2x&b+2y&c+2z@x&y&z)| Expressing elements of 2nd row as sum of two elements = |■8(𝐚&𝐛&𝐜@𝐚&𝐛&𝐜@x&y&z)| + |■8(a&b&c@2x&2y&2z@x&y&z)| By Property 5: If some or all elements of a row or column of a determinant are expressed as sum of two (or more) terms ,then the determinant is expressed as a sum of two (or more) determinants. R1 & R2 are identical Using property: If any two rows or columns are identical, then value of determinant is 0 = 0 + |■8(a&b&c@2x&2y&2z@x&y&z)| = |■8(a&b&c@𝟐x&𝟐y&𝟐z@x&y&z)| Since, all elements of 2nd row are multiplied by 2, we can take 2 outside the determinant, = 2|■8(a&b&c@x&y&z@x&y&z)| R2 & R3 are identical = 2 × 0 Using property: if any two rows or columns are identical, then value of determinant is 0 = 0 = R.H.S Thus L.H.S = R.H.S Hence proved