

Ex 9.3
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo



Transcript
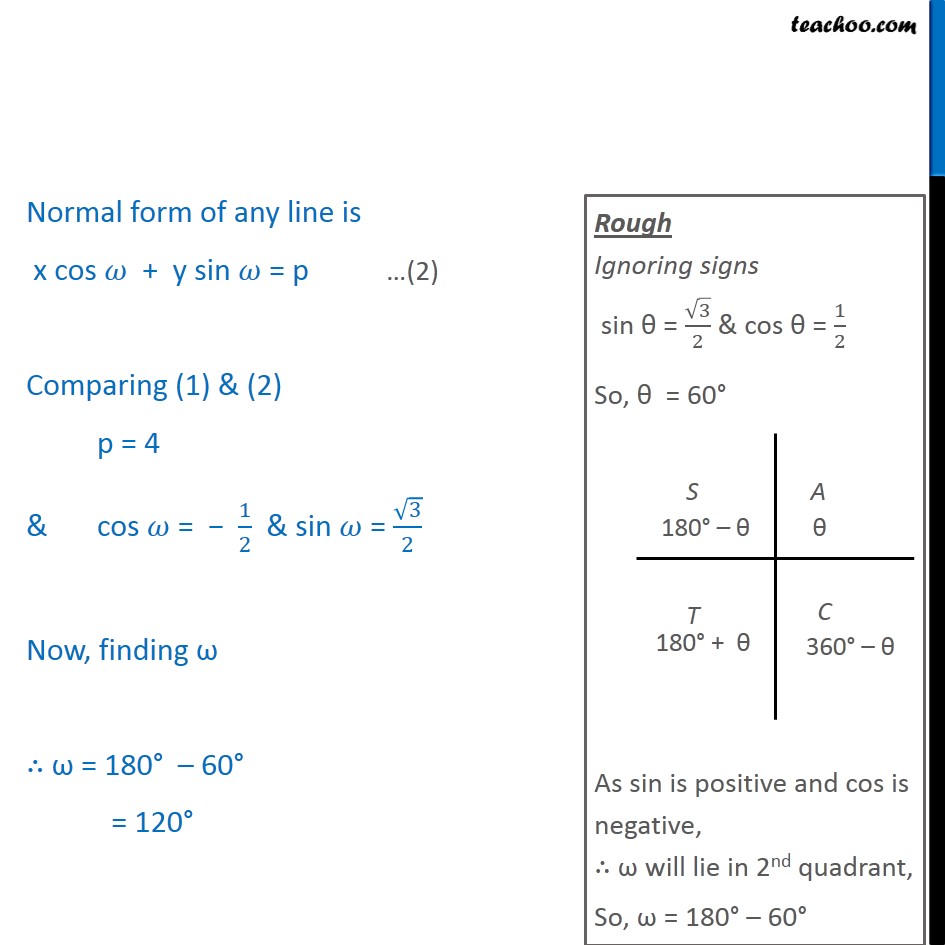
Ex10.3, 3 Reduce the following equations into normal form. Find their perpendicular distances from the origin and angle between perpendicular and the positive x-axis. x 3 y + 8 = 0 x 3 y + 8 = 0 8 = x + 3 x + 3 = 8 Divide equation by (( 1)2 + ( 3)^2 ) = (1 + 3)= 4 = 2 ( + 3 )/2 = 8/2 ( )/2 + 3/2y = 4 x(( 1)/2) + y ( 3/2) = 4 Normal form of any line is x cos + y sin = p Comparing (1) & (2) p = 4 & cos = 1/2 & sin = 3/2 Now, finding = 180 60 = 120 So, the normal form of line is x cos 120 + y sin 120 = 4 Hence perpendicular distance from origin = p = 4 & angle between perpendicular & the + ve x-axis = = 120