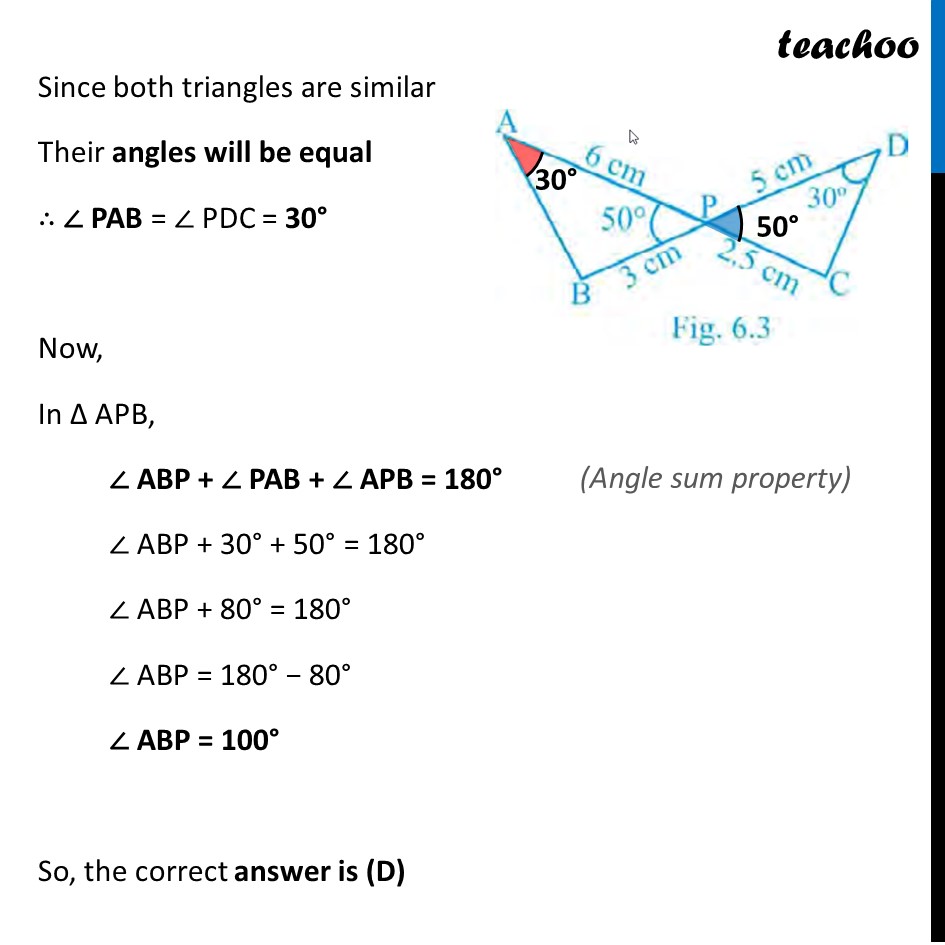
In Fig.6.3, two line segments AC and BD intersect each other at the point P such that PA = 6 cm, PB = 3 cm, PC = 2.5 cm, PD = 5 cm, ∠ APB = 50° and ∠ CDP = 30°. Then, ∠ PBA is equal to
(A) 50° (B) 30° (C) 60° (D) 100°
![NCERT Exemplar [MCQ] - In Fig.6.3, two line segments AC and BD interse - NCERT Exemplar - MCQ](https://cdn.teachoo.com/808ad77d-26c0-4542-8f15-9aeec6af3aae/slide14.jpg)
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo
![NCERT Exemplar [MCQ] - In Fig.6.3, two line segments AC and BD interse - NCERT Exemplar - MCQ](https://cdn.teachoo.com/808ad77d-26c0-4542-8f15-9aeec6af3aae/slide14.jpg)

Transcript
Question 7 In Fig.6.3, two line segments AC and BD intersect each other at the point P such that PA = 6 cm, PB = 3 cm, PC = 2.5 cm, PD = 5 cm, ∠ APB = 50° and ∠ CDP = 30°. Then, ∠ PBA is equal to (A) 50° (B) 30° (C) 60° (D) 100° In Δ APB and Δ DPC 𝐴𝑃/𝐵𝑃=𝐷𝑃/𝐶𝑃 ∠ APB = ∠ DPC ∴ Δ APB ~ Δ DPC (Both ratios are same) (Vertically opposite angles) (SAS Similarity) Since both triangles are similar Their angles will be equal ∴ ∠ PAB = ∠ PDC = 30° Now, In Δ APB, ∠ ABP + ∠ PAB + ∠ APB = 180° ∠ ABP + 30° + 50° = 180° ∠ ABP + 80° = 180° ∠ ABP = 180° − 80° ∠ ABP = 100° So, the correct answer is (D) (Angle sum property)