
Examples
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo



Transcript
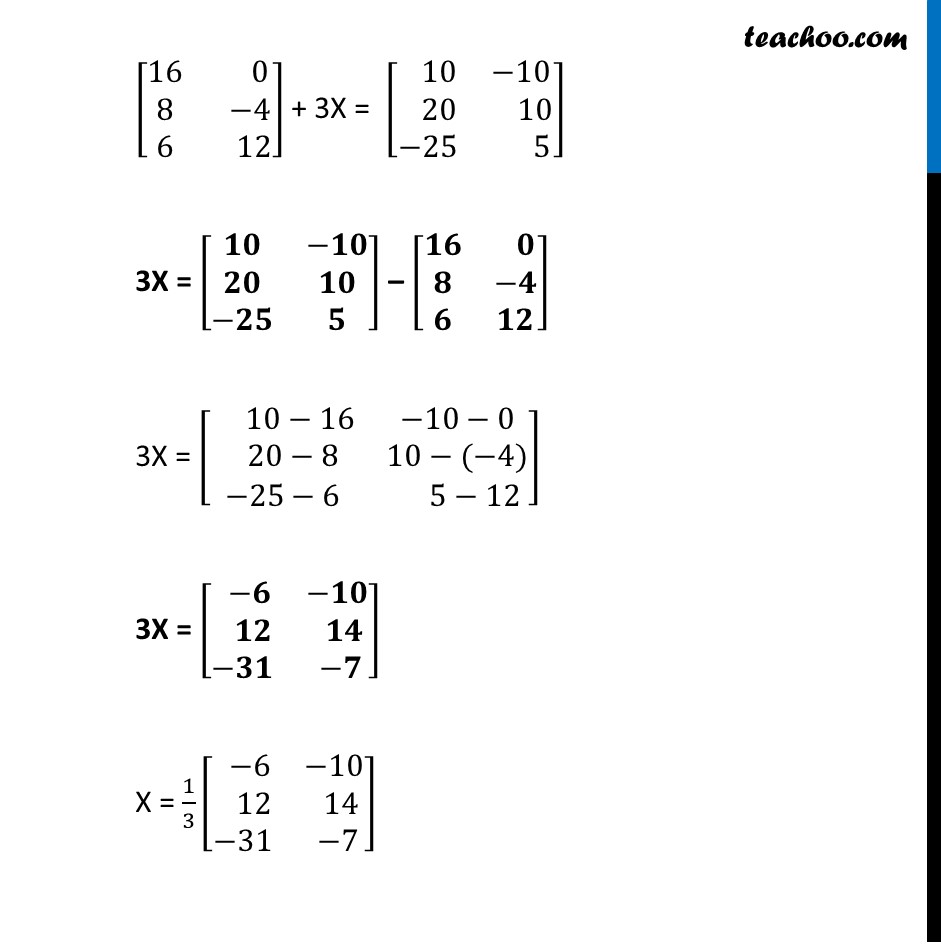
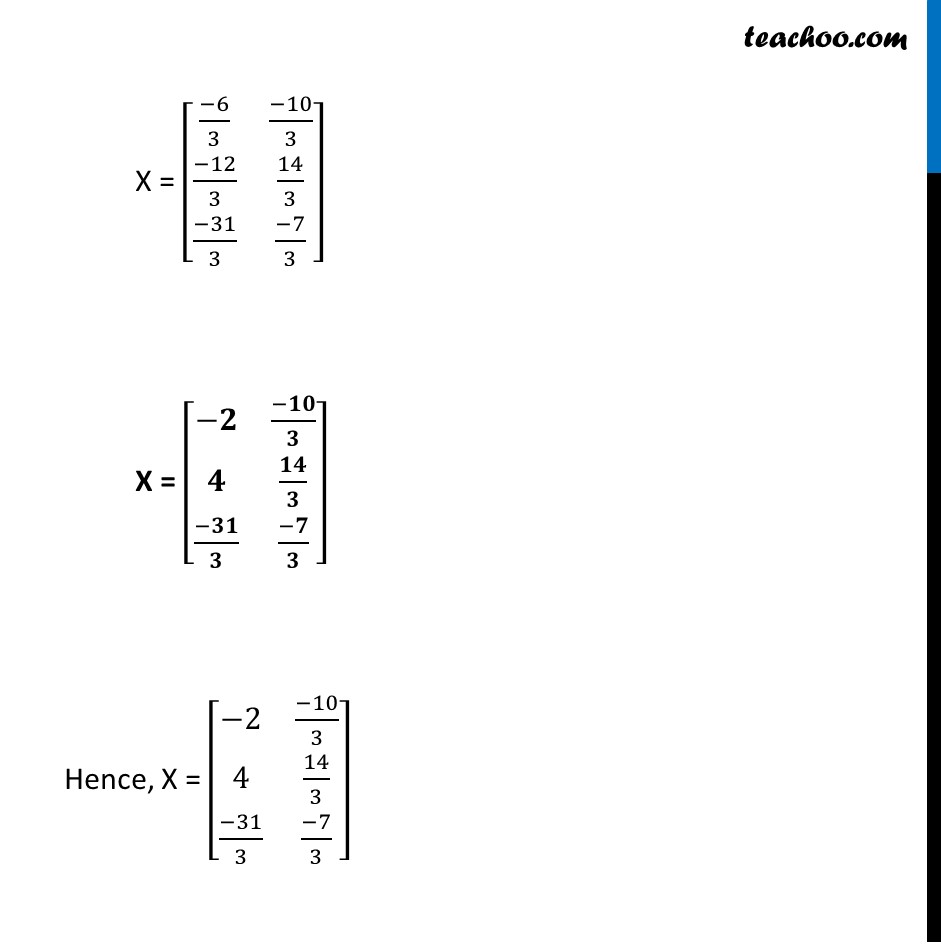
Example 8 If A = [■8(8&0@4&−2@3&6)] and B = [■8(2&−2@4&2@−5&1)] then find the matrix X, such that 2A + 3X = 5B. Given that 2A + 3X = 5B Putting values 2 [■8(𝟖& 𝟎@𝟒&−𝟐@𝟑& 𝟔)] + 3X = 5 [■8( 𝟐&−𝟐@ 𝟒& 𝟐@−𝟓& 𝟏)] [■8(8 × 2 & 0 × 2@4 × 2&−2 × 2@3 × 2& 6 × 2)] + 3X = [■8( 2 × 5 &−2 × 5@ 4 × 5& 2 × 5@−5 × 5& 1 × 5)] [■8(16& 0@8& −4@6& 12)] + 3X = [■8( 10&−10@ 20& 10@−25& 5)] 3X = [■8(𝟏𝟎&−𝟏𝟎@𝟐𝟎&𝟏𝟎@−𝟐𝟓&𝟓)] – [■8(𝟏𝟔& 𝟎@𝟖&−𝟒@𝟔&𝟏𝟐)] 3X = [■8( 10−16&−10−0@ 20−8&10−(−4)@−25−6& 5−12)] 3X = [■8( −𝟔&−𝟏𝟎@ 𝟏𝟐& 𝟏𝟒@−𝟑𝟏& −𝟕)] X = 1/3 [■8( −6&−10@ 12& 14@−31& −7)] X = [■8((−6)/3&(−10)/3@(−12)/3&14/3@(−31)/3&(−7)/3)] X = [■8(−𝟐&(−𝟏𝟎)/𝟑@𝟒&𝟏𝟒/𝟑@(−𝟑𝟏)/𝟑&(−𝟕)/𝟑)] Hence, X = [■8(−2&(−10)/3@4&14/3@(−31)/3&(−7)/3)]