![Ex 3.3, 10 (iii) Class 12 - Express Matrix [3 3 -1 -2 -2 1 -4 -5 2] as - Ex 3.3](https://cdn.teachoo.com/10f3008f-7bdd-463f-8e3f-dcffbf99e03c/slide41.jpg)

Ex 3.3
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo
![Ex 3.3, 10 (iii) Class 12 - Express Matrix [3 3 -1 -2 -2 1 -4 -5 2] as - Ex 3.3](https://cdn.teachoo.com/10f3008f-7bdd-463f-8e3f-dcffbf99e03c/slide41.jpg)



🎉 Smart choice! You just saved 2+ minutes of ads and got straight to the good stuff. That's what being a Teachoo Black member is all about.
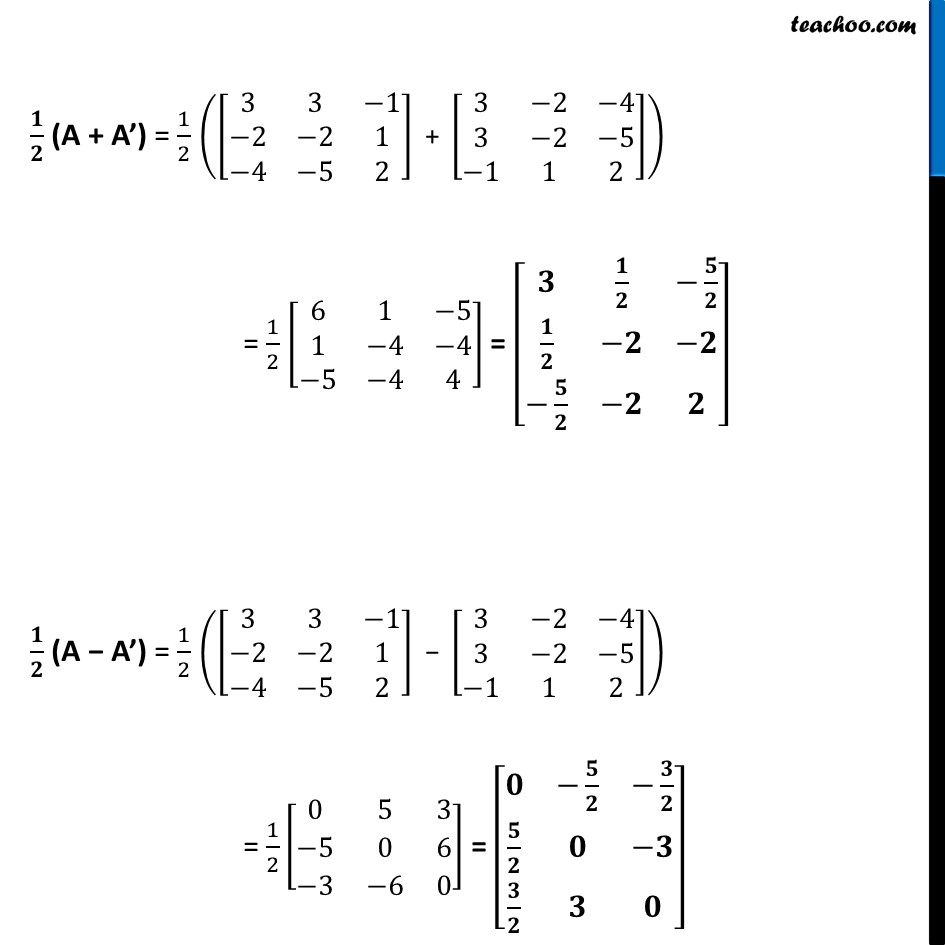
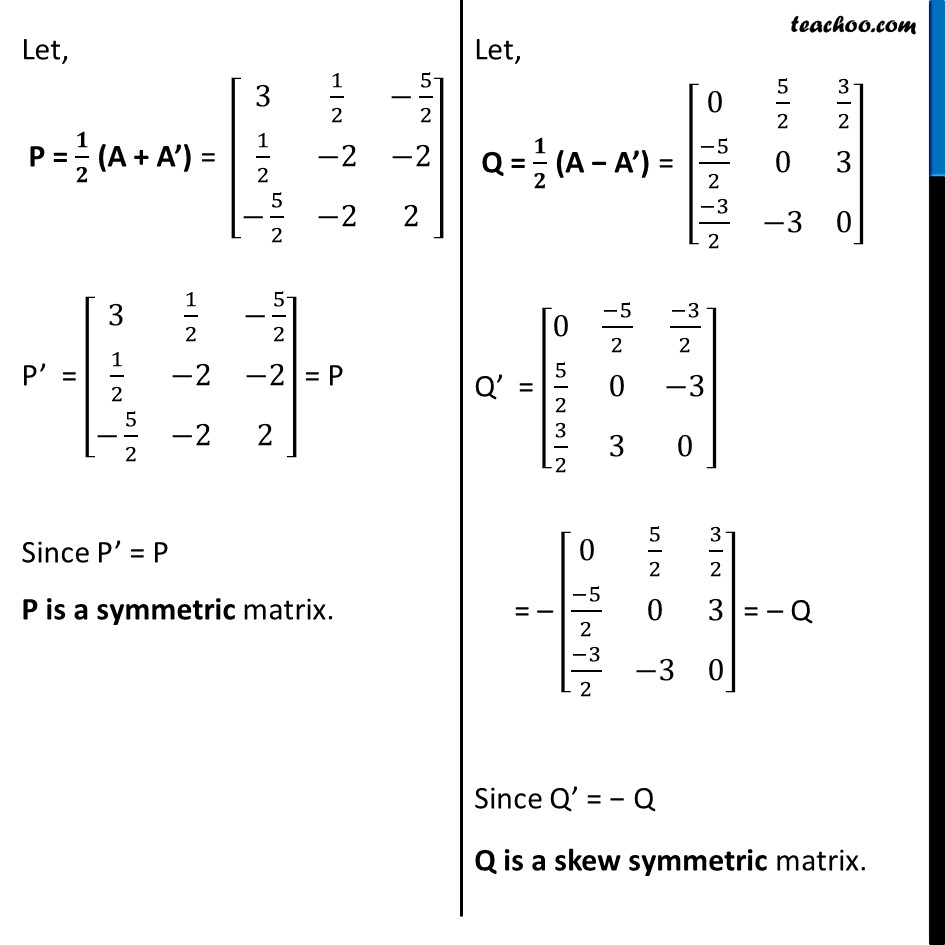
Ex 3.3, 10 Express the following matrices as the sum of a symmetric and a skew symmetric matrix: (iii) [■8(3&3&−1@−2&−2&1@−4&−5&2)] Let A = [■8(3&3&−1@−2&−2&1@−4&−5&2)] A’ = [■8(3&−2&−4@3&−2&−5@−1&1&2)] 𝟏/𝟐 (A + A’) = 1/2 ([■8(3&3&−1@−2&−2&1@−4&−5&2)]" + " [■8(3&−2&−4@3&−2&−5@−1&1&2)]) = 1/2 [■8(6&1&−5@1&−4&−4@−5&−4&4)] = [■8(𝟑&𝟏/𝟐&−𝟓/𝟐@𝟏/𝟐&−𝟐&−𝟐@−𝟓/𝟐&−𝟐&𝟐)] 𝟏/𝟐 (A − A’) = 1/2 ([■8(3&3&−1@−2&−2&1@−4&−5&2)]" − " [■8(3&−2&−4@3&−2&−5@−1&1&2)]) = 1/2 [■8(0&5&3@−5&0&6@−3&−6&0)] = [■8(𝟎&−𝟓/𝟐&−𝟑/𝟐@𝟓/𝟐&𝟎&−𝟑@𝟑/𝟐&𝟑&𝟎)] Let, P = 𝟏/𝟐 (A + A’) = [■8(3&1/2&−5/2@1/2&−2&−2@−5/2&−2&2)] P’ = [■8(3&1/2&−5/2@1/2&−2&−2@−5/2&−2&2)] = P Since P’ = P P is a symmetric matrix. Let, Q = 𝟏/𝟐 (A − A’) = [■8(0&5/2&3/2@(−5)/2&0&3@(−3)/2&−3&0)] Q’ = [■8(0&(−5)/2&(−3)/2@5/2&0&−3@3/2&3&0)] = – [■8(0&5/2&3/2@(−5)/2&0&3@(−3)/2&−3&0)] = – Q Since Q’ = − Q Q is a skew symmetric matrix. Now, P + Q = 1/2 (A + A’) + 1/2 (A − A’) = A Thus, A is a sum of symmetric & skew symmetric matrix