




Ex 13.1
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo







Transcript
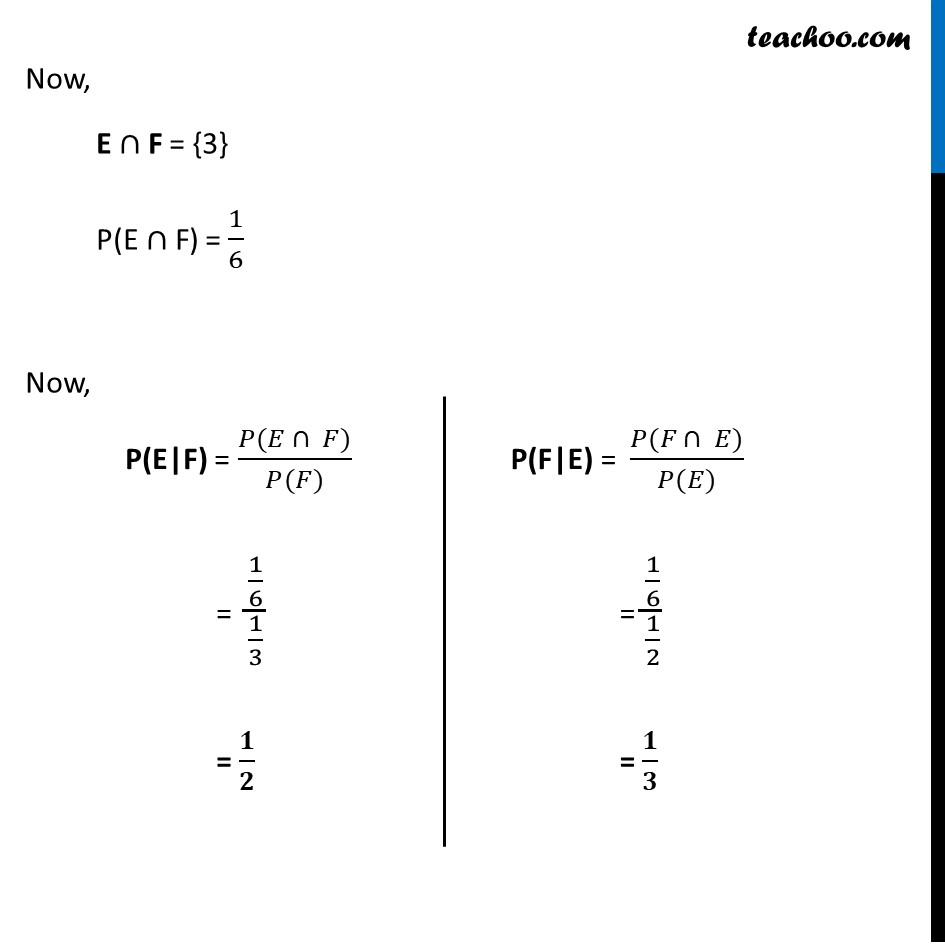
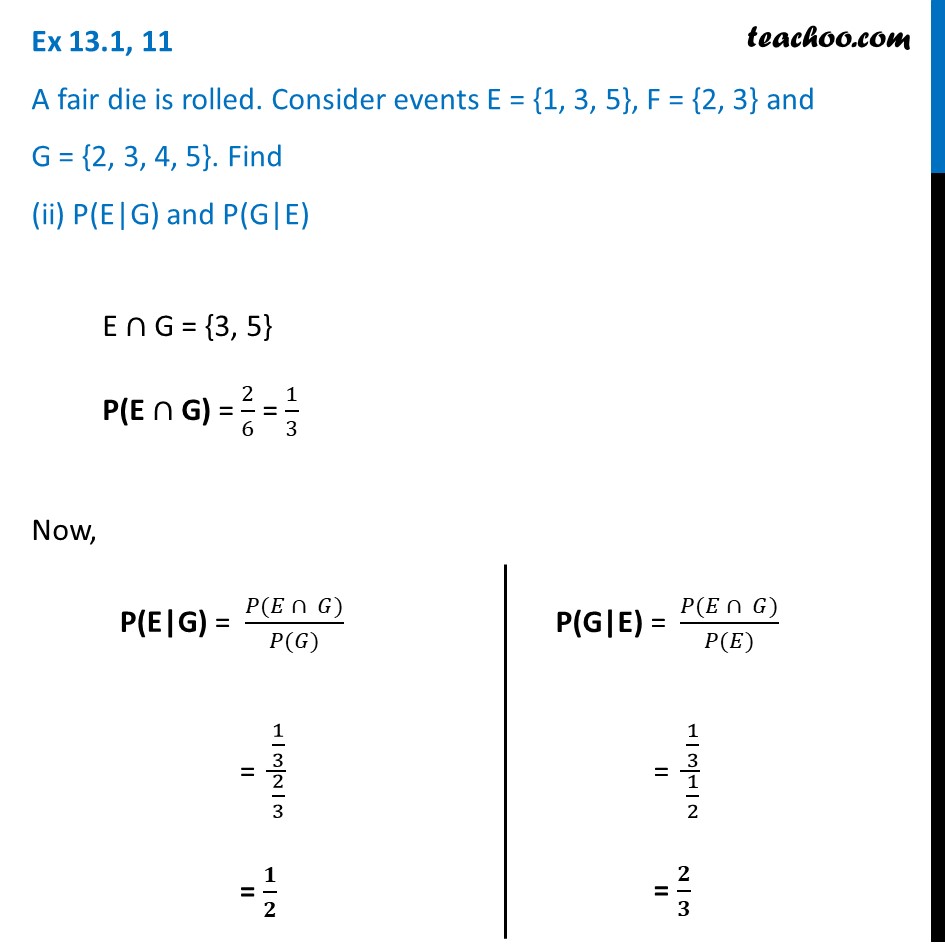
Ex 13.1, 11 A fair die is rolled. Consider events E = {1, 3, 5}, F = {2, 3} and G = {2, 3, 4, 5}. Find (i) P(E|F) and P (F|E)A fair die is rolled S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} Event E E = {1, 3, 5} P(E) = 3/6 = 1/2 Event F F = {2, 3} P(F) = 2/6 = 1/3 Event G G = {2, 3, 4, 5} P(G) = 4/6 = 2/3 We need to find P(E|F) and P(F|E) Now, "E"∩"F" = {3} P("E"∩"F") = 1/6 Now, P(E|F) = (𝑃(𝐸 ∩ 𝐹))/(𝑃(𝐹)) = (1/6)/(1/3) = 𝟏/𝟐 P(F|E) = (𝑃(𝐹 ∩ 𝐸))/(𝑃(𝐸)) = (1/6)/(1/2) = 𝟏/𝟑 Ex 13.1, 11 A fair die is rolled. Consider events E = {1, 3, 5}, F = {2, 3} and G = {2, 3, 4, 5}. Find (iii) P((E ∪ F)|G) and P((E ∩ F)|G)P ( ("E"∪"F) | G ") Let "E"∪"F" = A So, A = {1, 2, 3, 5} P(A) = 4/6 Now, "A"∩"G" = {2, 3, 5} So, P("A"∩"G") = 3/6 Thus, P("A|G") = (𝑃(𝐴 ∩ 𝐺))/(𝑃(𝐺)) = (3/6)/(4/6) = 𝟑/𝟒 Therefore, P ( ("E"∪"F) | G ") = 𝟑/𝟒 Similarly, let’s do for P ( ("E"∩"F) | G" ) P( ("E"∩"F) | G ") Let "E"∩"F" = B So, B = {3} P("B") = 1/6 Now, "B"∩"G" = {3} So, P("B"∩"G") = 1/6 Thus, P("B|G") = (𝑃(𝐵 ∩ 𝐺))/(𝑃(𝐺)) = (1/6)/(4/6) = 𝟏/𝟒 Therefore, P ( ("E"∩ "F) | G ") = 𝟏/𝟒