



Miscellaneous
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo





Transcript
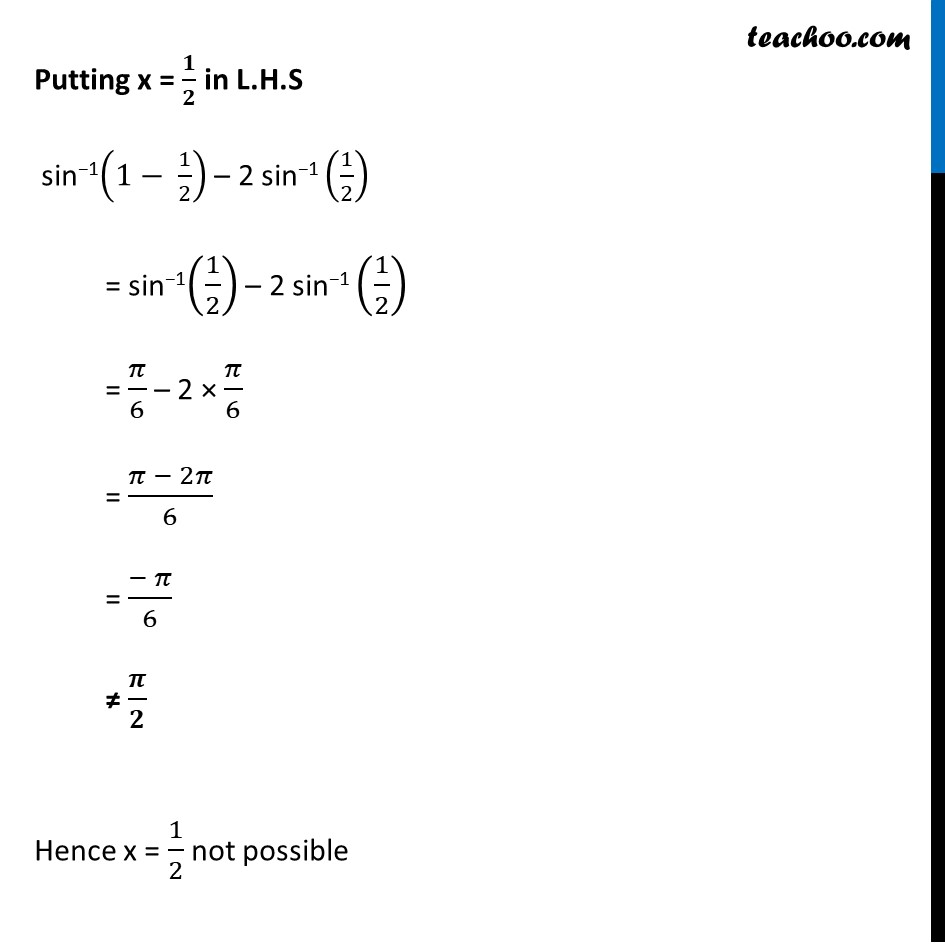
Misc 14 Solve sin−1(1 – x) – 2sin−1 x = π/2 , then x is equal to (A) 0, 1/2 (B) 1, 1/2 (C) 0 (D) 1/2 sin−1 (1 – x) – 2sin−1 x = π/2 –2sin−1 x = 𝝅/𝟐 – sin−1 (1 – x) − 2sin−1 x = cos−1 (1 – x) We know that sin−1 x + cos−1x = 𝝅/𝟐 Replace x by (1 − x) sin-1 (1 − x) + cos−1 (1 − x) = 𝜋/2 cos-1 (1 − x) = 𝜋/2 – sin−1 (1 − x) Let sin−1 x = a, Hence our equation becomes −2a = cos−1 (1 – x) cos (−2a) = 1 – x cos (2a) = (1 – x) 1 – 2 sin2 a = 1 – x We assumed that sin−1 x = a 1 – 2 [sin(sin−1 x)]2 = 1 – x 1 – 2x2 = 1 – x 1 – 2x2 – 1 + x = 0 1 – 1 – 2x2 + x = 0 –2x2 + x = 0 0 = 2x2 – x 2x2 – x = 0 x (2x – 1) = 0 So, x = 0 and x = 1/2 But x = 𝟏/𝟐 does not satisfy the equation Taking equation sin−1(1 – x) – 2sin−1 x = π/2 Putting x = 𝟏/𝟐 in L.H.S sin−1(1− 1/2) – 2 sin−1 (1/2) = sin−1(1/2) – 2 sin−1 (1/2) = 𝜋/6 – 2 × 𝜋/6 = (𝜋 − 2𝜋)/6 = (− 𝜋)/6 ≠ 𝝅/𝟐 Hence x = 1/2 not possible ∴ x = 0 is the only solution Option C is correct Answer