
Last updated at Dec. 13, 2024 by Teachoo




Transcript
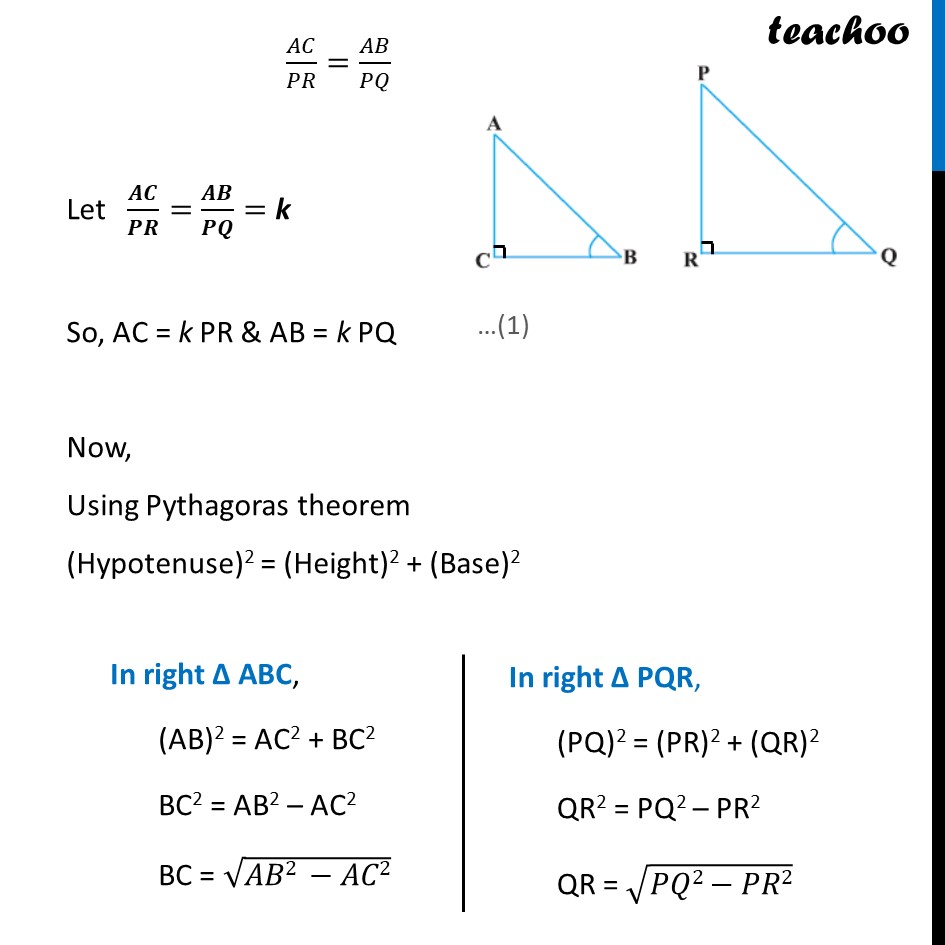
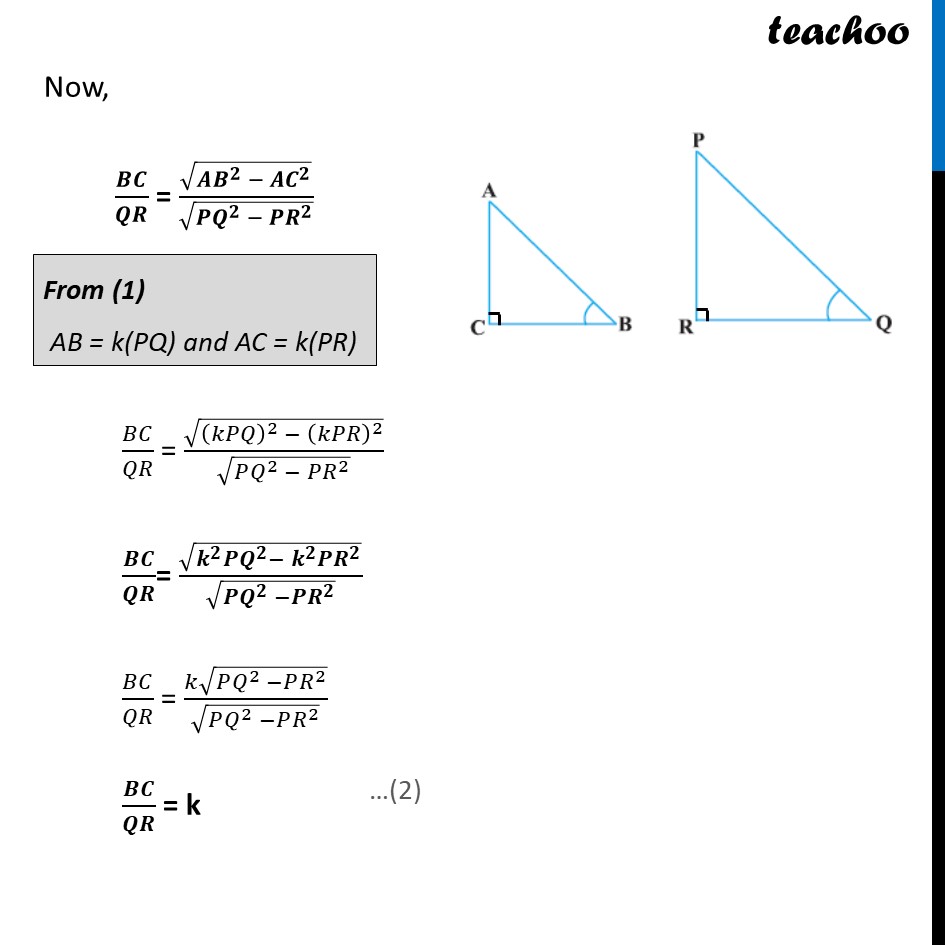
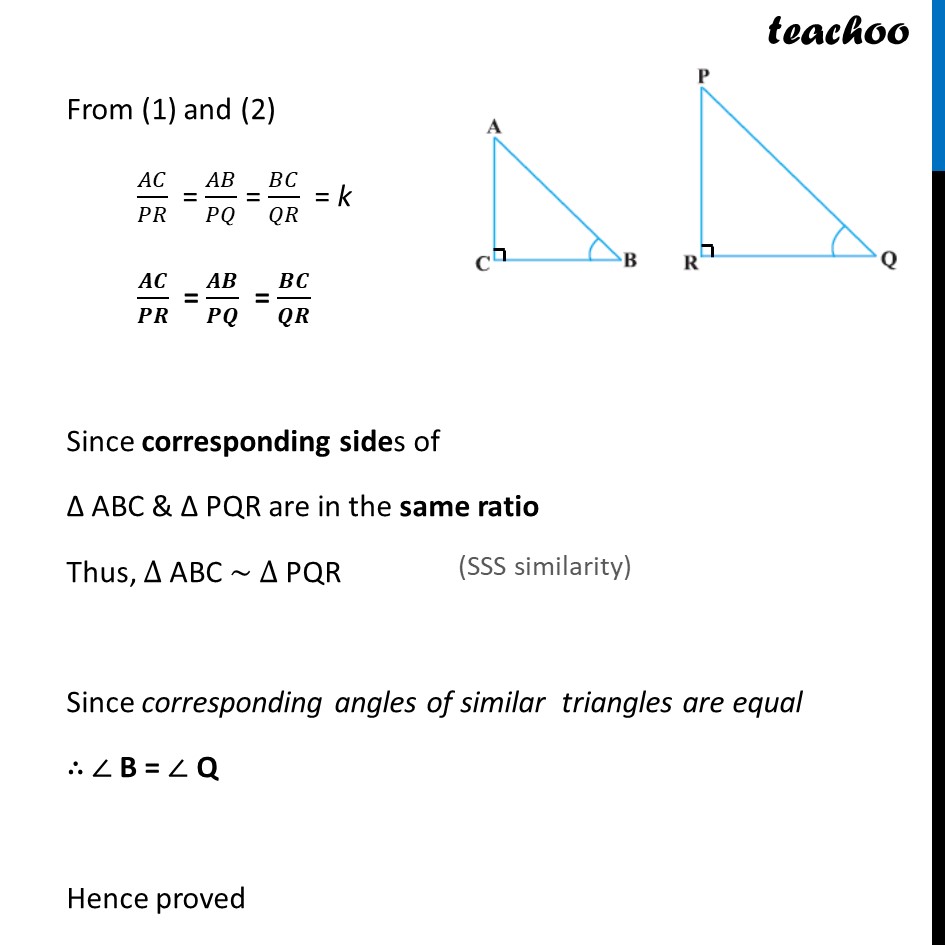
Example 2 If ∠ B and ∠ Q are acute angles such that sin B = sin Q, then prove that ∠ B = ∠ Q. Given: sin B = sin Q To prove: ∠ B = ∠ Q Proof: Let’s take two right angle triangles ABC & PQR Since, sin B = sin Q sin B = (𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑡𝑜 𝐵)/𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 sin B = 𝑨𝑪/𝑨𝑩 sin Q = (𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑡𝑜 𝑄)/𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 sin Q = 𝑷𝑹/𝑷𝑸 𝐴𝐶/𝑃𝑅=𝐴𝐵/𝑃𝑄 Let 𝑨𝑪/𝑷𝑹=𝑨𝑩/𝑷𝑸= k So, AC = k PR & AB = k PQ Now, Using Pythagoras theorem (Hypotenuse)2 = (Height)2 + (Base)2 In right Δ ABC, (AB)2 = AC2 + BC2 BC2 = AB2 – AC2 BC = √(𝐴𝐵2 −𝐴𝐶2) In right Δ PQR, (PQ)2 = (PR)2 + (QR)2 QR2 = PQ2 – PR2 QR = √(𝑃𝑄2−𝑃𝑅2) Now, 𝑩𝑪/𝑸𝑹 = √(𝑨𝑩^𝟐 − 𝑨𝑪^𝟐 )/√(𝑷𝑸^𝟐 − 𝑷𝑹^𝟐 ) From (1) AB = k(PQ) and AC = k(PR) From (1) and (2) 𝐴𝐶/𝑃𝑅 = 𝐴𝐵/𝑃𝑄 = 𝐵𝐶/𝑄𝑅 = k 𝑨𝑪/𝑷𝑹 = 𝑨𝑩/𝑷𝑸 = 𝑩𝑪/𝑸𝑹 Since corresponding sides of Δ ABC & Δ PQR are in the same ratio Thus, ∆ ABC ~ ∆ PQR Since corresponding angles of similar triangles are equal ∴ ∠ B = ∠ Q Hence proved 𝐵𝐶/𝑄𝑅 = √((𝑘𝑃𝑄)^2 − (𝑘𝑃𝑅)^2 )/√(𝑃𝑄^2 − 𝑃𝑅^2 ) 𝑩𝑪/𝑸𝑹= √(𝒌^𝟐 𝑷𝑸^𝟐− 𝒌^𝟐 𝑷𝑹^𝟐 )/√(𝑷𝑸^𝟐 −𝑷𝑹^𝟐 ) 𝐵𝐶/𝑄𝑅 = (𝑘√(𝑃𝑄^2 −𝑃𝑅^2 ))/√(𝑃𝑄^2 −𝑃𝑅^2 ) 𝑩𝑪/𝑸𝑹 = k