

Ex 8.3
Last updated at December 16, 2024 by Teachoo



Transcript
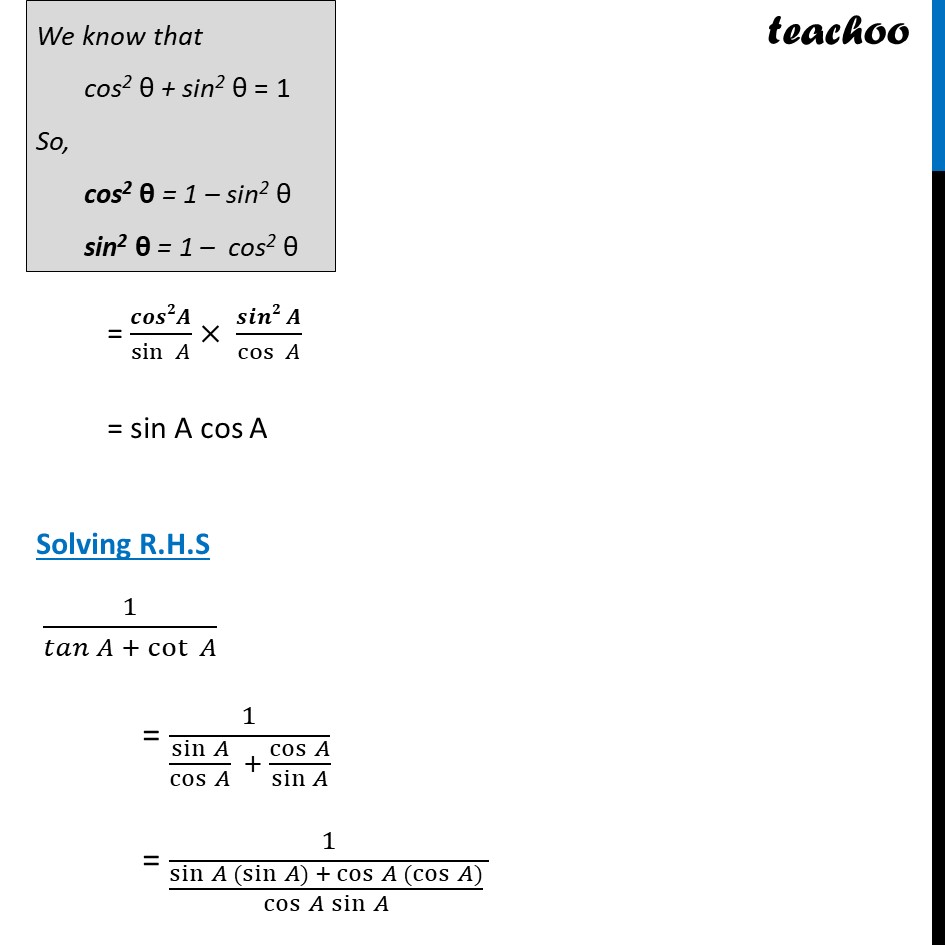
Ex 8.3, 4 Prove the following identities, where the angles involved are acute angles for which the expressions are defined. (ix) (cosec A – sin A)(sec A – cos A) = 1/(𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝐴 +cot 𝐴) [Hint : Simplify LHS and RHS separately] Solving L.H.S (cosec A – sin A) (sec A – cos A) = (1/sin〖 𝐴〗 − sin𝐴 )(1/cos〖 𝐴〗 − cos 𝐴) = ((𝟏 − 𝒔𝒊𝒏𝟐 𝑨))/sin〖 𝐴〗 × ((𝟏 − 𝒄𝒐𝒔𝟐 𝑨))/cos〖 𝐴〗 We know that cos2 θ + sin2 θ = 1 So, cos2 θ = 1 – sin2 θ sin2 θ = 1 – cos2 θ = 𝒄𝒐𝒔𝟐𝑨/sin〖 𝐴〗 × (𝒔𝒊𝒏𝟐 𝑨)/cos〖 𝐴〗 = sin A cos A Solving R.H.S 1/(𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝐴 + cot 𝐴) = 1/(sin𝐴/cos𝐴 + cos𝐴/sin𝐴 ) = 1/(sin〖𝐴 (sin〖𝐴) + cos〖𝐴 (cos〖𝐴)〗 〗 〗 〗/cos〖𝐴 sin𝐴 〗 ) = 1/((𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝐴 + 𝑐𝑜𝑠2 𝐴)/cos〖𝐴 sin𝐴 〗 ) = 1/((𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝐴 + 𝑐𝑜𝑠2 𝐴)/cos〖𝐴 sin𝐴 〗 ) = sin〖 𝐴 . cos 𝐴〗/(𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝐴 + 𝑐𝑜𝑠2 𝐴) As sin2 A + cos2 A = 1 = sin〖 𝐴 . 〖 cos〗 𝐴〗/1 = sin A cos A = L.H.S Hence proved