

Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo



Transcript
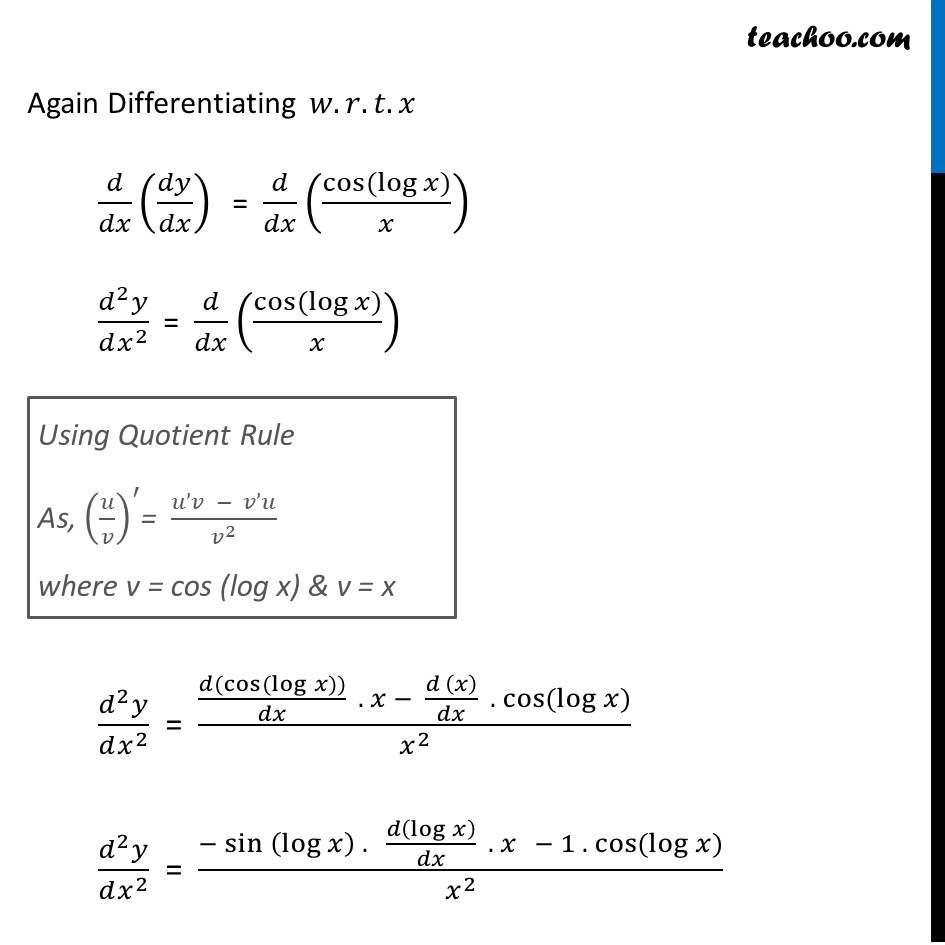
Ex 5.7, 10 Find the second order derivatives of the function 〖 sin〗〖 (log〖𝑥)〗 〗 Let y = 〖 sin〗〖 (log〖𝑥)〗 〗 Differentiating 𝑤.𝑟.𝑡.𝑥 . 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑(〖 sin〗〖 (log〖𝑥)〗 〗))/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = cos(log𝑥) . (𝑑(log〖𝑥)〗)/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = cos(log𝑥) . 1/𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (cos(log𝑥))/𝑥 Again Differentiating 𝑤.𝑟.𝑡.𝑥 𝑑/𝑑𝑥 (𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥) = 𝑑/𝑑𝑥 ((cos(log𝑥))/𝑥) (𝑑^2 𝑦)/(𝑑𝑥^2 ) = 𝑑/𝑑𝑥 ((cos(log𝑥))/𝑥) (𝑑^2 𝑦)/(𝑑𝑥^2 ) = ((𝑑(cos(log𝑥)))/𝑑𝑥 . 𝑥 − (𝑑 (𝑥))/𝑑𝑥 . cos(log𝑥))/𝑥^2 (𝑑^2 𝑦)/(𝑑𝑥^2 ) = (−〖sin 〗(log𝑥 ) . 𝑑(log𝑥 )/𝑑𝑥 . 𝑥 − 1 . cos(log𝑥))/𝑥^2 Using Quotient Rule As, (𝑢/𝑣)^′= (𝑢’𝑣 − 𝑣’𝑢)/𝑣^2 where v = cos (log x) & v = x (𝑑^2 𝑦)/(𝑑𝑥^2 ) = (−〖sin 〗(log𝑥 ) . 1/𝑥 . 𝑥 − cos (log𝑥))/𝑥^2 (𝑑^2 𝑦)/(𝑑𝑥^2 ) = (−〖sin 〗(log𝑥 ) − cos(log𝑥))/𝑥^2 (𝒅^𝟐 𝒚)/(𝒅𝒙^𝟐 ) = (− [〖𝒔𝒊𝒏 〗(𝒍𝒐𝒈𝒙 ) + 𝒄𝒐𝒔(𝒍𝒐𝒈𝒙)])/𝒙^𝟐