



Miscellaneous
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo










Transcript
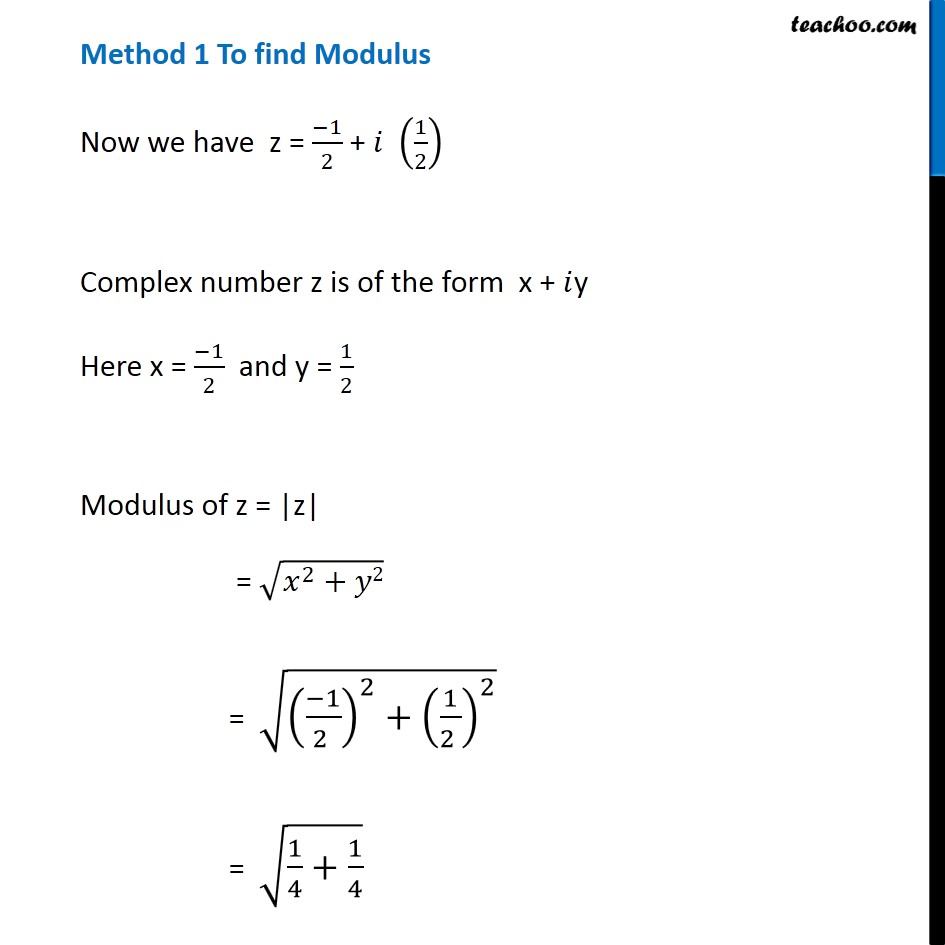
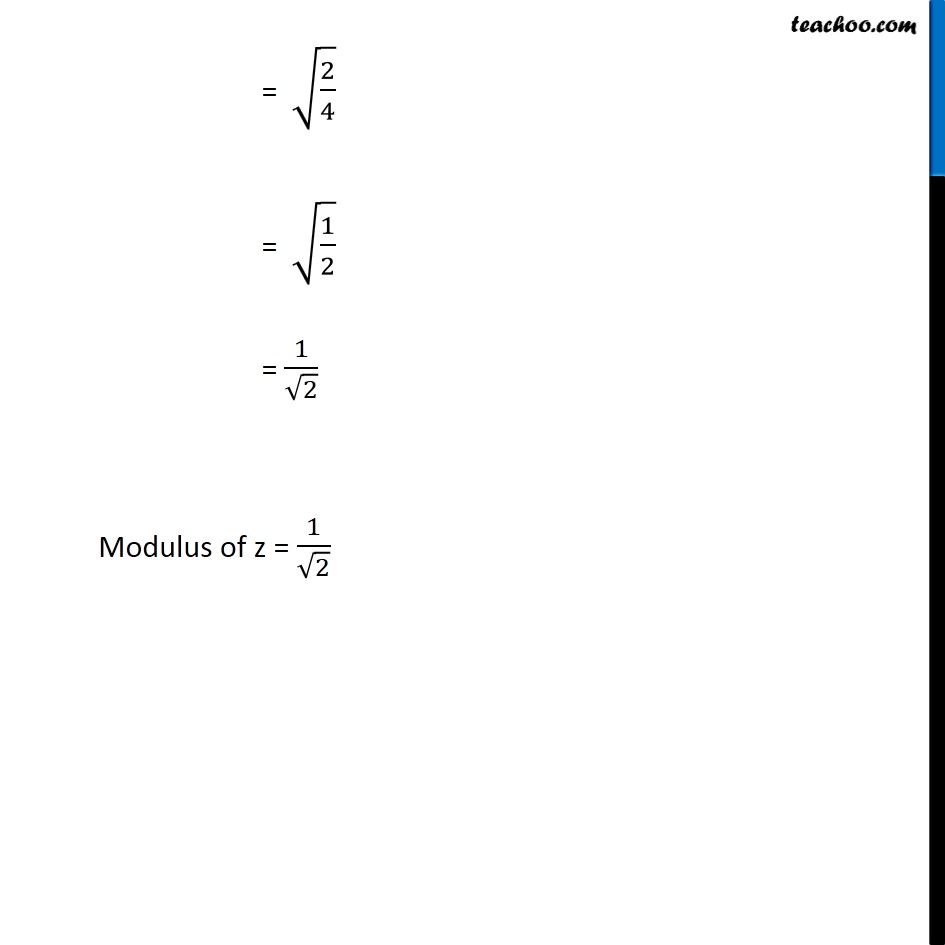
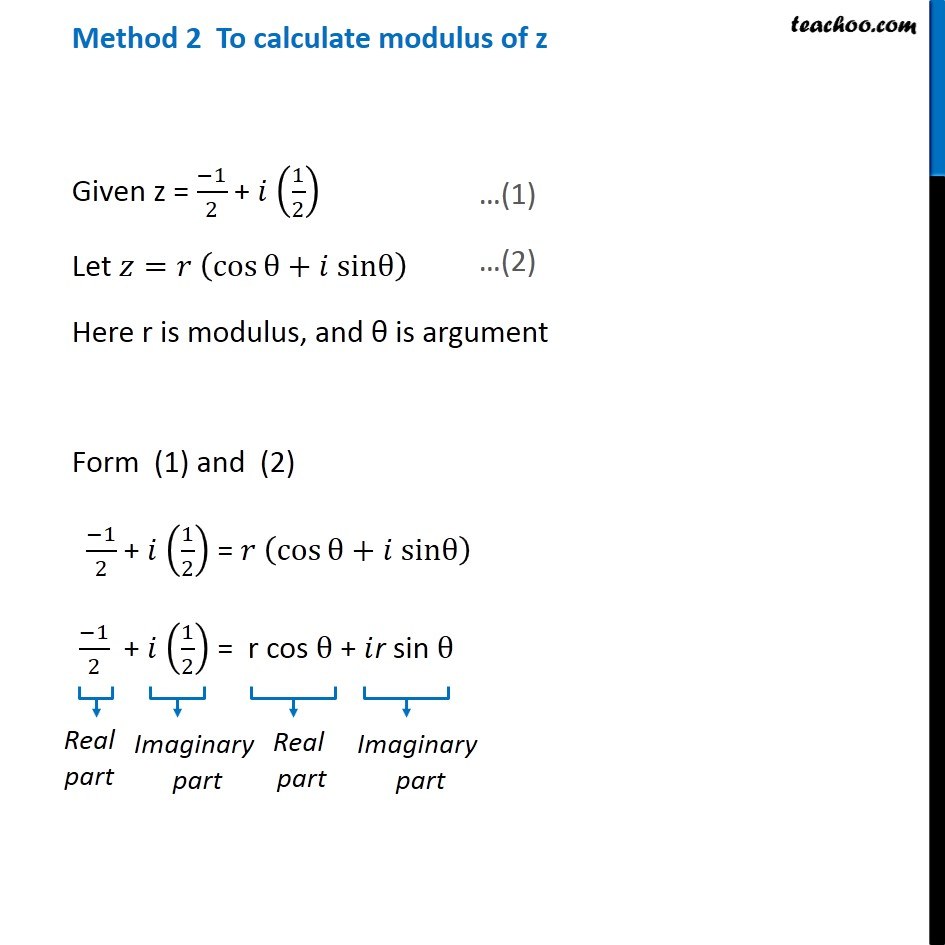
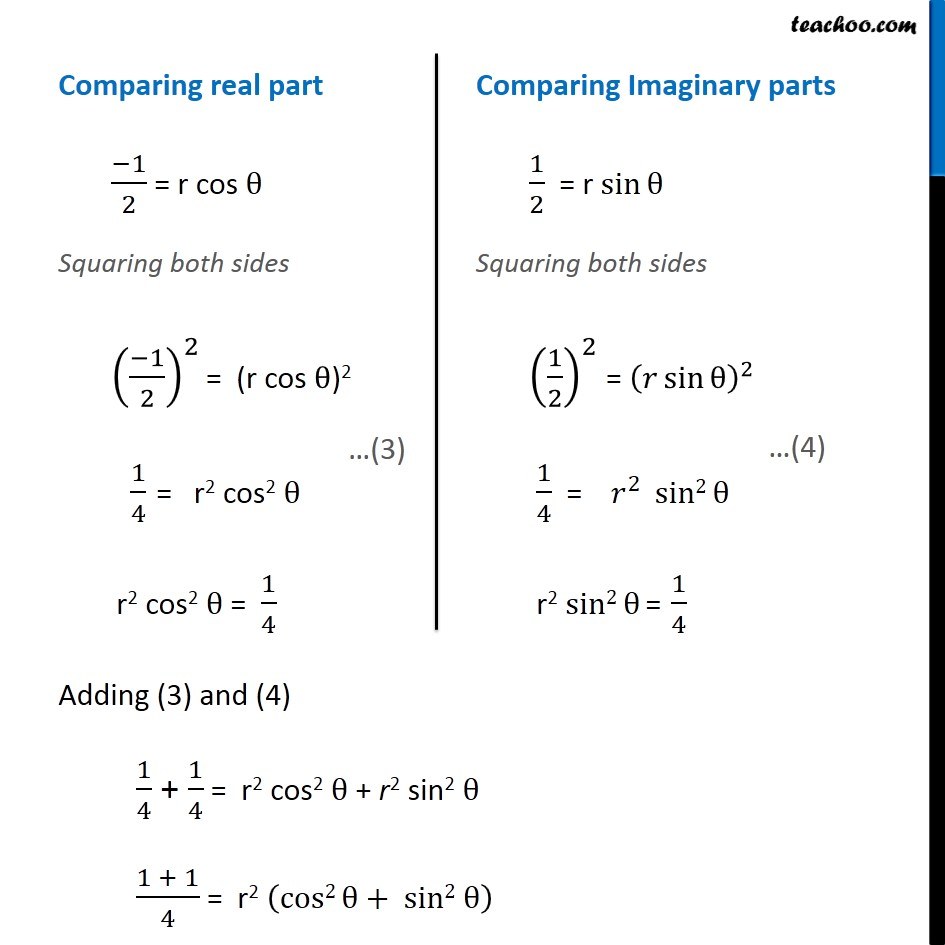
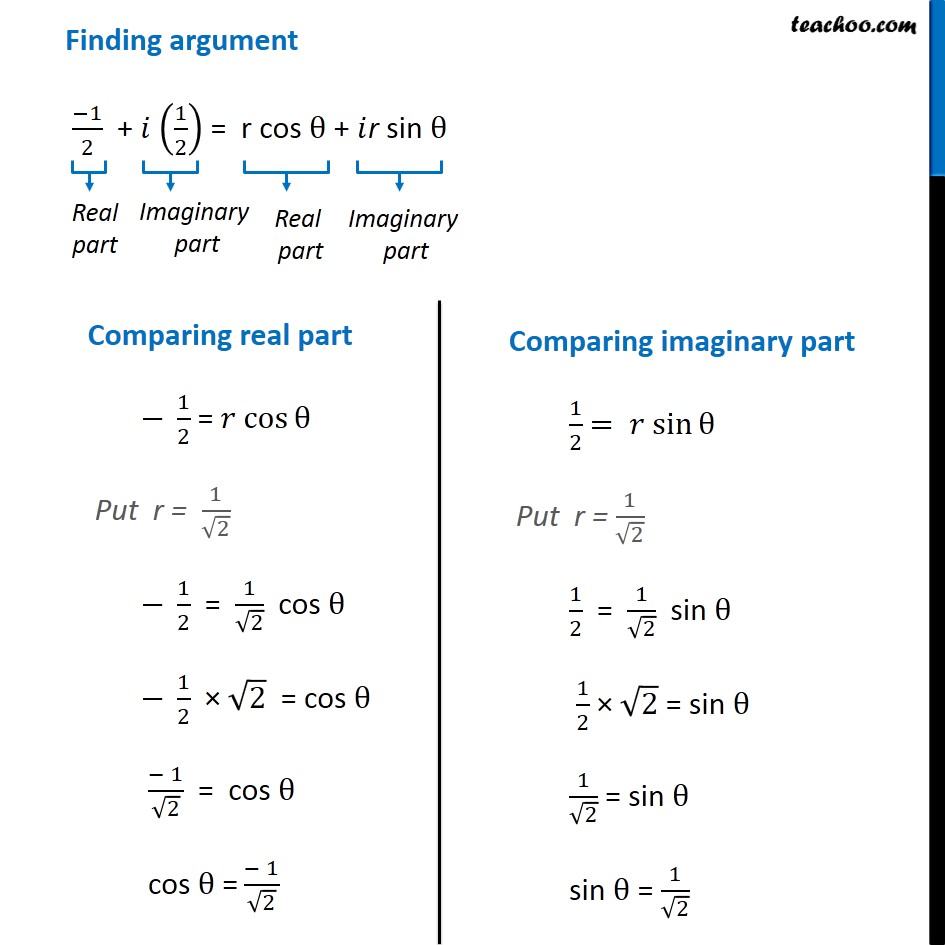
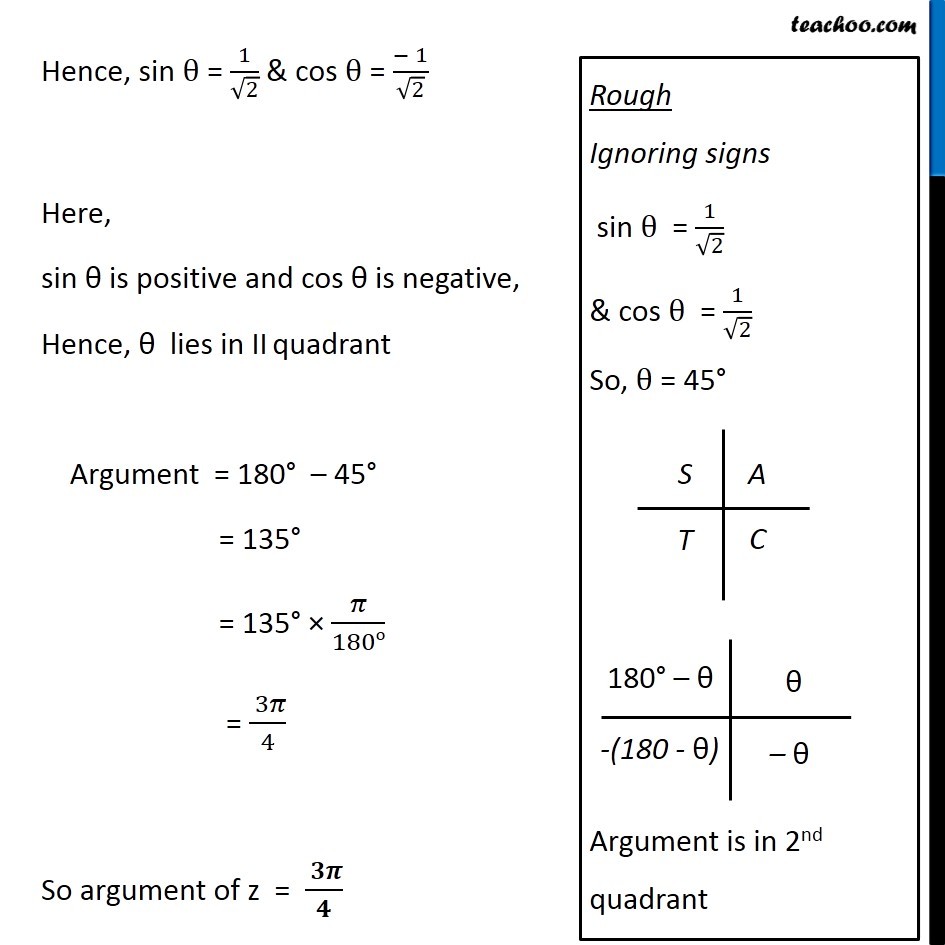
Question 6 Find the modulus and argument of the complex number ( 1 + 2i)/(1 − 3i) . First we solve ( 1 + 2𝑖)/(1 − 3𝑖) Let 𝑧 = ( 1 + 2𝑖)/(1 − 3𝑖) Rationalizing the same = ( 1 + 2𝑖)/(1 − 3𝑖) x ( 1 + 3𝑖)/(1 + 3𝑖) = ((1 + 2𝑖) ( 1 + 3𝑖))/((1 − 3𝑖) ( 1 + 3𝑖)) = (1 (1 + 3𝑖) + 2𝑖 (1 + 3𝑖))/((1 − 3𝑖) (1 + 3𝑖) ) = ( 1 + 3𝑖+ 2𝑖+ 6𝑖2)/((1 − 3𝑖) (1 + 3𝑖) ) Using ( a – b ) ( a + b ) = a2 - b2 = ( 1+ 5𝑖+ 6𝑖2)/((1)2 − (3𝑖)2) = (1 + 5𝑖+ 6𝑖2)/(1 − 9𝑖2) Putting 𝑖2 = - 1 = (1 + 5𝑖 + 6 (−1))/(1 − 9 (−1)) = (1 + 5𝑖 − 6 )/(1 + 9 ) = ( \− 5 + 5𝑖)/10 = ( 5 (−1 +𝑖))/10 = (− 1+ 𝑖)/2 = (− 1)/2+𝑖 ( 1/2 ) Thus, 𝑧 = (− 1)/2+𝑖 ( 1/2 ) Method 1 To find Modulus Now we have z = (− 1)/2 + 𝑖 (1/2) Complex number z is of the form x + 𝑖 y Here x = (− 1)/2 and y = 1/2 Modulus of z = |z| = √(𝑥^2+𝑦2) = √(( (− 1)/(2 ))^2+( 1/(2 ))^2 ) = √(1/4+1/4) = √(2/4) = √(1/2) = 1/√2 Modulus of z = 1/√2 Method 2 To calculate modulus of z Given z = (−1)/2 + 𝑖 (1/2) Let 𝑧=𝑟 (cosθ+𝑖 sinθ) Here r is modulus, and θ is argument Form (1) and (2) (−1)/2 + 𝑖 (1/2) = 𝑟 (cosθ+𝑖 sinθ) (−1)/2 + 𝑖 (1/2) = r cos θ + 𝑖r sin θ Comparing real part (− 1)/2 = r cos θ Adding (3) and (4) 1/4 + 1/4 = r2 cos2 θ + r2 sin2 θ (1+1)/4 = r2 (cos2 θ+ sin2 θ) 2/4 = r2 × 1 1/2 = r2 1/√2 = r Modulus of z = 1/√2 Finding argument (−1)/2 + 𝑖 (1/2) = r cos θ + 𝑖r sin θ Hence, sin θ = 1/√2 & cos θ = (− 1)/√2 Here, sin θ is positive and cos θ is negative, Hence, θ lies in IVth quadrant Argument = 180° – 45° = 135° = 135° × 𝜋/180o = ( 3 𝜋)/4 So argument of z = ( 3 𝜋)/4