

Chapter 6 Class 10 Triangles
Chapter 6 Class 10 Triangles
Last updated at Dec. 13, 2024 by Teachoo




Transcript
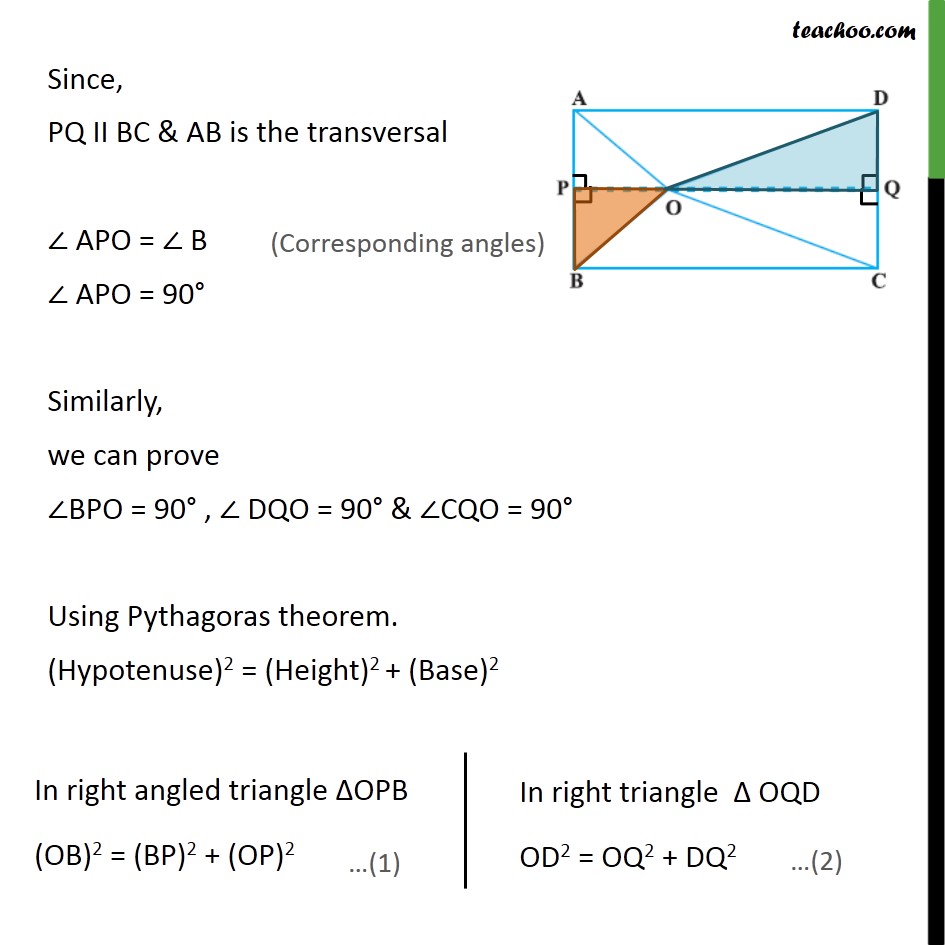
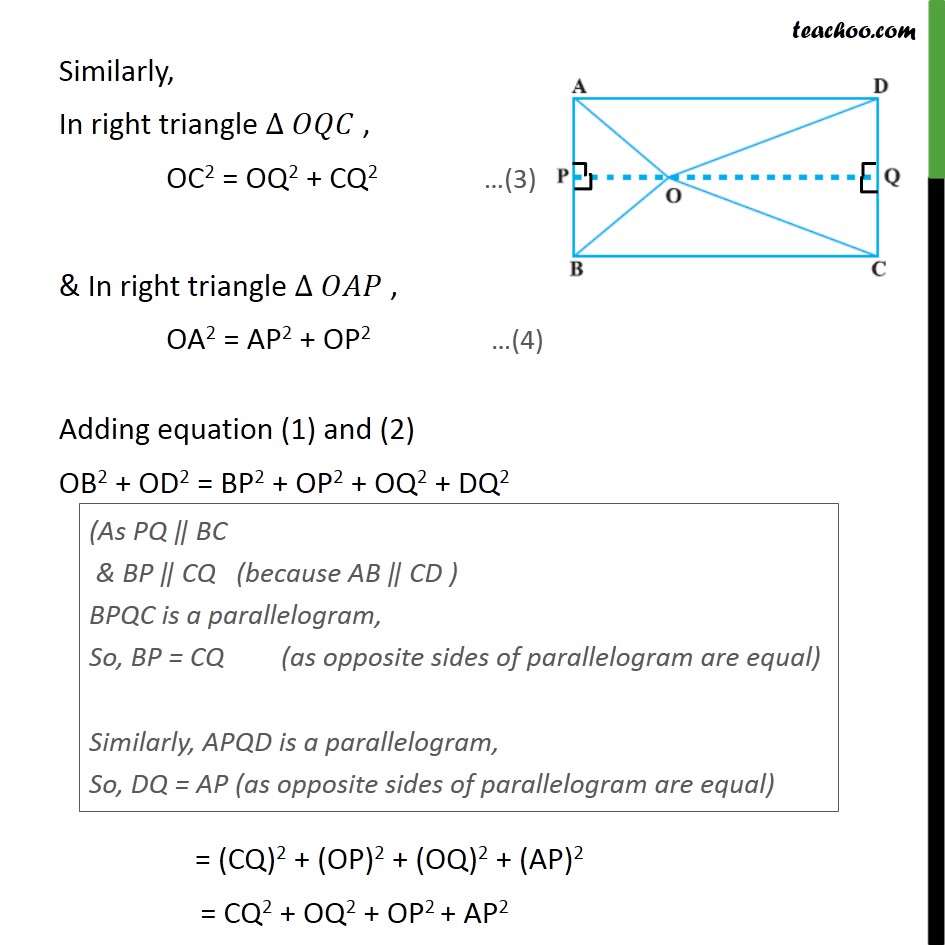
Question 6 O is any point inside a rectangle ABCD (see Fig. 6.52). Prove that OB2 + OD2 = OA2 + OC2. Given : Rectangle ABCD , and a point O inside rectangle . To prove :- OB2 + OD2 = OA2 + OC2 Proof :- Let us draw a line PQ, through O which is parallel to BC. Hence, PQ II BC ⇒ PQ II AD All angles of a rectangle are 90° , So, ∠ A = ∠ B = ∠ C = ∠ D = 90° Since, PQ II BC & AB is the transversal ∠ APO = ∠ B ∠ APO = 90° Similarly, we can prove ∠BPO = 90° , ∠ DQO = 90° & ∠CQO = 90° Using Pythagoras theorem. (Hypotenuse)2 = (Height)2 + (Base)2 Similarly, In right triangle ∆ 𝑂𝑄𝐶 , OC2 = OQ2 + CQ2 …(3) & In right triangle ∆ 𝑂𝐴𝑃 , OA2 = AP2 + OP2 …(4) Adding equation (1) and (2) OB2 + OD2 = BP2 + OP2 + OQ2 + DQ2 = (CQ)2 + (OP)2 + (OQ)2 + (AP)2 = CQ2 + OQ2 + OP2 + AP2 = OC2 + OA2 Thus, OB2 + OD2 = OC2 + OA2 Hence proved