




Chapter 8 Class 12 Application of Integrals
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo










Transcript
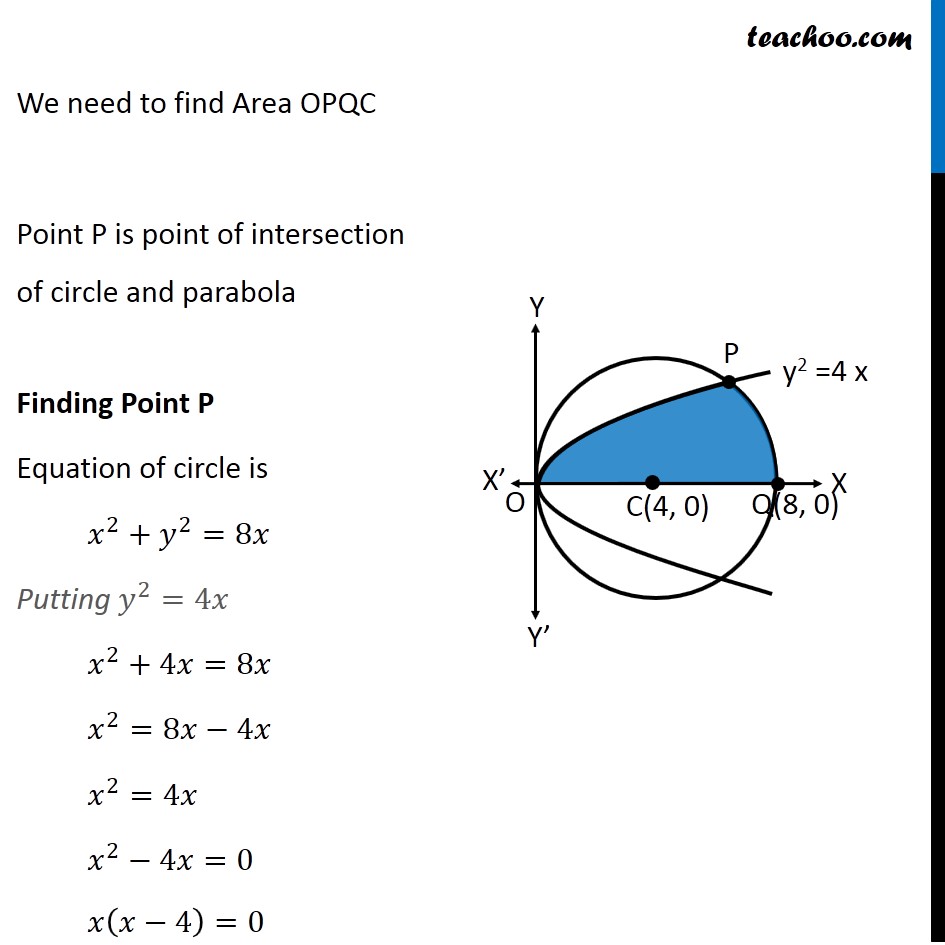
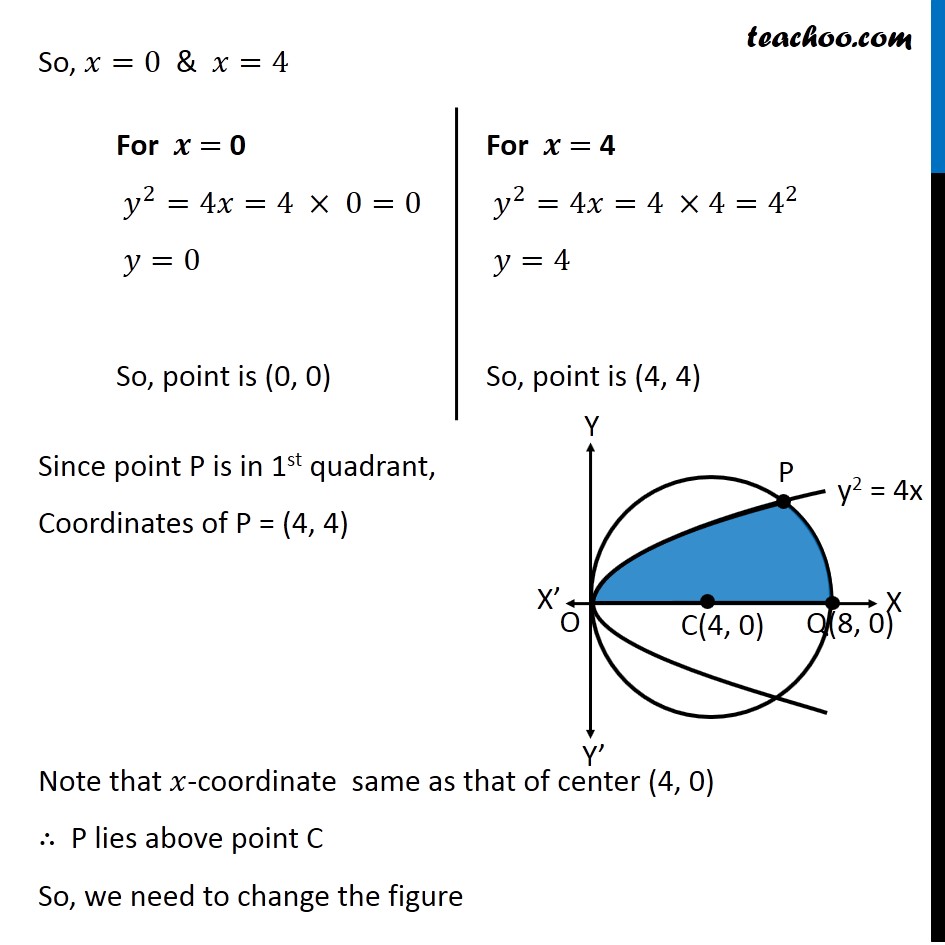
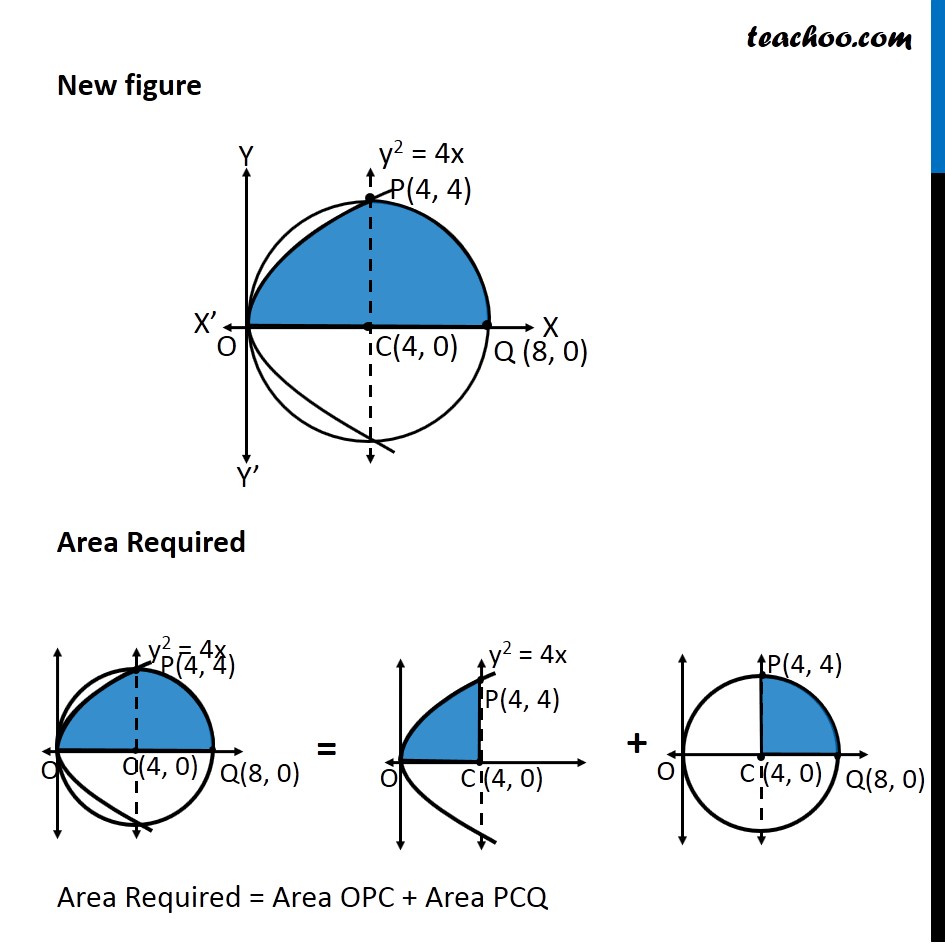
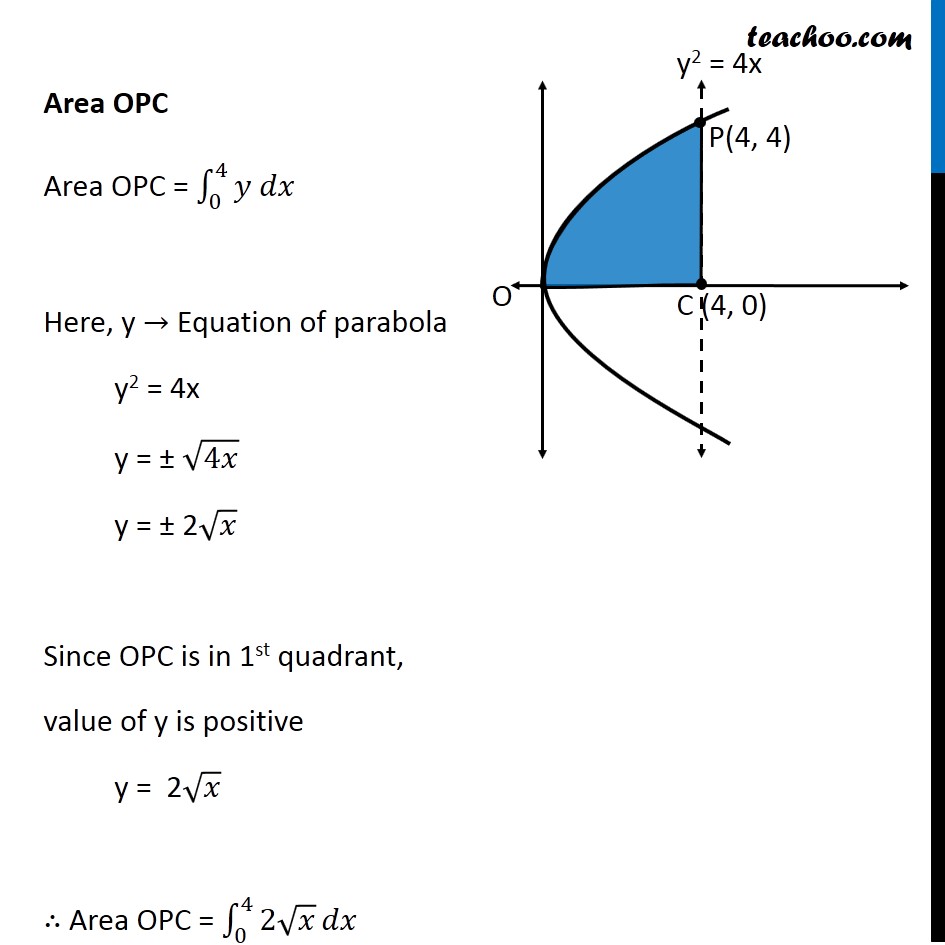
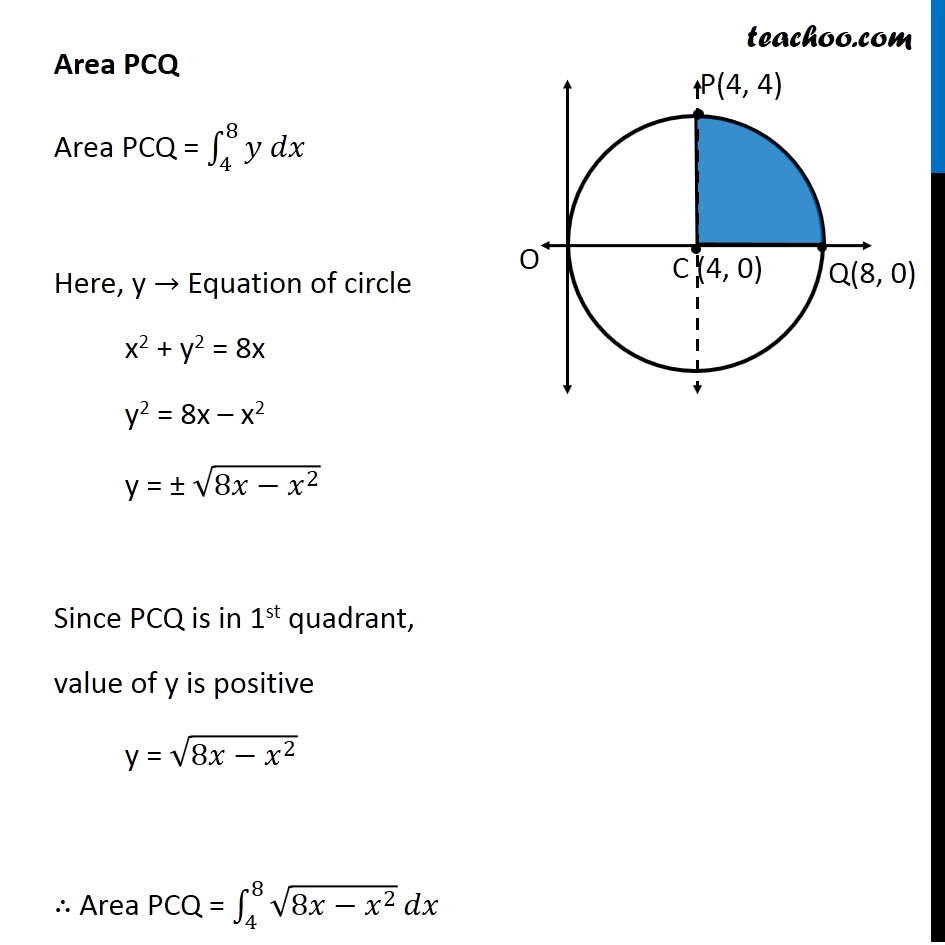
Question 5 Find the area lying above x-axis and included between the circle 𝑥2 +𝑦2=8𝑥 and inside of the parabola 𝑦2=4𝑥 Since equation of circle is of form (𝑥−𝑎)^2+(𝑦−𝑏)^2=𝑟^2 , We convert our equation 𝑥^2+𝑦^2=8𝑥 𝑥^2−8𝑥+𝑦^2=0 𝑥^2−2 ×4 ×𝑥+𝑦^2=0 𝑥^2−2 ×4 ×𝑥+4^2−4^2+𝑦^2=0 (𝑥−4)^2+𝑦^2=4^2 So, Circle has center (4 , 0) & Radius =4 We need to find Area OPQC Point P is point of intersection of circle and parabola Finding Point P Equation of circle is 𝑥^2+𝑦^2=8𝑥 Putting 𝑦^2=4𝑥 𝑥^2+4𝑥=8𝑥 𝑥^2=8𝑥−4𝑥 𝑥^2=4𝑥 𝑥^2−4𝑥=0 𝑥(𝑥−4)=0 So, 𝑥=0 & 𝑥=4 For 𝒙 = 0 𝑦^2=4𝑥=4 × 0=0 𝑦=0 So, point is (0, 0) For 𝒙 = 4 𝑦^2=4𝑥=4 ×4=4^2 𝑦=4 So, point is (4, 4) So, 𝑥=0 & 𝑥=4 Since point P is in 1st quadrant, Coordinates of P = (4, 4) Note that 𝑥-coordinate same as that of center (4, 0) ∴ P lies above point C So, we need to change the figure New figure Area Required Area Required = Area OPC + Area PCQ Area OPC Area OPC = ∫_0^4▒〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥〗 Here, y → Equation of parabola y2 = 4x y = ± √4𝑥 y = ± 2√𝑥 Since OPC is in 1st quadrant, value of y is positive y = 2√𝑥 ∴ Area OPC = ∫_0^4▒〖2√𝑥〗 𝑑𝑥 = 2 ∫_0^4▒𝑥^(1/2) 𝑑𝑥 = 2 [𝑥^(1/2 + 1)/(1/2 + 1)]_0^4 = 2 [𝑥^(3/2)/(3/2)]_0^4 = 2 × 2/3 [(4)^(3/2)−(0)^(3/2) ] = 4/3 [8−0] = 32/3 Area PCQ Area PCQ = ∫_4^8▒〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥〗 Here, y → Equation of circle x2 + y2 = 8x y2 = 8x – x2 y = ± √(8𝑥−𝑥^2 ) Since PCQ is in 1st quadrant, value of y is positive y = √(8𝑥−𝑥^2 ) ∴ Area PCQ = ∫_4^8▒√(8𝑥−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥 = ∫_4^8▒√(−(𝑥^2−8𝑥)) 𝑑𝑥 = ∫_4^8▒√(−(𝑥^2−8𝑥+16−16)) 𝑑𝑥 = ∫_4^8▒√(−(𝑥^2−8𝑥+16)−(−16)) 𝑑𝑥 = ∫_4^8▒√(16−(𝑥^2−8𝑥+16)) 𝑑𝑥 = ∫_4^8▒√(16−(𝑥−4)^2 ) 𝑑𝑥 = ∫_4^8▒√(4^2−(𝑥−4)^2 ) 𝑑𝑥 = [((𝑥 − 4))/2 √(4^2−〖(𝑥−4)〗^2 )+4^2/2 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 ((𝑥 − 4))/4〗 " " ]_4^8 It is of form √(𝑎^2−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥=𝑥/2 √(𝑎^2−𝑥^2 )+𝑎^2/2 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 𝑥/𝑎+𝑐〗 Here, a = 4, x = x – 4 = [((𝑥 − 4))/2 √(16−(𝑥^2−8𝑥+4^2))+16/2 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 ((𝑥 − 4))/4〗 " " ]_4^8 = [((𝑥 − 4))/2 √(−(𝑥^2−8𝑥))+8 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 ((𝑥 − 4))/4〗 " " ]_4^8 = [((8 − 4))/2 √(−(8^2−8(8)))+8 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 ((8 − 4))/4〗 ] – [((4 − 4))/2 √(−(4^2−8(4)))+8 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 ((4 − 4))/4〗 ] = [4/2 √0+8 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 1〗 ] – [0+8 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 0〗 ] = 8 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 1〗 – 8 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 0〗 = 8(𝜋/2) – 8 × 0 = 4𝜋 As 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 1〗 = 𝜋/2 & 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 0〗 = 0 Thus, Area Required = Area OPC + Area PCQ = 32/3 + 4𝜋 = 𝟒/𝟑 (8 + 3𝝅) square units