



Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo









Transcript
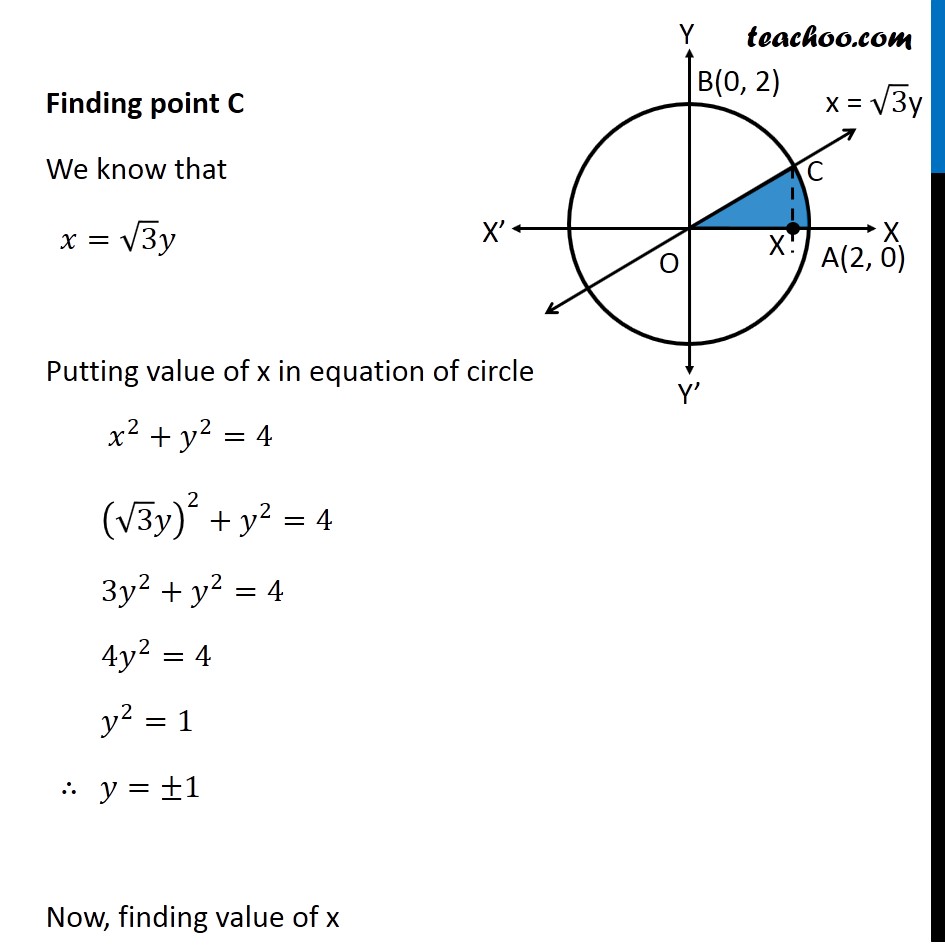
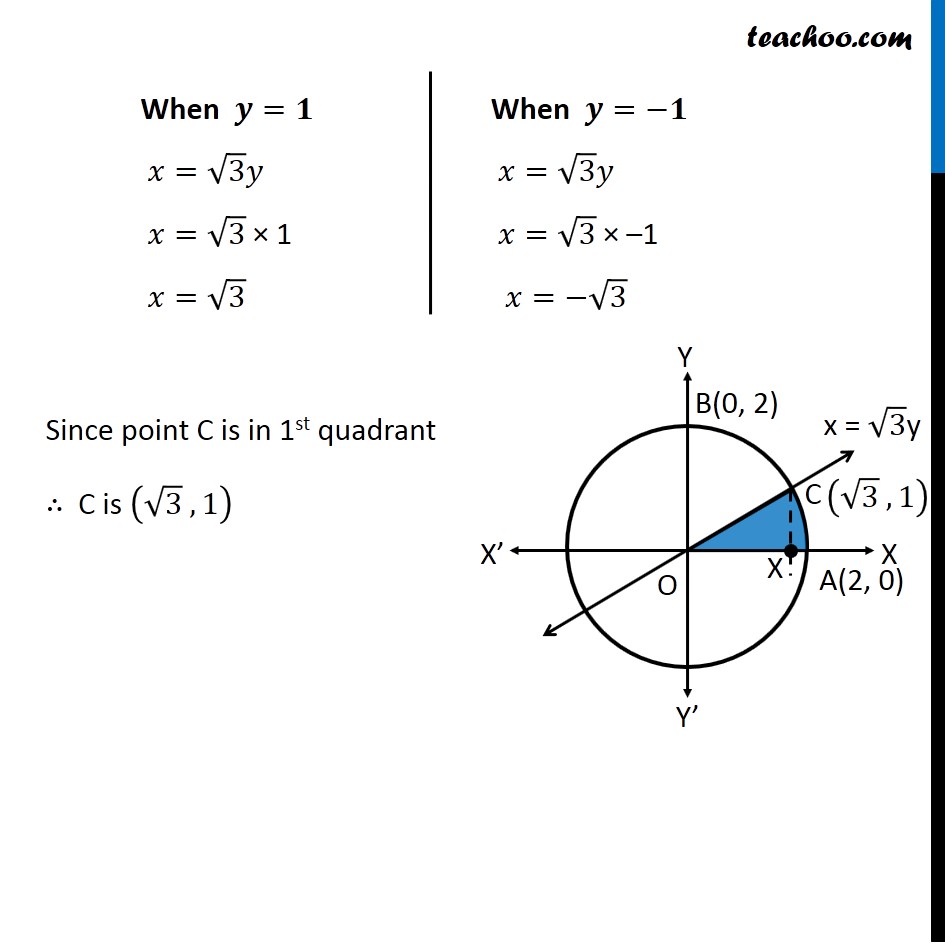
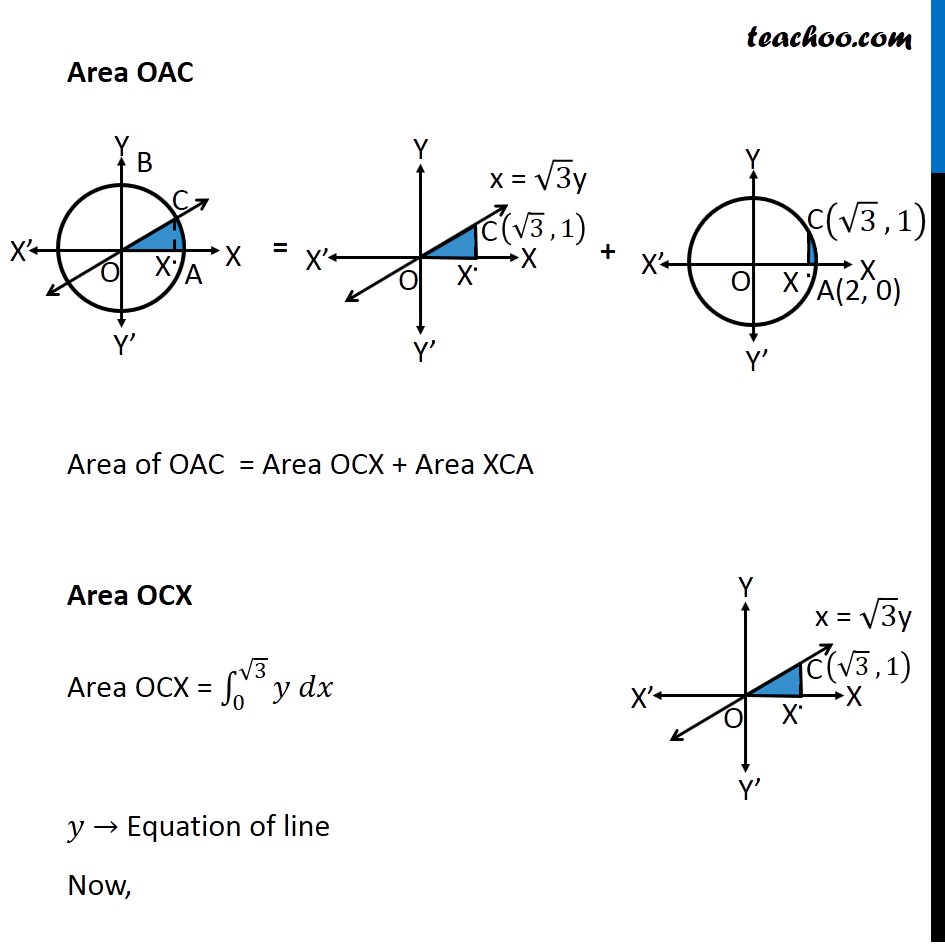
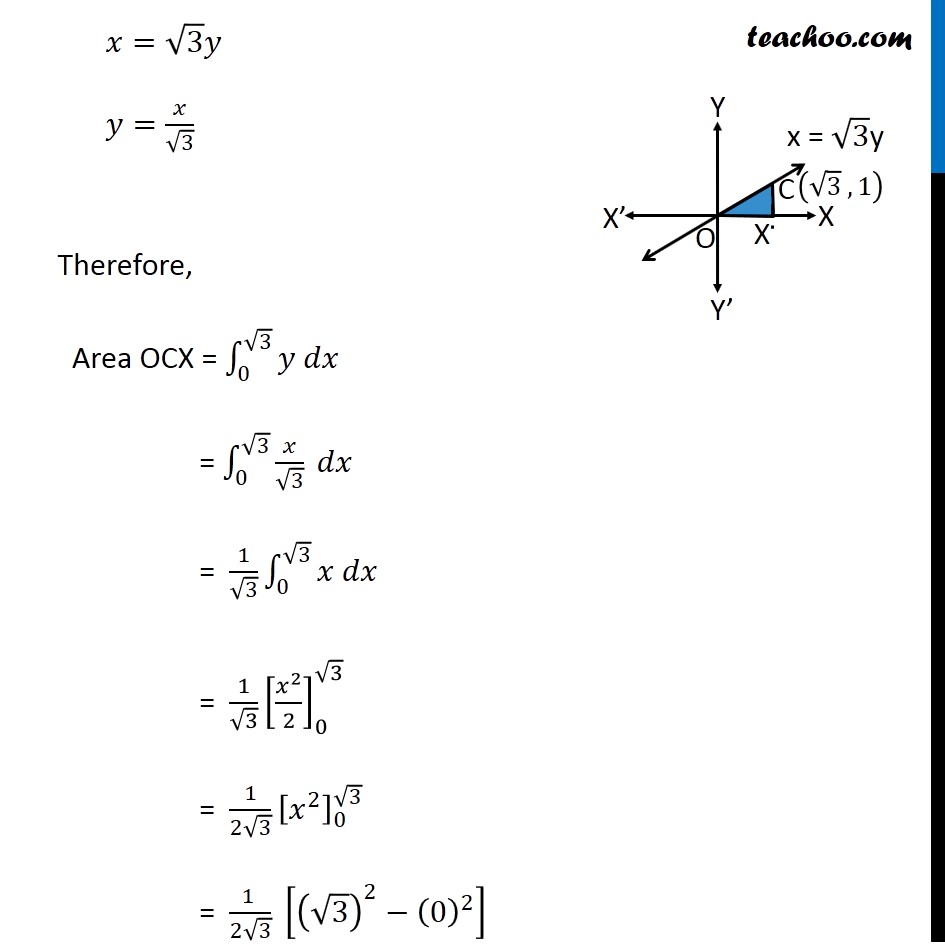
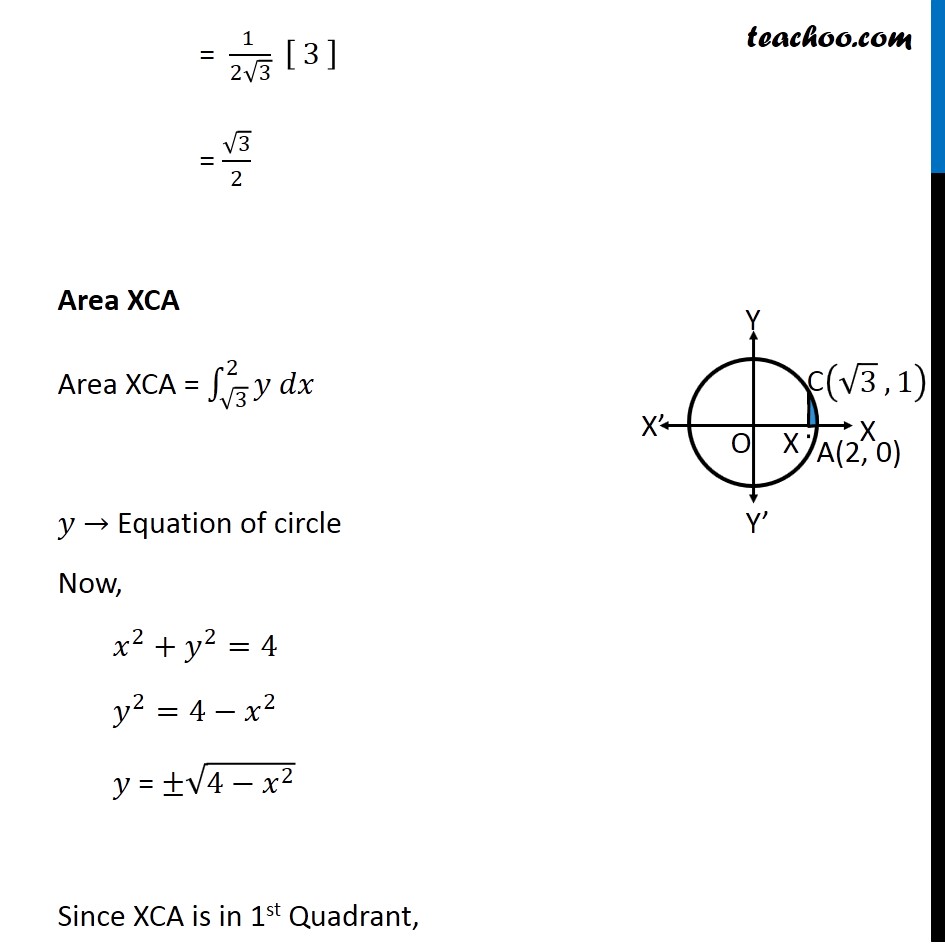
Question 4 Find the area of the region in the first quadrant enclosed by 𝑥−axis, line 𝑥 = √3 𝑦 and the circle 𝑥2 + 𝑦2 = 4. Given Equation of circle 𝑥^2+𝑦^2=4 𝑥^2+𝑦^2=(2)^2 ∴ Radius 𝑟 = 2 So, point A is (2, 0) and point B is (0, 2) Let line 𝑥=√3 𝑦 intersect the circle at point C Therefore, We have to find Area of AOC Finding point C We know that 𝑥=√3 𝑦 Putting value of x in equation of circle 𝑥^2+𝑦^2=4 (√3 𝑦)^2+𝑦^2=4 3𝑦^2+𝑦^2=4 4𝑦^2=4 𝑦^2=1 ∴ 𝑦=±1 Now, finding value of x When 𝒚=𝟏 𝑥=√3 𝑦 𝑥=√3 × 1 𝑥=√3 When 𝒚=−𝟏 𝑥=√3 𝑦 𝑥=√3 × –1 𝑥=−√3 Since point C is in 1st quadrant ∴ C is (√3 , 1) Area OAC Area of OAC = Area OCX + Area XCA Area OCX Area OCX = ∫_0^(√3)▒〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥〗 𝑦 → Equation of line Now, 𝑥=√3 𝑦 𝑦=𝑥/√3 Therefore, Area OCX = ∫_0^(√3)▒〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥〗 = ∫_0^(√3)▒〖𝑥/√3 𝑑𝑥〗 = 1/√3 ∫_0^(√3)▒〖𝑥 𝑑𝑥〗 = 1/√3 [𝑥^2/2]_0^√3 = 1/(2√3) [𝑥^2 ]_0^√3 = (1 )/(2√3) [(√3)^2−(0)^2 ] = (1 )/(2√3) [ 3 ] = √3/2 Area XCA Area XCA = ∫_(√3)^2▒〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥〗 𝑦 → Equation of circle Now, 𝑥^2+𝑦^2=4 𝑦^2=4−𝑥^2 𝑦 = ±√(4−𝑥^2 ) Since XCA is in 1st Quadrant, = (1 )/(2√3) [ 3 ] = √3/2 Area XCA Area XCA = ∫_(√3)^2▒〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥〗 𝑦 → Equation of circle Now, 𝑥^2+𝑦^2=4 𝑦^2=4−𝑥^2 𝑦 = ±√(4−𝑥^2 ) Since XCA is in 1st Quadrant, Value of 𝑦 will be positive ∴ 𝑦 = √(4−𝑥^2 ) Area XCA = ∫_(√3)^2▒ √(4−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥 = ∫_(√3)^2▒ √((2)^2−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥 = [1/2 𝑥√((2)^2−𝑥^2 )+(2)^2/2 sin^(−1)〖𝑥/2〗 ]_(√3)^2 = [1/2 𝑥√(4−𝑥^2 )+2 sin^(−1)〖𝑥/2〗 ]_(√3)^2 = 1/2 (2) √(4−2^2 )+2 sin^(−1)〖2/2〗−1/2 (√3) √(4−(√3)^2 )−2 sin^(−1)〖√3/2〗 It is of form √(𝑎^2−𝑥^2 ) 𝑑𝑥=1/2 𝑥√(𝑎^2−𝑥^2 )+𝑎^2/2 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^(−1)〖 𝑥/𝑎+𝑐〗 Replacing a by 2 , we get = 0 + 2 sin^(−1)(1) – √3/2 √(4−3)−2 sin^(−1)〖√3/2〗 = 2 sin^(−1)(1) – √3/2 − 2 sin^(−1)〖√3/2〗 = (−√3)/2+2[sin^(−1)〖(1)−𝑠𝑖𝑛^(−1) 〗 √3/2] = (−√3)/2+2[𝜋/2−𝜋/3] = (−√3)/2+2[𝜋/6] = (−√3)/2+𝜋/3 Therefore, Area of OAC = Area OCX + Area XCA = √3/2−√3/2+(𝜋 )/3 = (𝜋 )/3 square units ∴ Required Area = 𝝅/𝟑 square units