
Examples
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo



Transcript
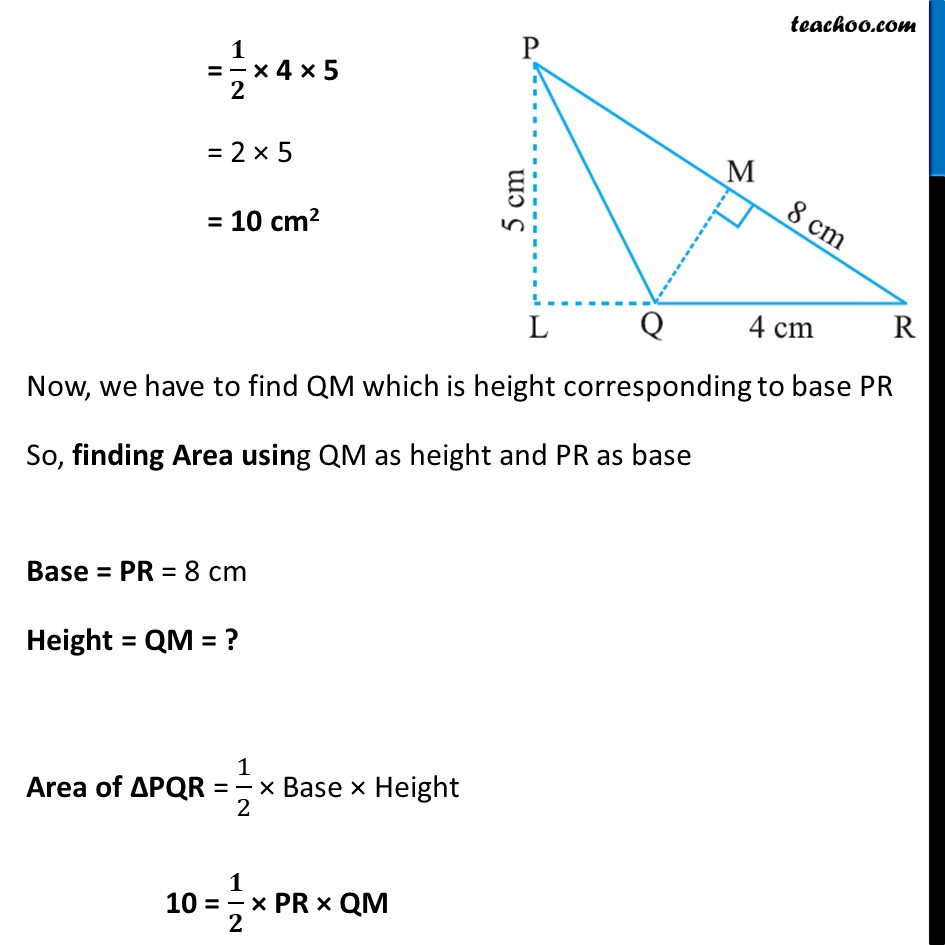
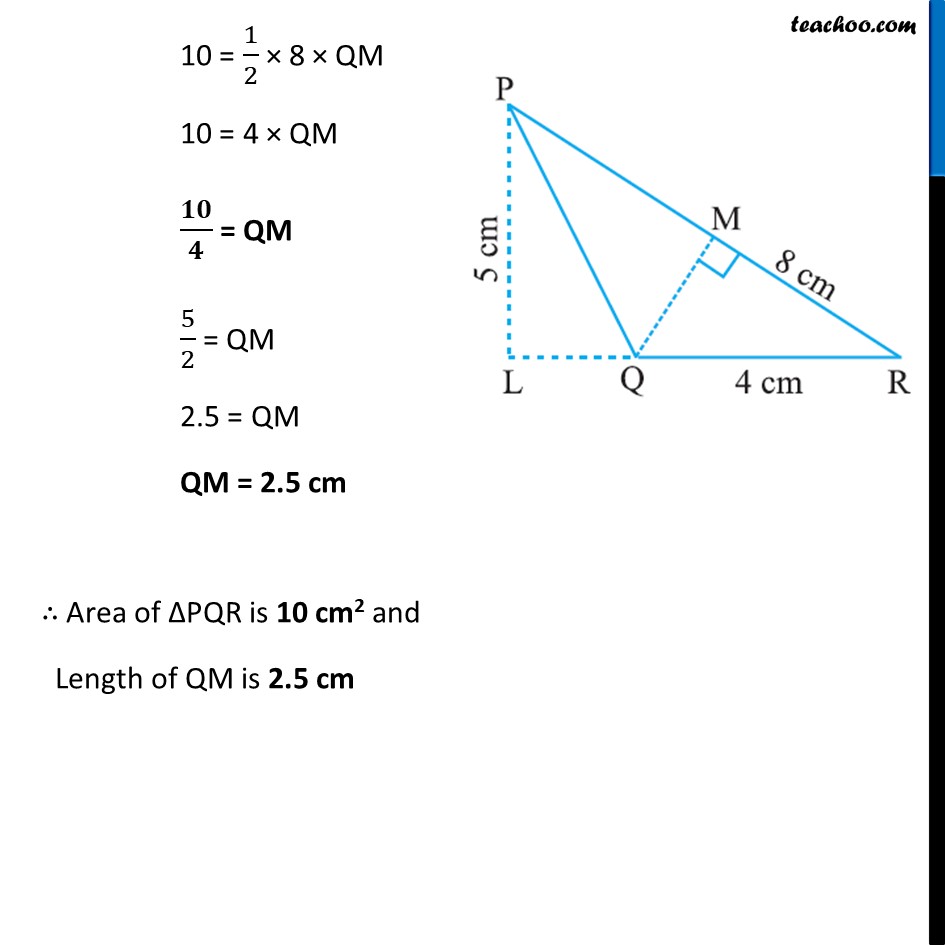
Example 6 In ΔPQR, PR = 8 cm, QR = 4 cm and PL = 5 cm (Fig 11.22). Find: (i) the area of the ΔPQR Find: (ii) QMFinding area of ∆PQR using QR as base and PL as height Here, Base = QR = 4 cm Height = PL = 5 cm Area of ∆PQR = 1/2 × Base × Height = 𝟏/𝟐 × 4 × 5 = 2 × 5 = 10 cm2 Now, we have to find QM which is height corresponding to base PR So, finding Area using QM as height and PR as base Base = PR = 8 cm Height = QM = ? Area of ∆PQR = 1/2 × Base × Height 10 = 𝟏/𝟐 × PR × QM 10 = 1/2 × 8 × QM 10 = 4 × QM 𝟏𝟎/𝟒 = QM 5/2 = QM 2.5 = QM QM = 2.5 cm ∴ Area of ∆PQR is 10 cm2 and Length of QM is 2.5 cm