

Variations on the Egyptian System and the Notion of Base
Variations on the Egyptian System and the Notion of Base
Last updated at November 24, 2025 by Teachoo






Transcript
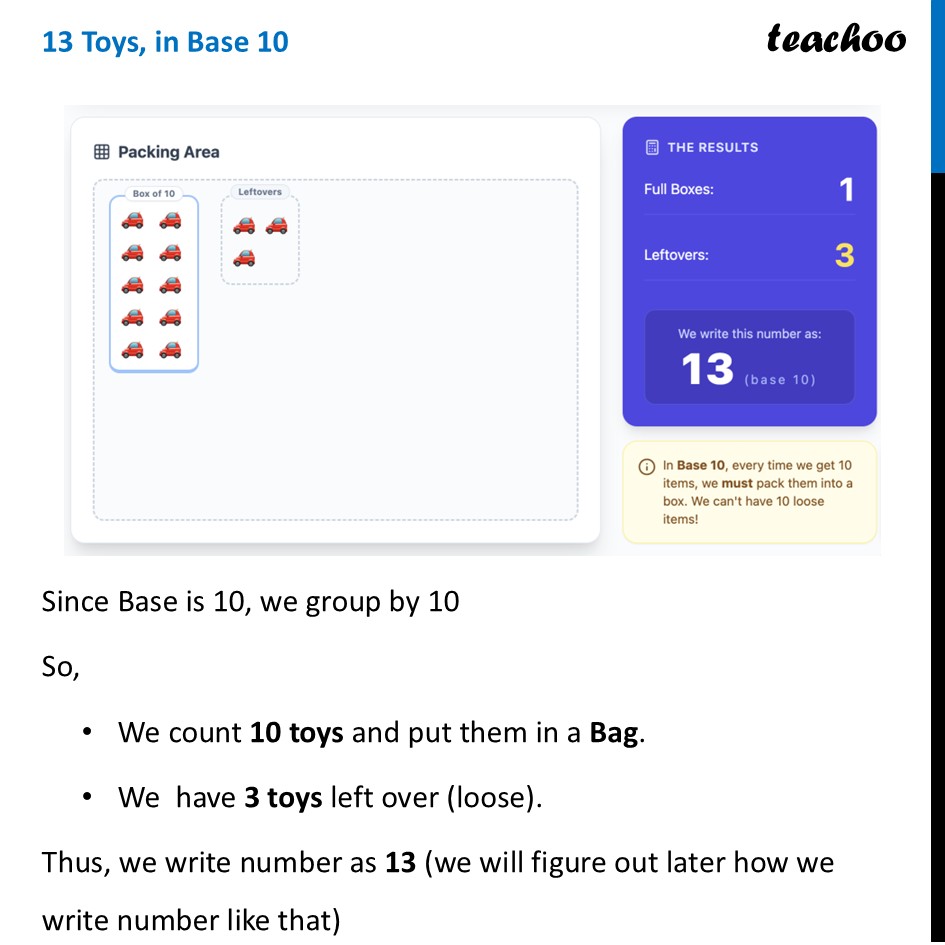
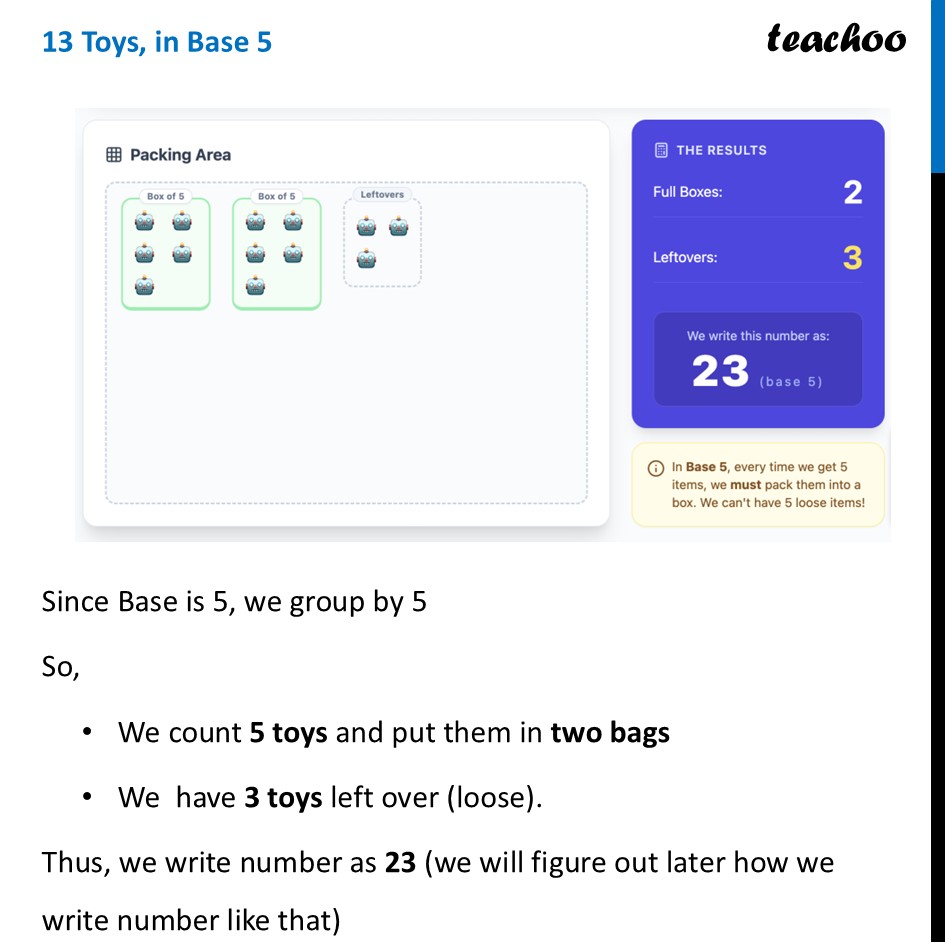
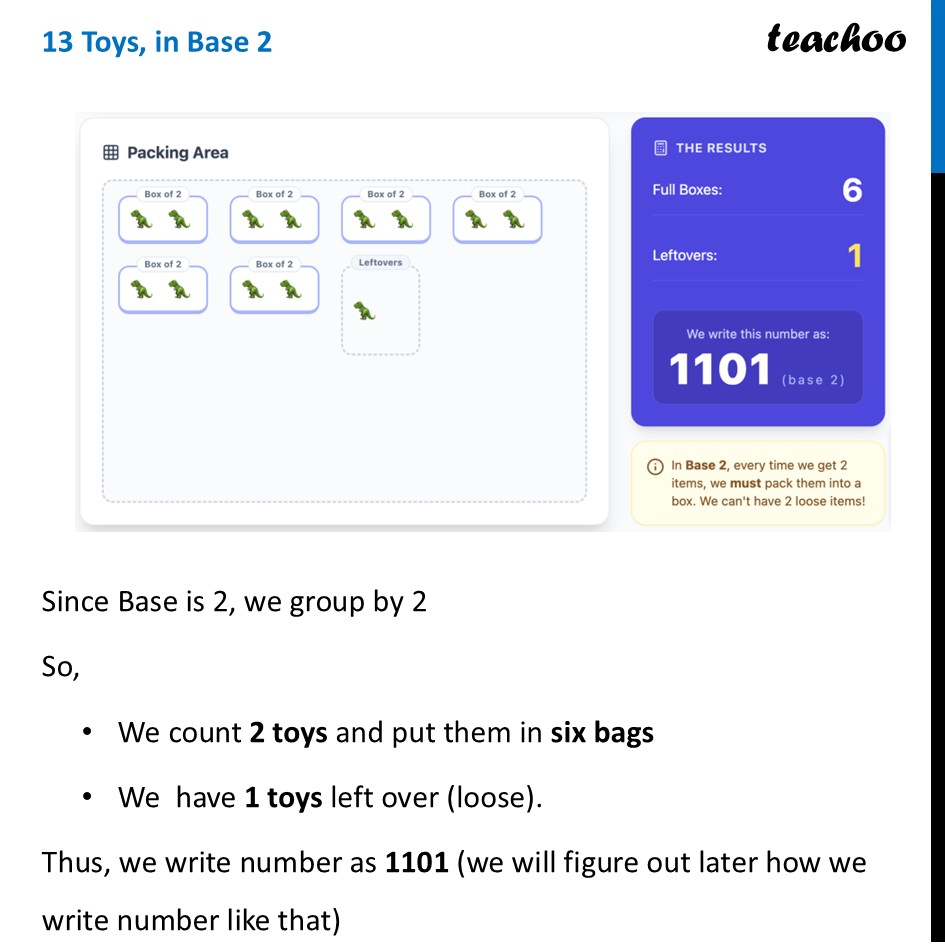
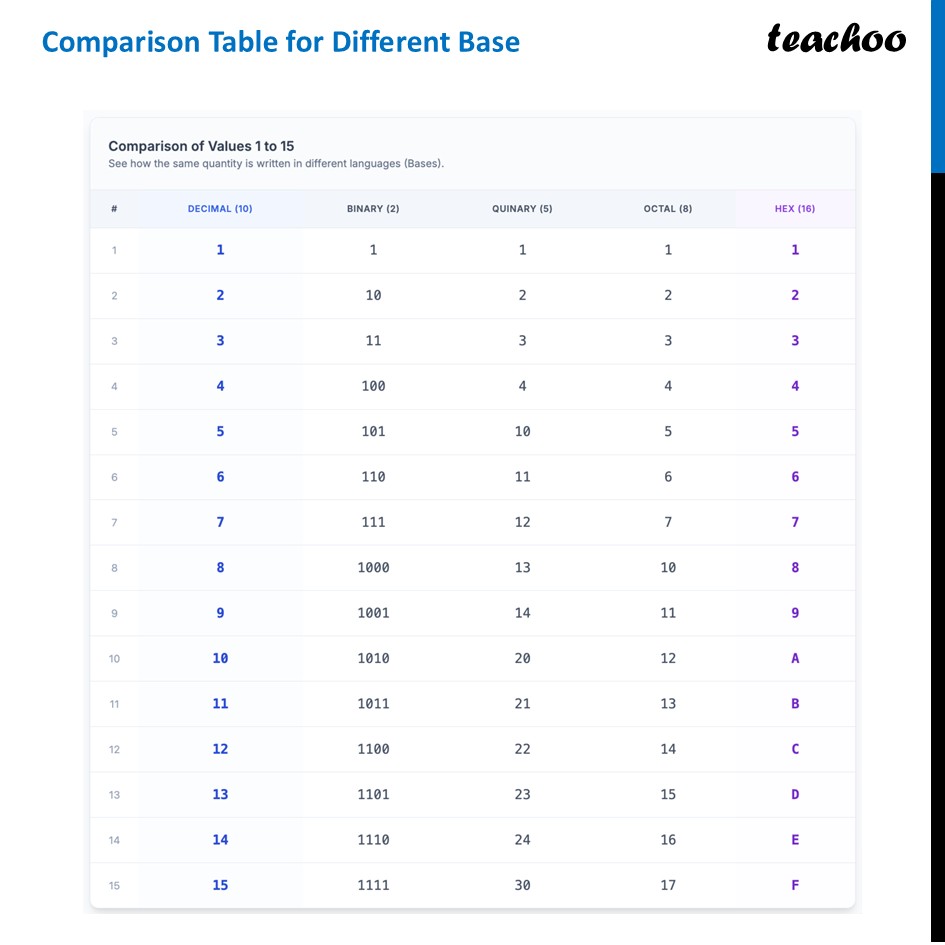
Base (in Number Systems)Imagine you are cleaning your room and picking up toys from the floor. You want to count them. The "Base" is simply the size of the bag you use to group things together. In our normal life, we use Base 10. This means our "bag" holds exactly 10 items. As soon as you have 10 items, you must close the bag and start a new one. Let’s take some examples 13 Toys, in Base 10Since Base is 10, we group by 10 So, We count 10 toys and put them in a Bag. We have 3 toys left over (loose). Thus, we write number as 13 (we will figure out later how we write number like that) 13 Toys, in Base 5Since Base is 5, we group by 5 So, We count 5 toys and put them in two bags We have 3 toys left over (loose). Thus, we write number as 23 (we will figure out later how we write number like that) 13 Toys, in Base 2Since Base is 2, we group by 2 So, We count 2 toys and put them in six bags We have 1 toys left over (loose). Thus, we write number as 1101 (we will figure out later how we write number like that) SummaryThe "Base" tells you two things: How many digits you can use (Base 10 uses 0-9. Base 5 uses 0-4). When you have to move to the next column (The next place value). System The "Rule" The Visual Unique Digits Used Base 10 Bundle every 10 1 Bundle of ten, 3 loose 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Base 5 Bundle every 5 2 Bundles of five, 3 loose 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 Base 2 Bundle every 2 (Computers use this!) 0, 1Comparison Table for Different BaseComparison of Values 1 to 15 See how the same quantity is written in different languages (Bases). " DECIMAL (10) BINARY (2) QUINARY (5) OCTAL (8) HEX (16) 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 10 2 2 2 3 3 11 3 3 3 4 4 100 4 4 4 5 5 101 10 5 5 6 6 110 11 6 6 7 7 111 12 7 7 8 8 1000 13 10 8 9 9 1001 14 11 9 10 10 1010 20 12 A 11 11 1011 21 13 B 12 12 1100 22 14 C 13 13 1101 23 15 D 14 14 1110 24 16 E 15 15 1111 30 17 F