


Miscellaneous
Last updated at December 16, 2024 by Teachoo








Transcript
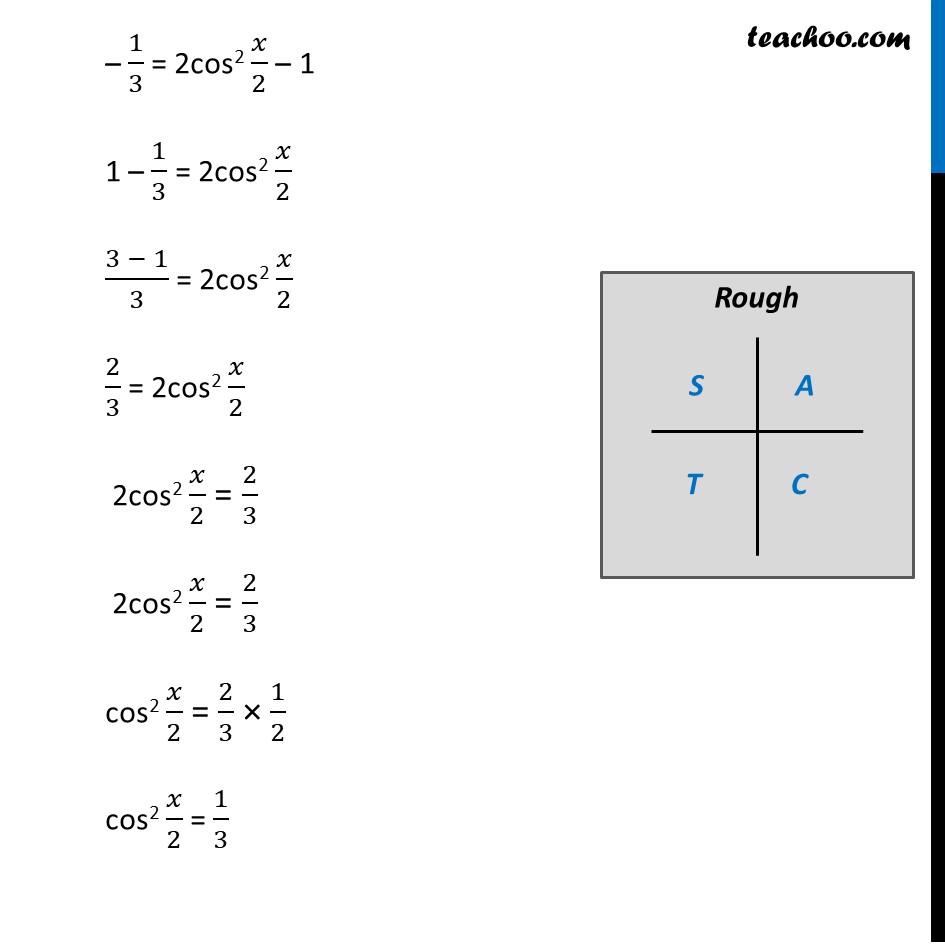
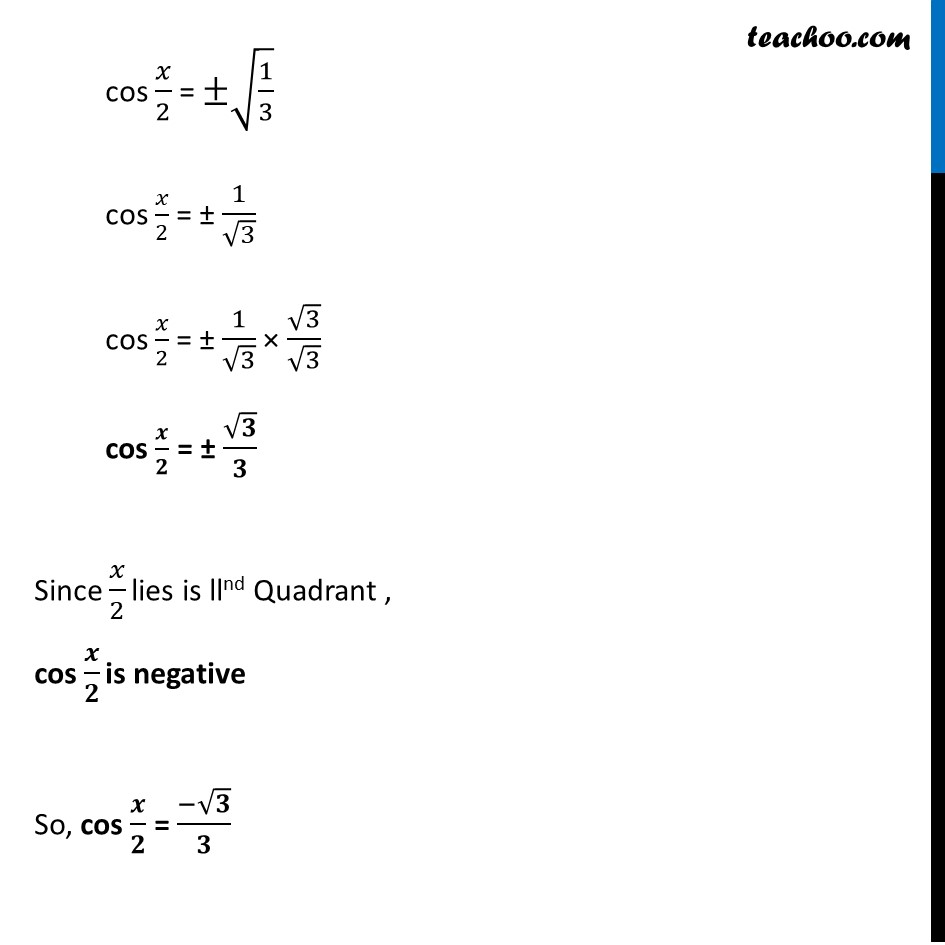
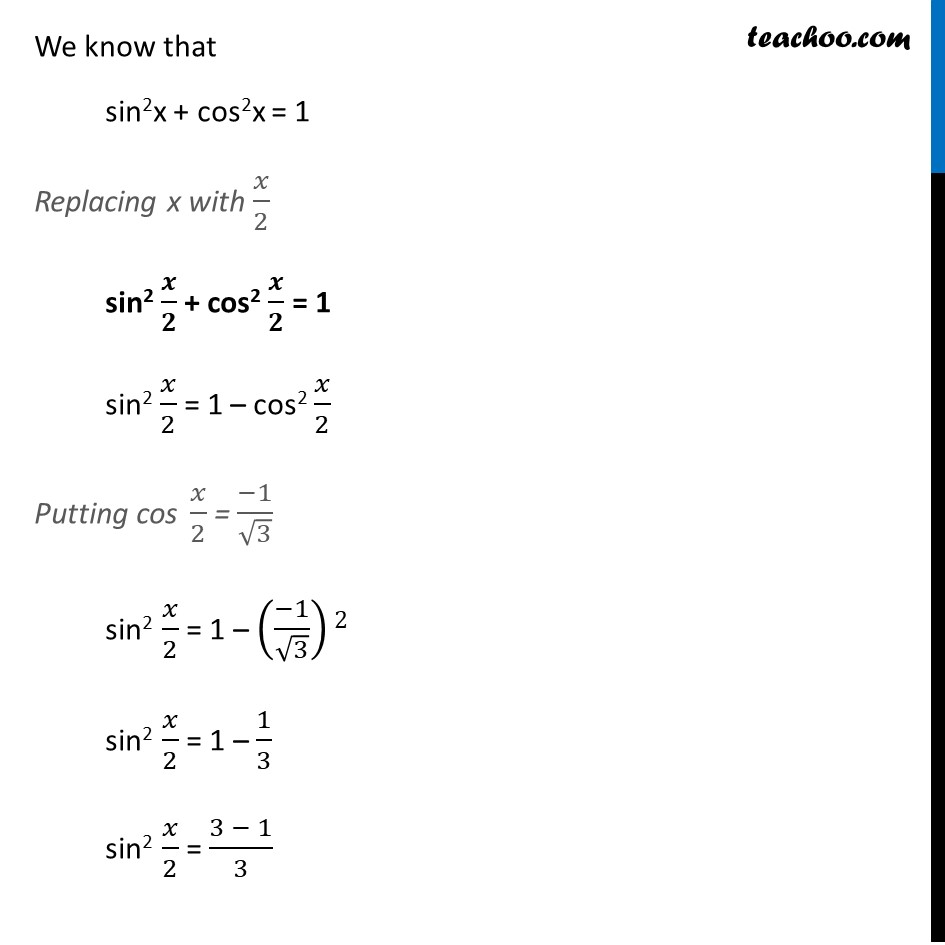
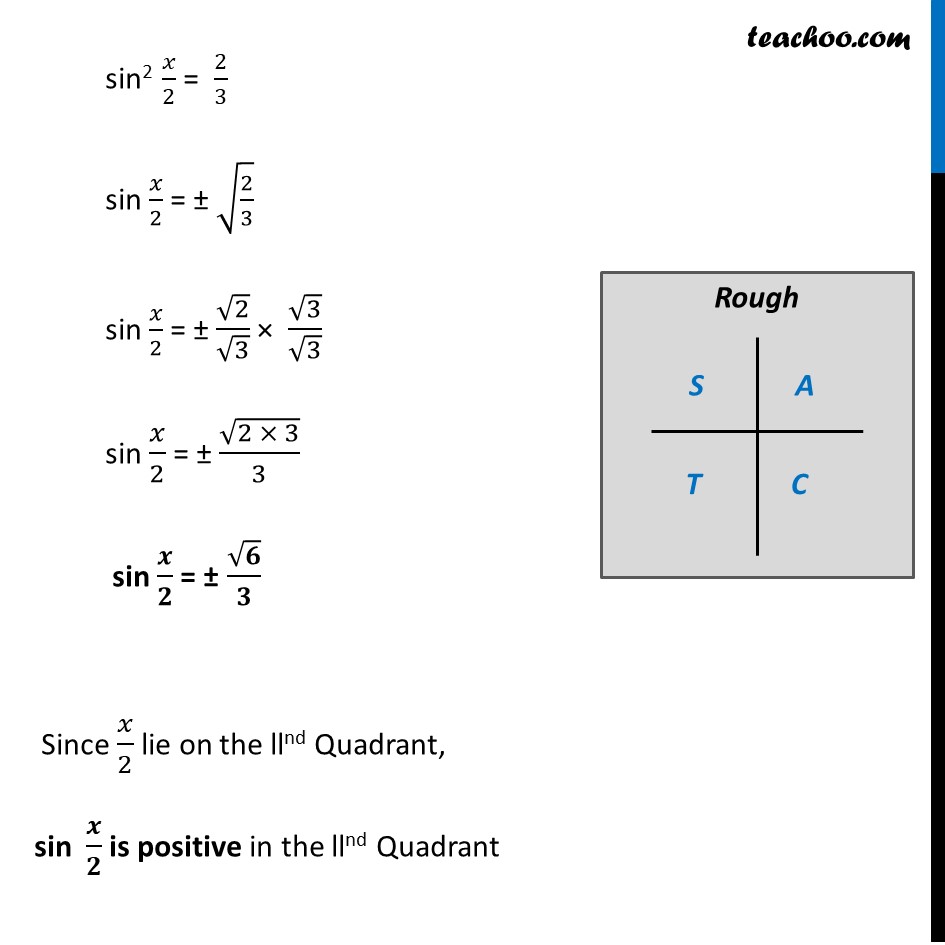
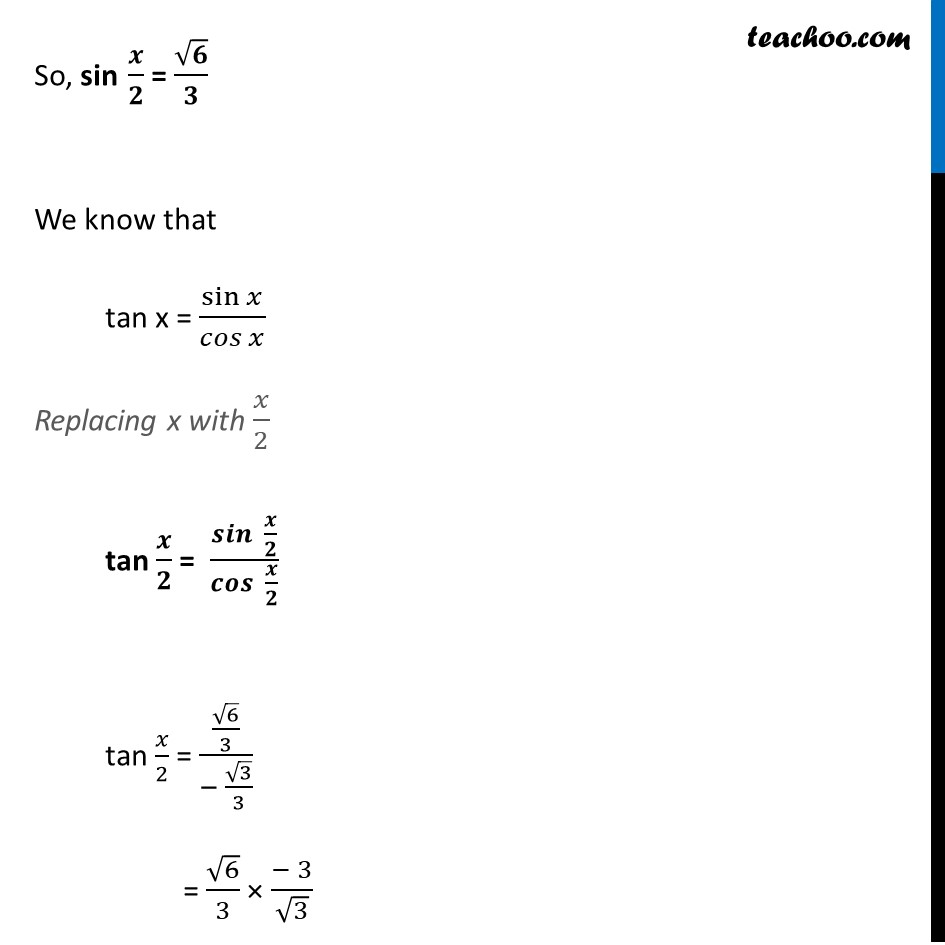
Misc 9 Find sin 𝑥/2, cos 𝑥/2 and tan 𝑥/2 for cos 𝑥 = − 1/3 , 𝑥 in quadrant III Since x is in quadrant III 180° < x < 270° Dividing by 2 all sides (180°)/2 < 𝑥/2 < (270°)/2 90° < 𝒙/𝟐 < 135° So, 𝑥/2 lies in IInd quadrant In IInd quadrant, sin is positive, cos & tan are negative sin 𝑥/2 Positive and cos 𝑥/2 and tan 𝑥/2 negative Given, cos x = −1/3 2 cos2 𝒙/𝟐 – 1 = −𝟏/𝟑 In IInd quadrant, sin is positive, cos & tan are negative sin 𝑥/2 Positive and cos 𝑥/2 and tan 𝑥/2 negative Given, cos x = −1/3 2 cos2 𝒙/𝟐 – 1 = −𝟏/𝟑 – 1/3 = 2cos2 𝑥/2 – 1 1 – 1/3 = 2cos2 𝑥/2 (3 − 1)/3 = 2cos2 𝑥/2 2/3 = 2cos2 𝑥/2 2cos2 𝑥/2 = 2/3 2cos2 𝑥/2 = 2/3 cos2 𝑥/2 = 2/3 × 1/2 cos2 𝑥/2 = 1/3 cos 𝑥/2 = ±√(1/3) cos 𝑥/2 = ± 1/√3 cos 𝑥/2 = ± 1/√3 × √3/√3 cos 𝒙/𝟐 = ± √𝟑/𝟑 Since 𝑥/2 lies is llnd Quadrant , cos 𝒙/𝟐 is negative So, cos 𝒙/𝟐 = (−√𝟑)/𝟑 We know that sin2x + cos2x = 1 Replacing x with 𝑥/2 sin2 𝒙/𝟐 + cos2 𝒙/𝟐 = 1 sin2 𝑥/2 = 1 – cos2 𝑥/2 Putting cos 𝑥/2 = (−1)/√3 sin2 𝑥/2 = 1 – ((−1)/√3)2 sin2 𝑥/2 = 1 – 1/3 sin2 𝑥/2 = (3 − 1)/3 sin2 𝑥/2 = 2/3 sin 𝑥/2 = ± √(2/3) sin 𝑥/2 = ± √2/√3 × √3/√3 sin 𝑥/2 = ± √(2 × 3)/3 sin 𝒙/𝟐 = ± √𝟔/𝟑 Since 𝑥/2 lie on the llnd Quadrant, sin 𝒙/𝟐 is positive in the llnd Quadrant So, sin 𝒙/𝟐 = √𝟔/𝟑 We know that tan x = sin𝑥/𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥 Replacing x with 𝑥/2 tan 𝒙/𝟐 = 𝒔𝒊𝒏〖 𝒙/𝟐〗/〖𝒄𝒐𝒔 〗〖𝒙/𝟐〗 tan 𝑥/2 = (√6/3)/(− √3/3) = √6/3 × (− 3)/√3 = – √6/√3 = – √(6/3) = – √2 Hence, tan 𝒙/𝟐 = – √𝟐 Therefore, tan 𝑥/2 = – √2 , cos 𝑥/2 = −√3/3 & sin 𝑥/2 = √6/3