

Finding values of expressions
Finding values of expressions
Last updated at Dec. 13, 2024 by Teachoo




Transcript
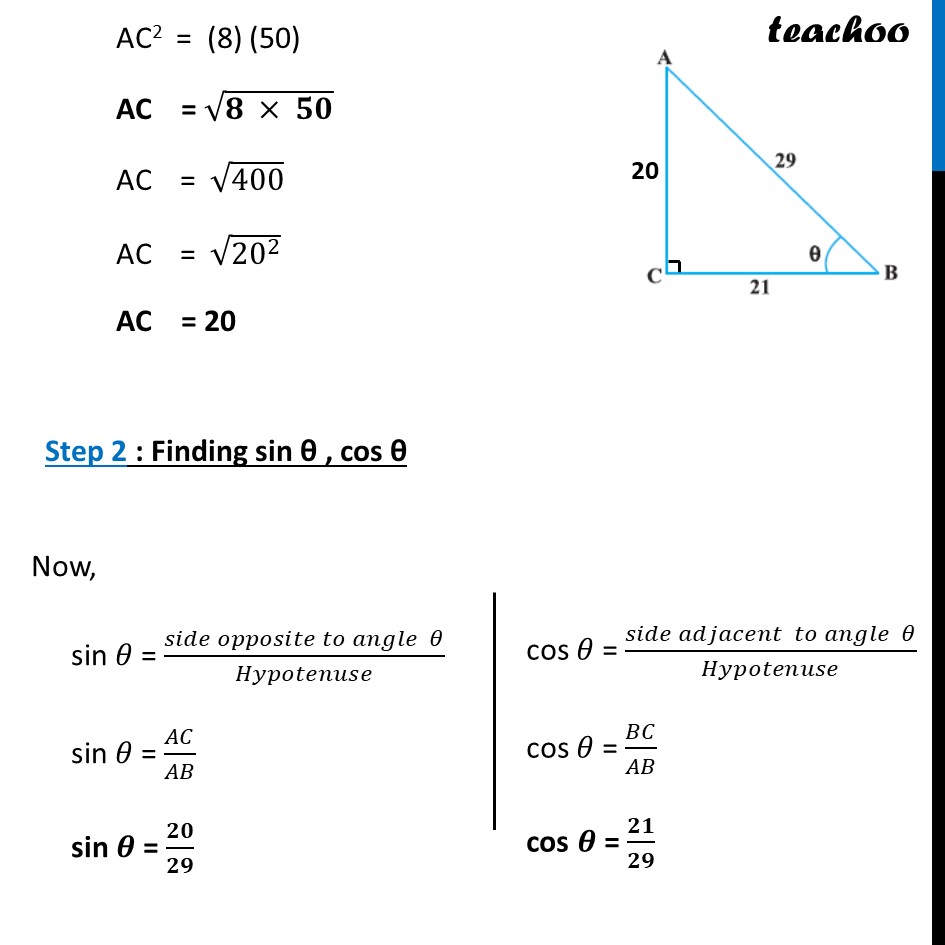
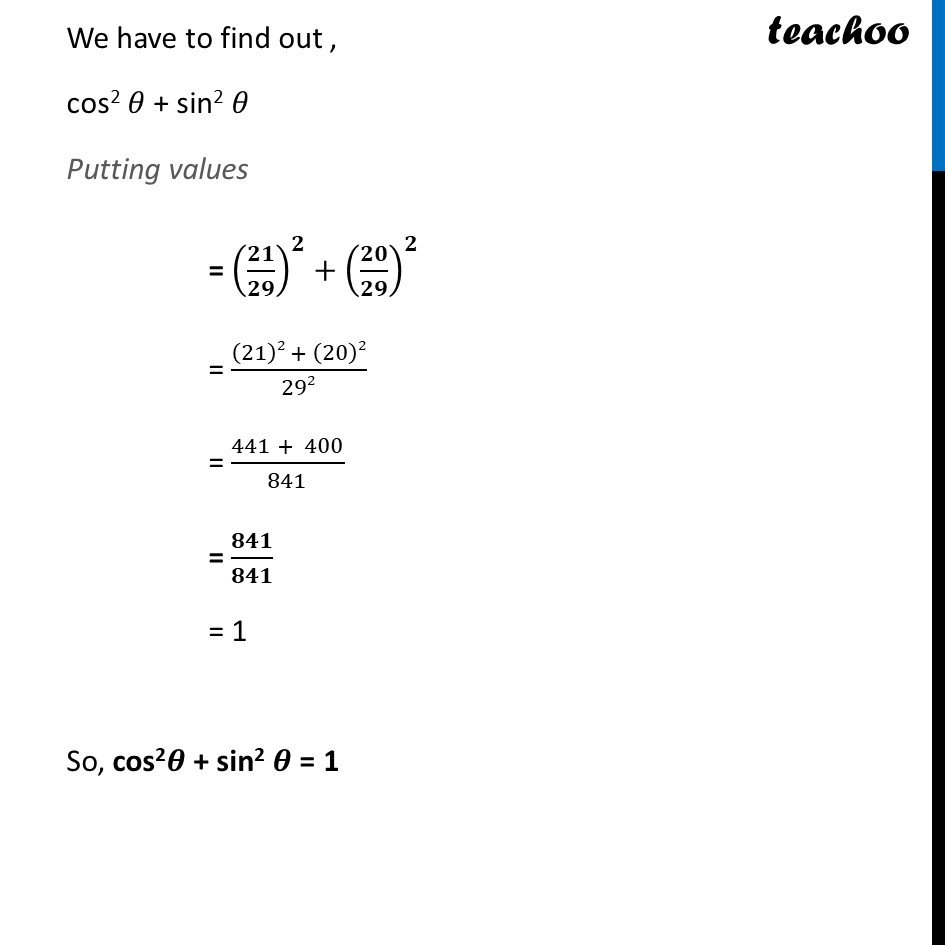
Example 3 Consider Δ ACB, right-angled at C, in which AB = 29 units, BC = 21 units and ∠ ABC = θ (see fig.). Determine the values of (i) cos2 θ + sin2 θ, Step 1 : Finding sides of triangle In right triangle ABC, Using Pythagoras theorem (Hypotenuse)2 = (Height)2 + (Base)2 AB2 = AC2 + BC2 AC2 = AB2 – BC2 AC2 = (29)2 – (21)2 Using a2 – b2 = (a + b) (a – b) AC2 = (29 – 21) (29 + 21) AC2 = (8) (50) AC = √(𝟖 × 𝟓𝟎) AC = √400 AC = √(20^2 ) AC = 20 Step 2 : Finding sin θ , cos θ Now, sin 𝜃 = (𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑡𝑜 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 𝜃)/𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 sin 𝜃 = 𝐴𝐶/𝐴𝐵 sin 𝜽 = 𝟐𝟎/𝟐𝟗 cos 𝜃 = (𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 𝜃)/𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 cos 𝜃 = 𝐵𝐶/𝐴𝐵 cos 𝜽 = 𝟐𝟏/𝟐𝟗 We have to find out , cos2 𝜃 + sin2 𝜃 Putting values = (𝟐𝟏/𝟐𝟗)^𝟐+(𝟐𝟎/𝟐𝟗)^𝟐 = ((21)2 + (20)2)/292 = (441 + 400)/841 = 𝟖𝟒𝟏/𝟖𝟒𝟏 = 1 So, cos2𝜽 + sin2 𝜽 = 1 Example 3 Consider Δ ACB, right-angled at C, in which AB = 29 units, BC = 21 units and ∠ ABC = θ(see fig.). Determine the values of (ii) cos2 θ – sin2 θ. cos2 𝜃 – sin2 𝜃 Putting values = (𝟐𝟏/𝟐𝟗)^𝟐−(𝟐𝟎/𝟐𝟗)^𝟐 = ((21)2 − (20)2)/292 Using a2 – b2 = (a + b) (a – b) = ((21 + 20)(21 − 20))/292 = 𝟒𝟏/𝟖𝟒𝟏