



Variable separation - Equation given
Variable separation - Equation given
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo







Transcript
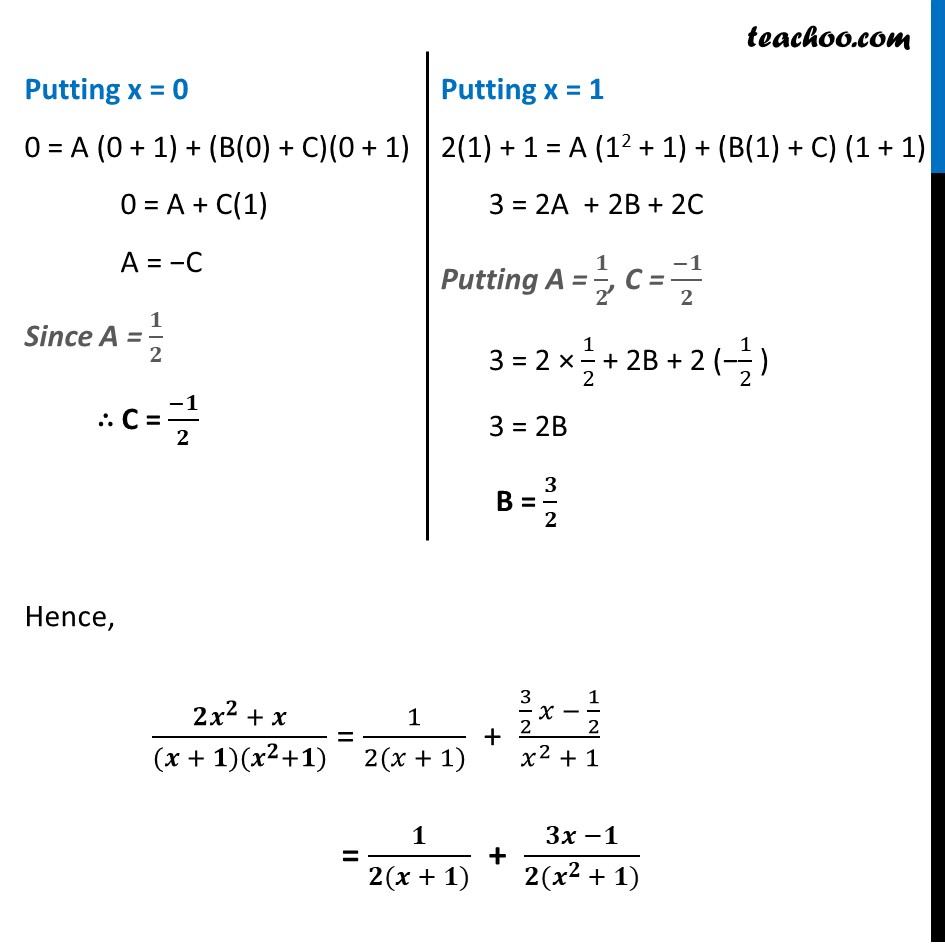
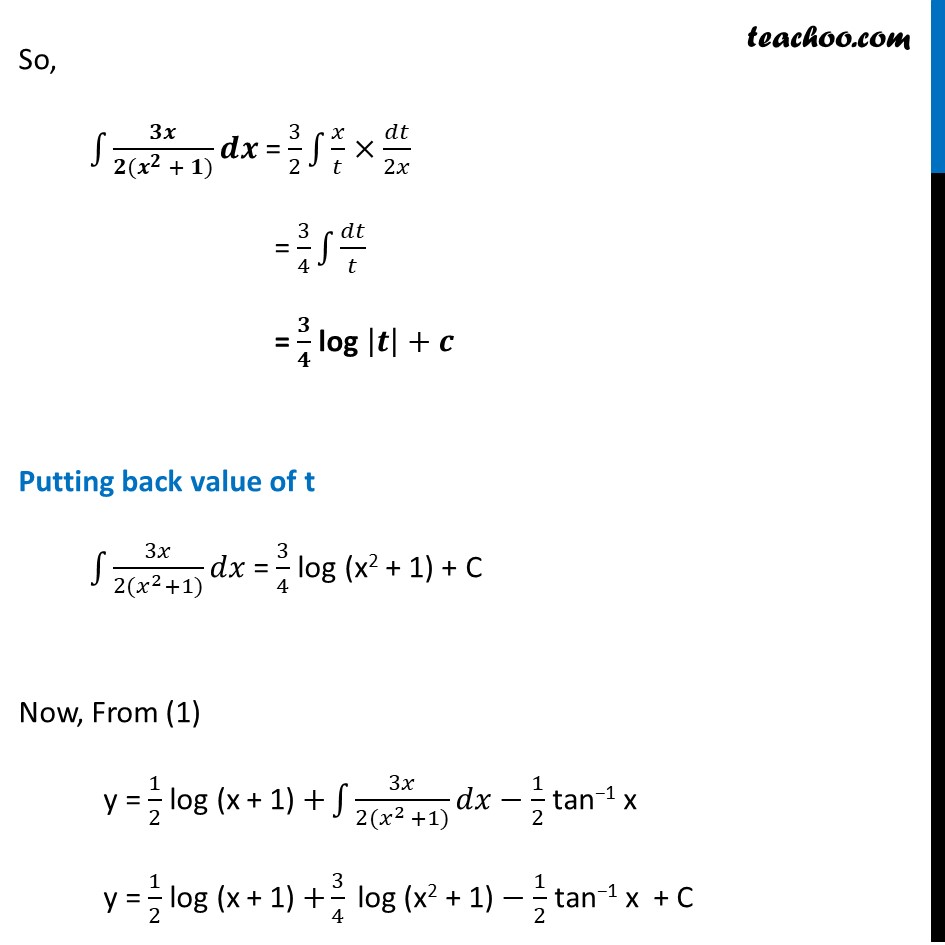
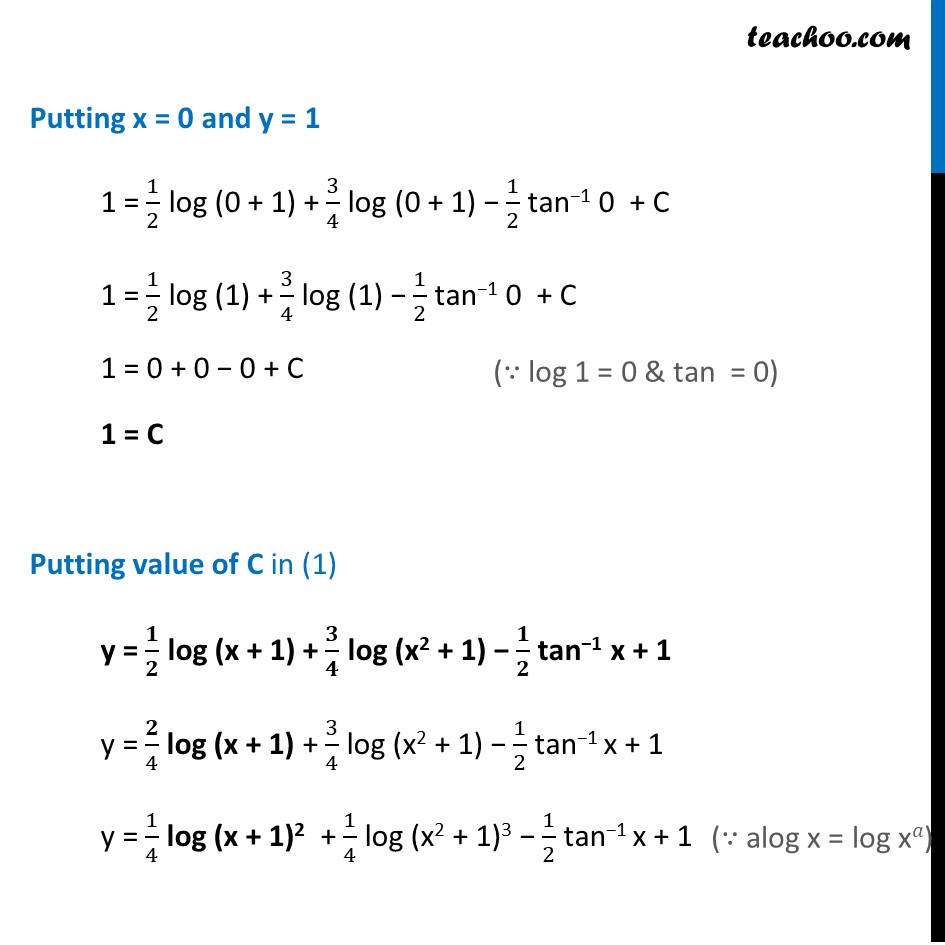
Ex 9.3, 11 Find a particular solution satisfying the given condition : (𝑥^3+𝑥^2+𝑥+1) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=2𝑥^2+𝑥; 𝑦=1 when 𝑥=0(𝑥^3+𝑥^2+𝑥+1) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=2𝑥^2+𝑥 𝒅𝒚 = (𝟐𝒙^𝟐 + 𝒙)/(𝒙^𝟑 + 𝒙^𝟐 + 𝒙 + 𝟏) 𝒅𝒙 Integrating both sides ∫1▒〖𝑑𝑦=∫1▒(2𝑥^2 + 𝑥)/(𝑥3 + 𝑥2 + 𝑥 + 1)〗 dx y = ∫1▒(𝟐𝒙^𝟐 + 𝒙)/( (𝒙 + 𝟏)(𝒙^𝟐 + 𝟏)) dx Rough x = −1 is a solution of x3 + x2 + x + 1 as (-1)2 + (-1)2 + (−1) + 1 = 0 Hence (x + 1) is one of its factors. So, we can write x3 + x2 + x + 1 = (x + 1) (x2 + 1) Integrating by partial fractions, using formula (𝟐𝒙^𝟐 +𝒙)/((𝒙 + 𝟏)(𝒙^𝟐+𝟏)) = 𝑨/(𝒙 + 𝟏)+(𝑩𝒙 + 𝑪)/(𝒙^𝟐 + 𝟏) (2𝑥^2 +𝑥)/((𝑥 + 1)(𝑥^2+1)) = (𝐴(𝑥^2+1) + (𝐵𝑥 + 𝑐)(𝑥 + 1))/((𝑥 + 1)(𝑥^2 + 1)) 2𝑥^2 + x = A (𝑥^2+ 1) + (Bx + C) (x + 1) Putting x = −1 2(−1)2 − 1 = A ((−1)2 + 1) + (B(−1) + C)(−1 + 1) 2 − 1 = A(2) + (–B + C)(0) 1 = 2A A = 𝟏/𝟐 Putting x = 0 0 = A (0 + 1) + (B(0) + C)(0 + 1) 0 = A + C(1) A = −C Since A = 𝟏/𝟐 ∴ C = (−𝟏)/𝟐 Putting x = 1 2(1) + 1 = A (12 + 1) + (B(1) + C) (1 + 1) 3 = 2A + 2B + 2C Putting A = 𝟏/𝟐, C = (−𝟏)/𝟐 3 = 2 × 1/2 + 2B + 2 (−1/2 ) 3 = 2B B = 𝟑/𝟐 Hence, (𝟐𝒙^𝟐 + 𝒙)/((𝒙 + 𝟏)(𝒙^𝟐+𝟏)) = 1/(2(𝑥 + 1)) + (3/2 𝑥 − 1/2)/(𝑥^2 + 1) = 𝟏/(𝟐(𝒙 + 𝟏)) + (𝟑𝒙 −𝟏)/(〖𝟐(𝒙〗^(𝟐 )+ 𝟏)) Now, our equation becomes y = ∫1▒〖(2𝑥^2 + 𝑥)/((𝑥 + 1)(𝑥^2 + 1)) 𝑑𝑥〗 y = ∫1▒〖𝟏/(𝟐(𝒙 + 𝟏))+𝟑𝒙/(𝟐(𝒙^(𝟐 )+𝟏)) − 𝟏/𝟐(𝒙^𝟐 + 𝟏) 𝒅𝒙〗 y = ∫1▒〖1/(2(𝑥 + 1)) 𝑑𝑥〗+∫1▒〖3𝑥/(2(𝑥^(2 )+1)) 𝑑𝑥〗−∫1▒〖 1/2(𝑥^2 + 1) 𝑑𝑥〗 y = 𝟏/𝟐 log (x + 1) +∫1▒〖𝟑𝒙/(𝟐(𝒙^(𝟐 )+𝟏)) 𝒅𝒙〗− 𝟏/𝟐 tan−1 x Integrating ∫1▒〖𝟑𝒙/(𝟐(𝒙^𝟐 + 𝟏)) 𝒅𝒙〗 Put t = x2 + 1 dt = 2x dx ∴ dx = 𝑑𝑡/2𝑥 So, ∫1▒〖𝟑𝒙/(𝟐(𝒙^𝟐 + 𝟏)) 𝒅𝒙〗 = 3/2 ∫1▒𝑥/𝑡×𝑑𝑡/2𝑥 = 3/4 ∫1▒𝑑𝑡/𝑡 = 𝟑/𝟒 log |𝒕|+𝒄 Putting back value of t ∫1▒〖3𝑥/(2(𝑥^2+1)) 𝑑𝑥〗 = 3/4 log (x2 + 1) + C Now, From (1) y = 1/2 log (x + 1) +∫1▒〖3𝑥/(2(𝑥^(2 )+1)) 𝑑𝑥〗− 1/2 tan−1 x y = 1/2 log (x + 1) +3/4 " log (x2 + 1)"− 1/2 tan−1 x + C Putting x = 0 and y = 1 1 = 1/2 log (0 + 1) + 3/4 log (0 + 1) − 1/2 tan−1 0 + C 1 = 1/2 log (1) + 3/4 log (1) − 1/2 tan−1 0 + C 1 = 0 + 0 − 0 + C 1 = C Putting value of C in (1) y = 𝟏/𝟐 log (x + 1) + 𝟑/𝟒 log (x2 + 1) − 𝟏/𝟐 tan−1 x + 1 y = 𝟐/4 log (x + 1) + 3/4 log (x2 + 1) − 1/2 tan−1 x + 1 y = 1/4 log (x + 1)2 + 1/4 log (x2 + 1)3 − 1/2 tan−1 x + 1 y = 1/4 [log〖 (𝑥+1)^2 〗+log〖(𝑥^2+1)^3 〗 ] "− " 1/2 " tan−1 x + 1 " As log 𝑎 + log b = log 𝑎b y = 𝟏/𝟒 𝒍𝒐𝒈〖〖 [(𝒙+𝟏)〗^𝟐 (𝒙^𝟐+𝟏)^𝟑] 〗 "− " 𝟏/𝟐 " tan−1 x + 1 "