

Special Cases of Division
Last updated at January 28, 2026 by Teachoo




Transcript
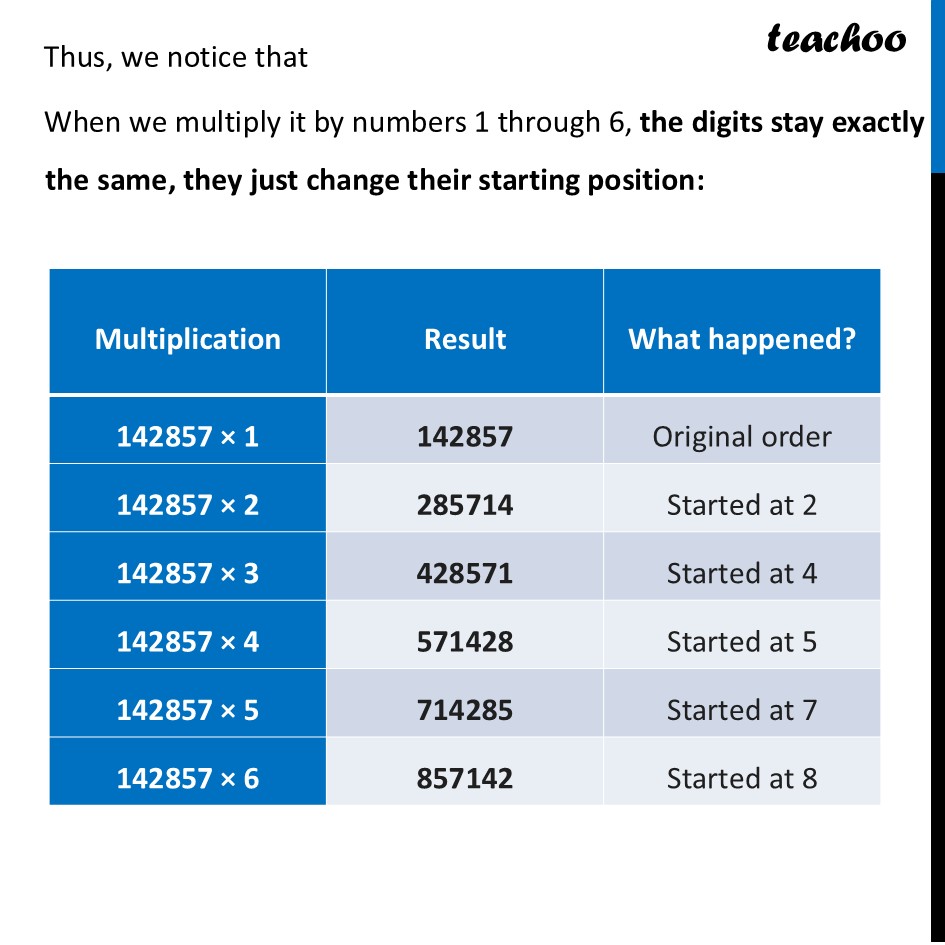
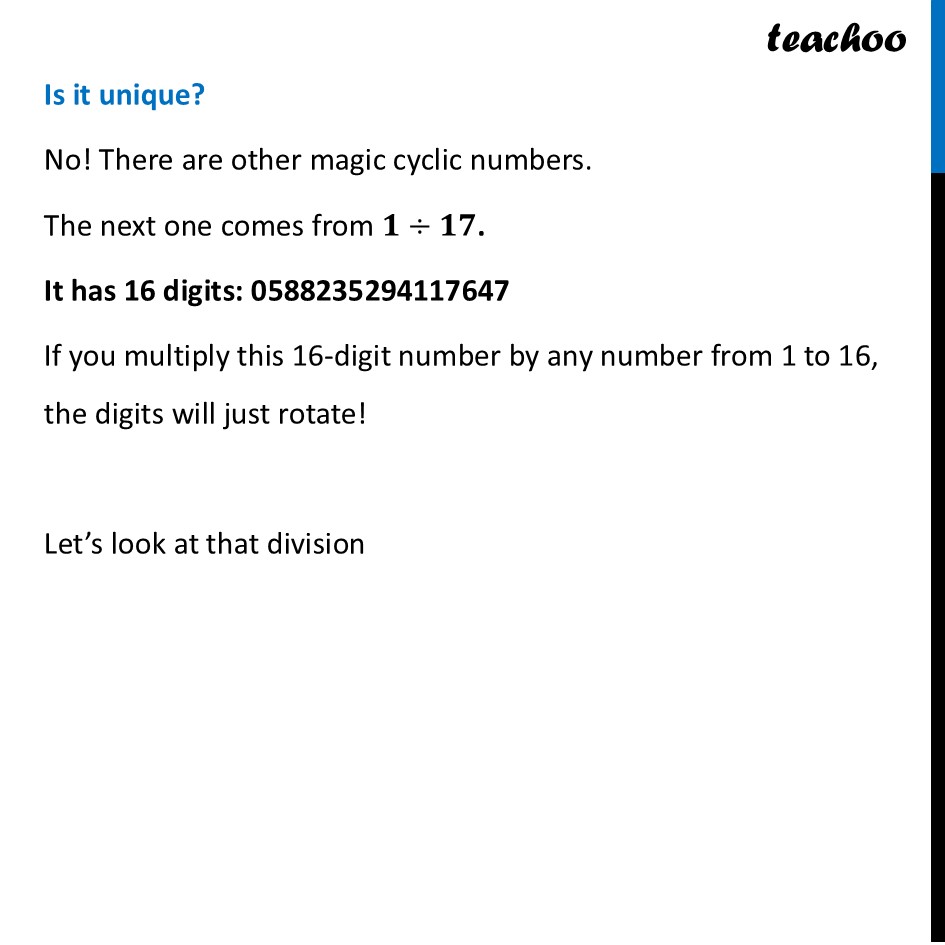
A Magic Number: 142857We know that 𝟏/𝟕=𝟎.𝟏𝟒𝟐𝟖𝟓𝟕 𝟏𝟒𝟐𝟖𝟓𝟕 𝟏𝟒𝟐𝟖𝟓𝟕… Let’s look at cases when 142857 is multiplied by 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1 × 142,857 = 142,857 2 × 142,857 = 285,714 3 × 142,857 = 428,571 4 × 142,857 = 571,428 5 × 142,857 = 714,285 6 × 142,857 = 857,142 Thus, we notice that When we multiply it by numbers 1 through 6, the digits stay exactly the same, they just change their starting position: MultiplicationResult What happened? The "Break" at 7 The cycle breaks when you multiply by 7. Because the original division was 1 ÷ 7, multiplying the result by 7 brings you back to a whole: 142857 × 7 = 999999 (In higher math, 0.999... is actually equal to 1!) Why does this happen? It happens because when you divide 1 by 7 using long division, the remainders always repeat in the same order: 1,3,2,6,4,5. Since the remainders are trapped in this loop, the answer digits are trapped in a loop too. Is it unique? No! There are other magic cyclic numbers. The next one comes from 𝟏÷𝟏𝟕. It has 16 digits: 0588235294117647 If you multiply this 16-digit number by any number from 1 to 16, the digits will just rotate! Let’s look at that division