
Last updated at December 12, 2025 by Teachoo








Transcript
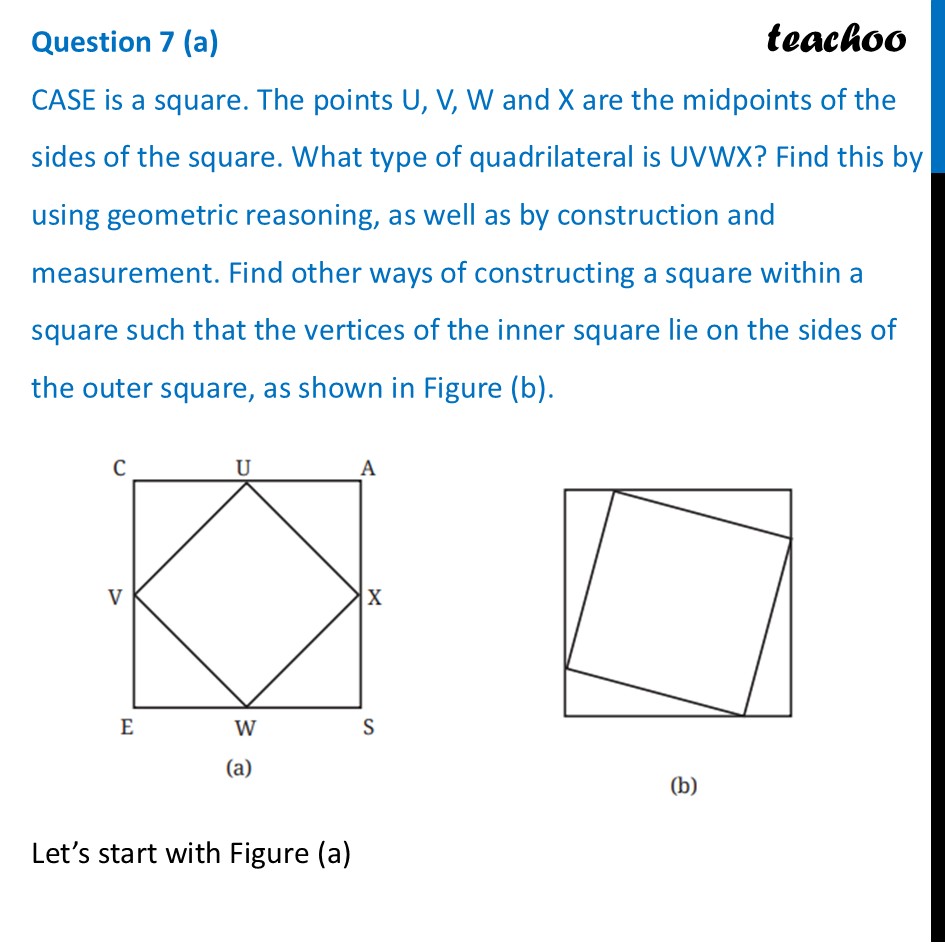
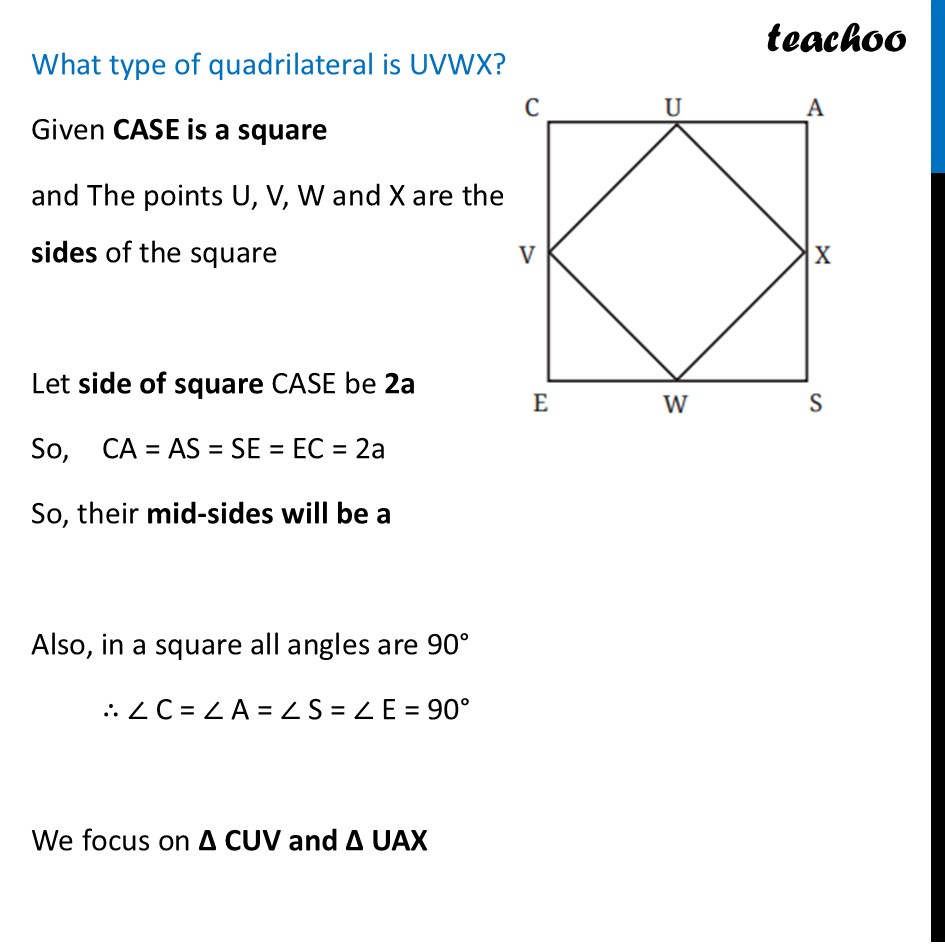
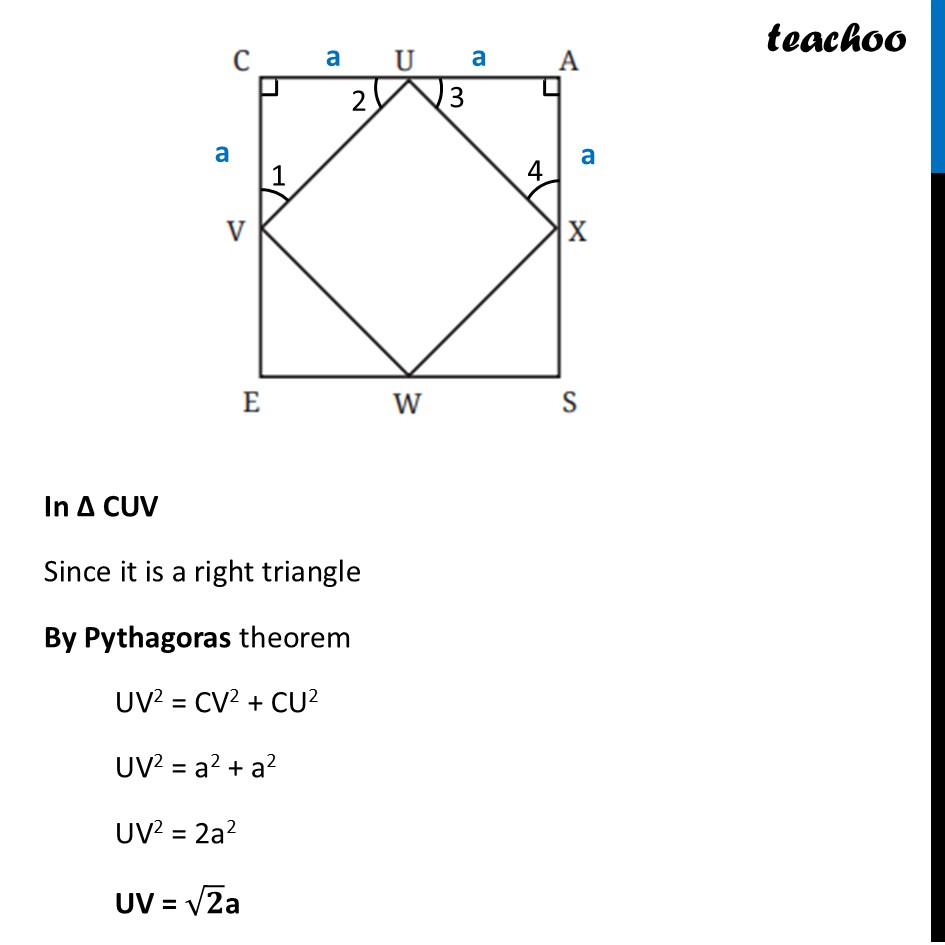
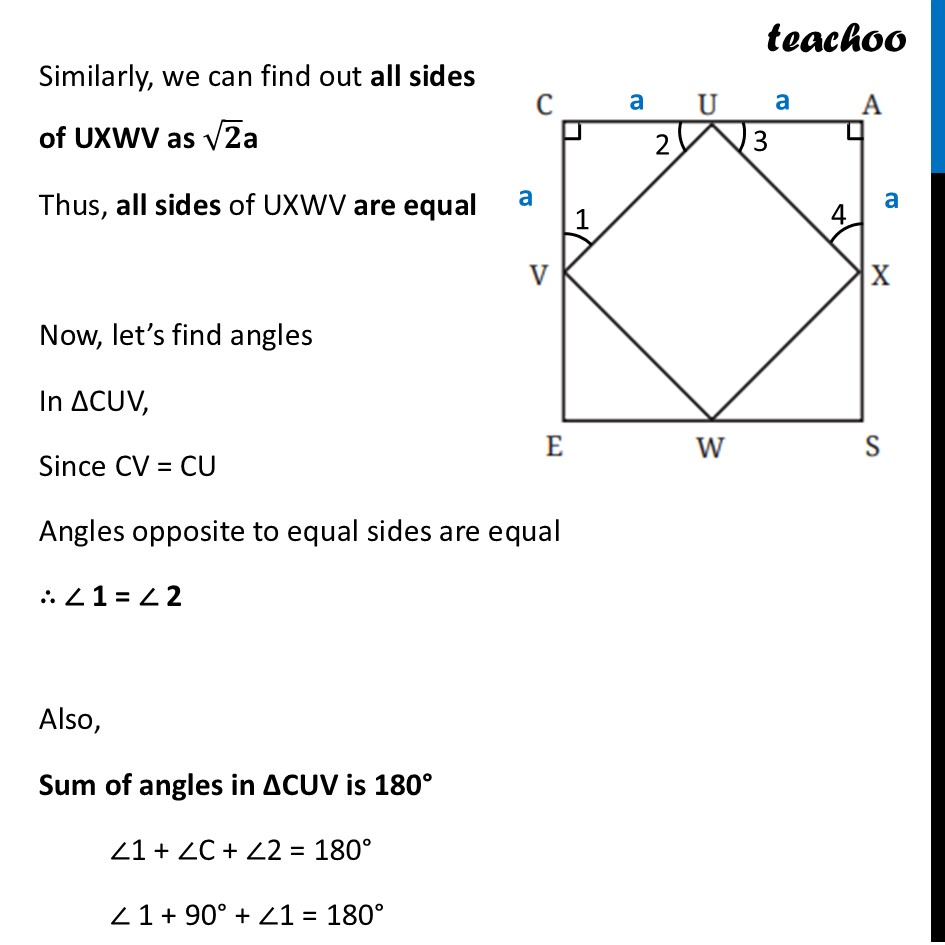
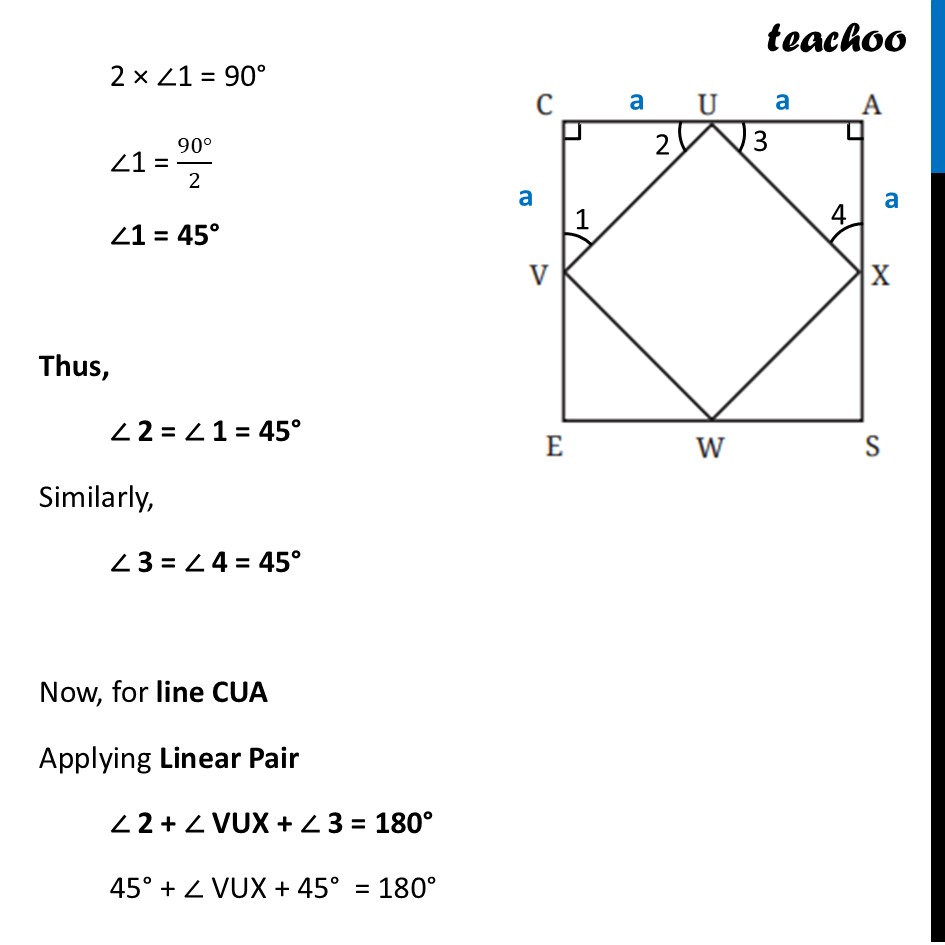
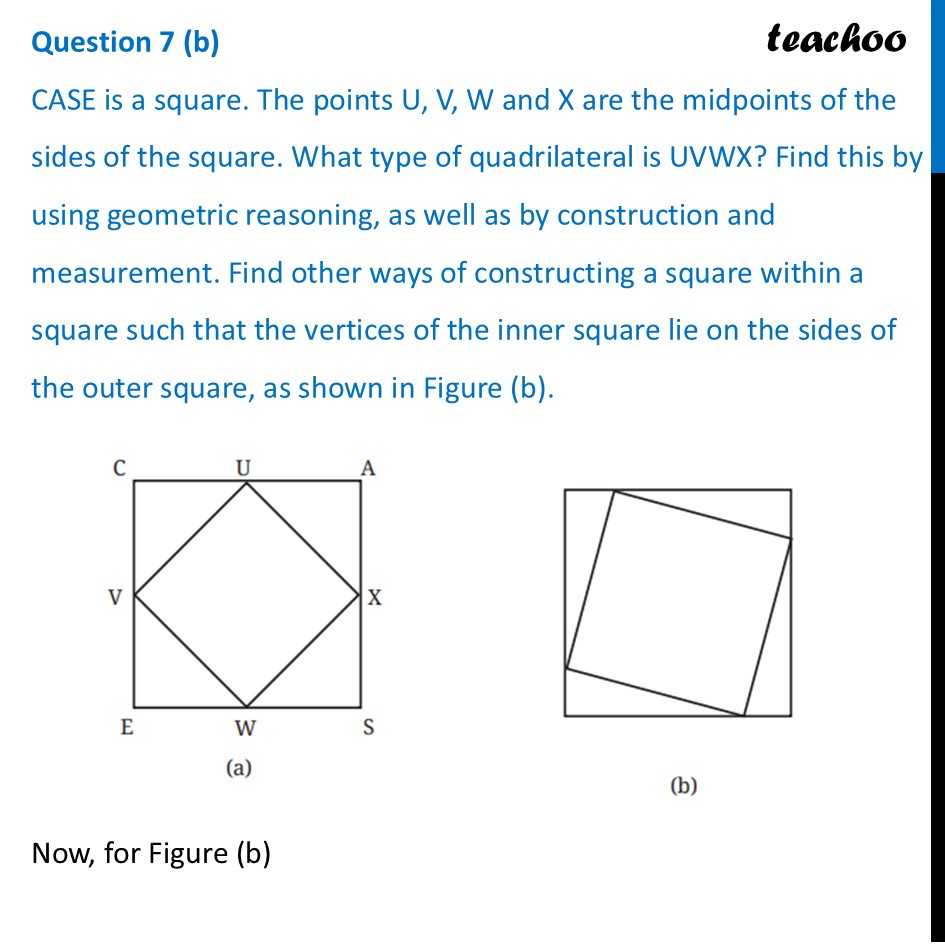
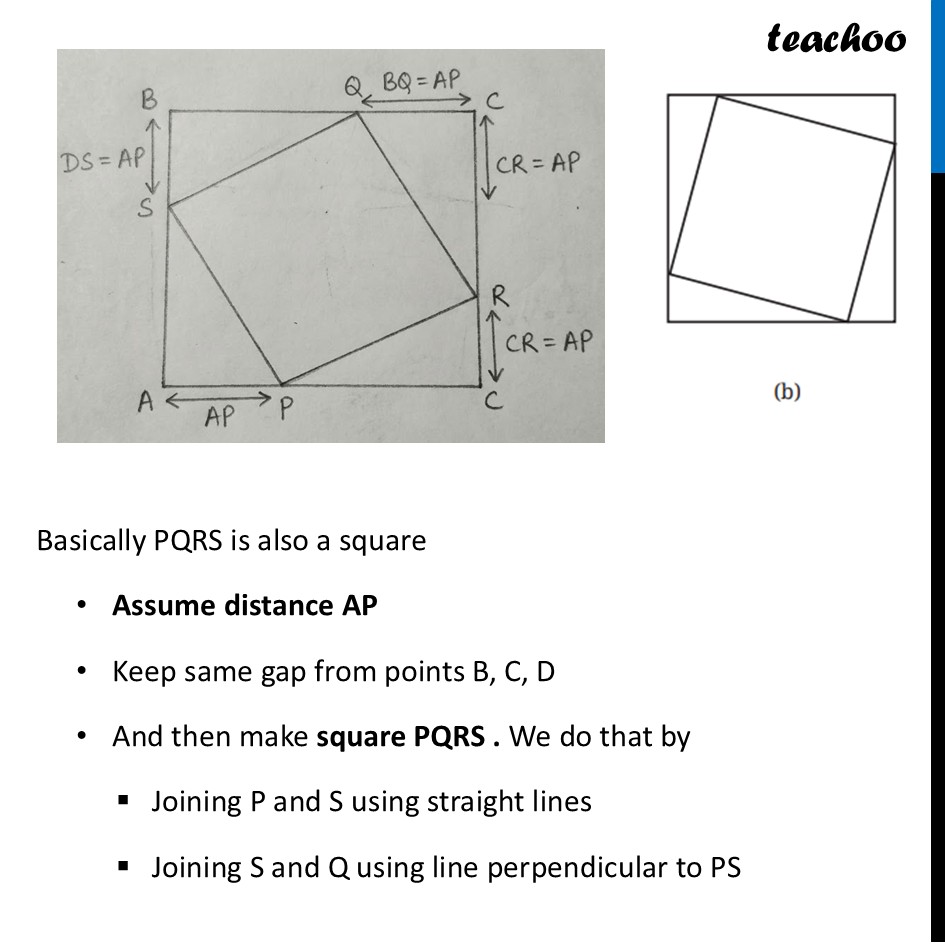
Question 7 (a) CASE is a square. The points U, V, W and X are the midpoints of the sides of the square. What type of quadrilateral is UVWX? Find this by using geometric reasoning, as well as by construction and measurement. Find other ways of constructing a square within a square such that the vertices of the inner square lie on the sides of the outer square, as shown in Figure (b).Let’s start with Figure (a) What type of quadrilateral is UVWX? Given CASE is a square and The points U, V, W and X are the midpoints of the sides of the square Let side of square CASE be 2a So, CA = AS = SE = EC = 2a So, their mid-sides will be a Also, in a square all angles are 90° ∴ ∠ C = ∠ A = ∠ S = ∠ E = 90° We focus on ∆ CUV and ∆ UAX In ∆ CUV Since it is a right triangle By Pythagoras theorem UV2 = CV2 + CU2 UV2 = a2 + a2 UV2 = 2a2 UV = √𝟐a Similarly, we can find out all sides of UXWV as √𝟐a Thus, all sides of UXWV are equal Now, let’s find angles In ∆CUV, Since CV = CU Angles opposite to equal sides are equal ∴ ∠ 1 = ∠ 2 Also, Sum of angles in ∆CUV is 180° ∠1 + ∠C + ∠2 = 180° ∠ 1 + 90° + ∠1 = 180° 2 × ∠1 = 90° ∠1 = (90°)/2 ∠1 = 45° Thus, ∠ 2 = ∠ 1 = 45° Similarly, ∠ 3 = ∠ 4 = 45° Now, for line CUA Applying Linear Pair ∠ 2 + ∠ VUX + ∠ 3 = 180° 45° + ∠ VUX + 45° = 180° ∠ VUX + 90° = 180° ∠ VUX = 180° – 90° ∠ VUX = 90° Similarly, we can prove all angles in UXWV as 90° So, in UXWV – all sides are equal and all angles are 90° Thus, we can say that UXWV is a square Question 7 (b) CASE is a square. The points U, V, W and X are the midpoints of the sides of the square. What type of quadrilateral is UVWX? Find this by using geometric reasoning, as well as by construction and measurement. Find other ways of constructing a square within a square such that the vertices of the inner square lie on the sides of the outer square, as shown in Figure (b).Now, for Figure (b) Basically PQRS is also a square Assume distance AP Keep same gap from points B, C, D And then make square PQRS . We do that by Joining P and S using straight lines Joining S and Q using line perpendicular to PS