
Last updated at December 12, 2025 by Teachoo








Transcript
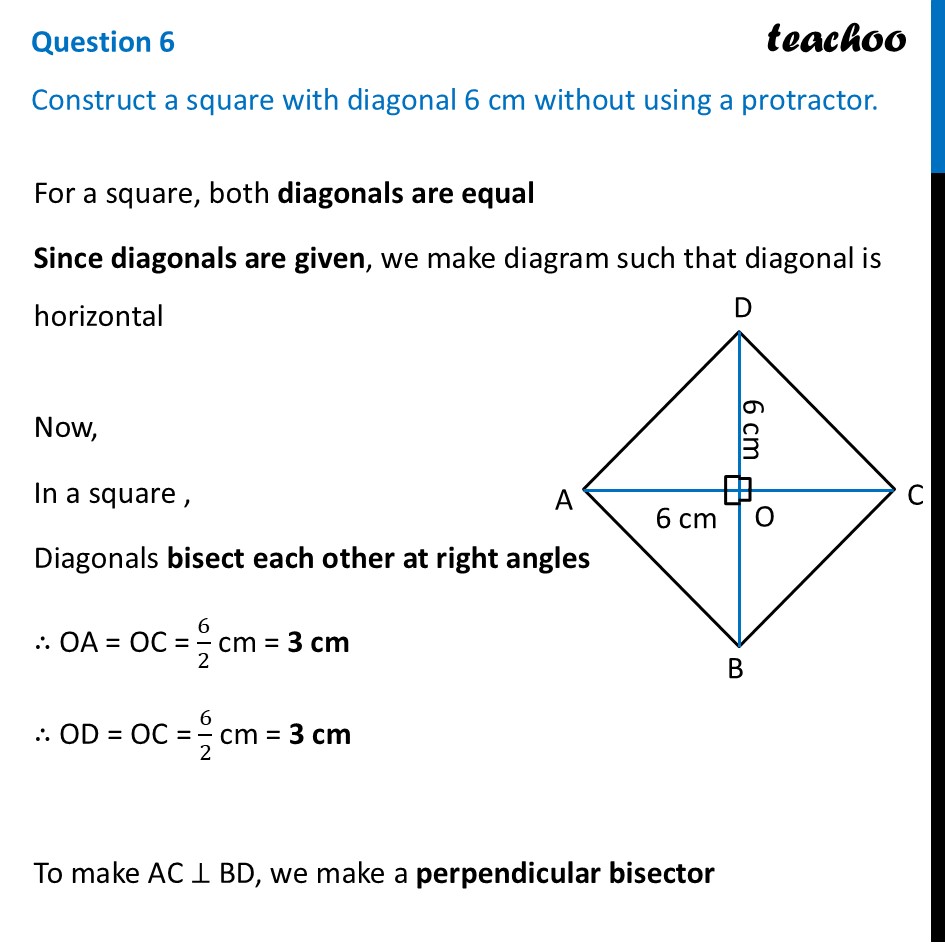
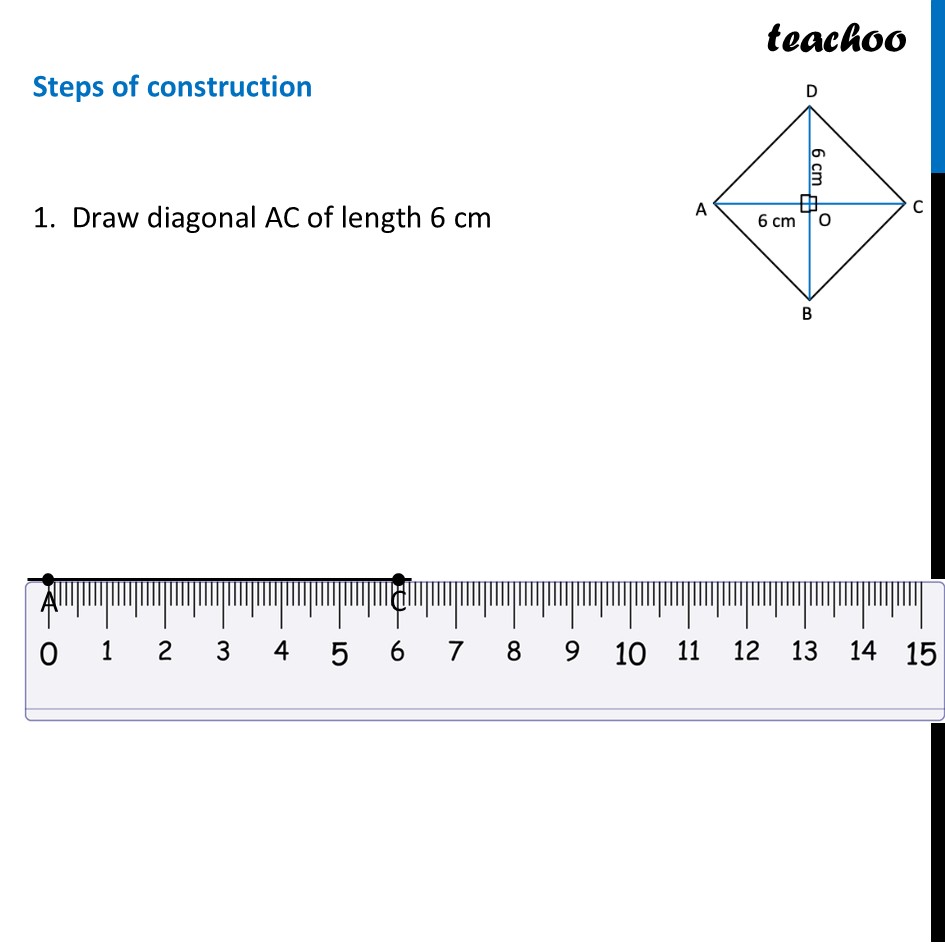
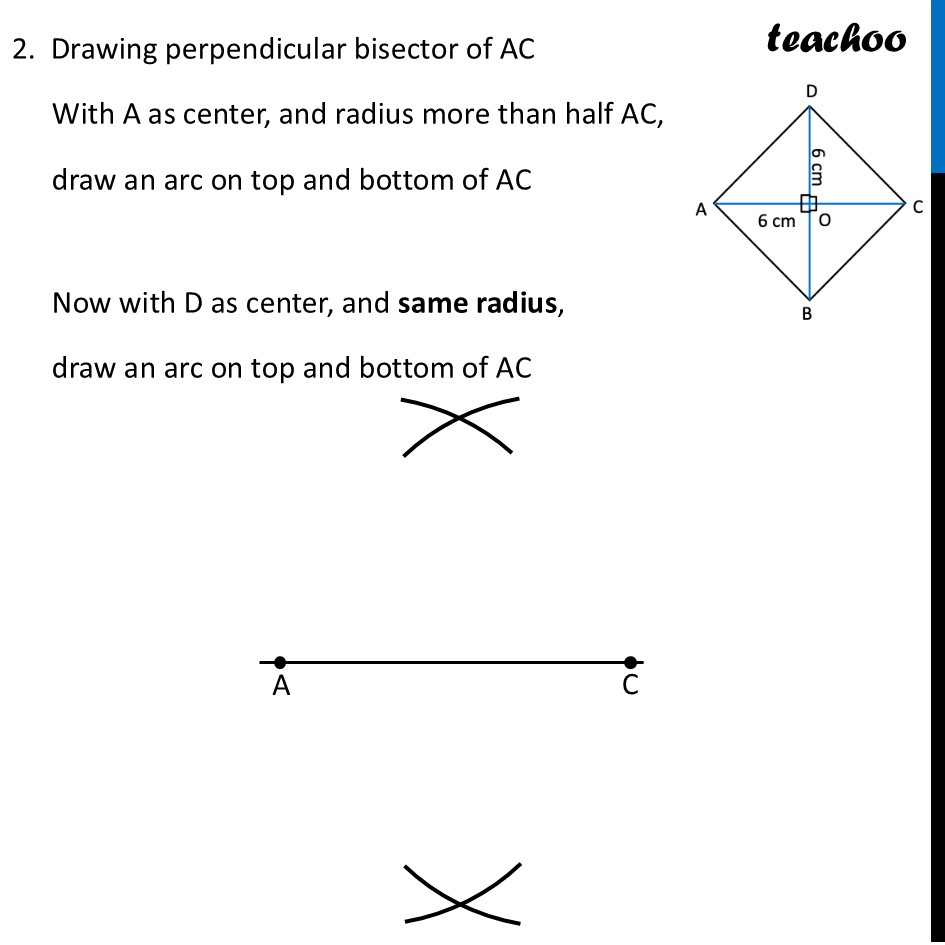
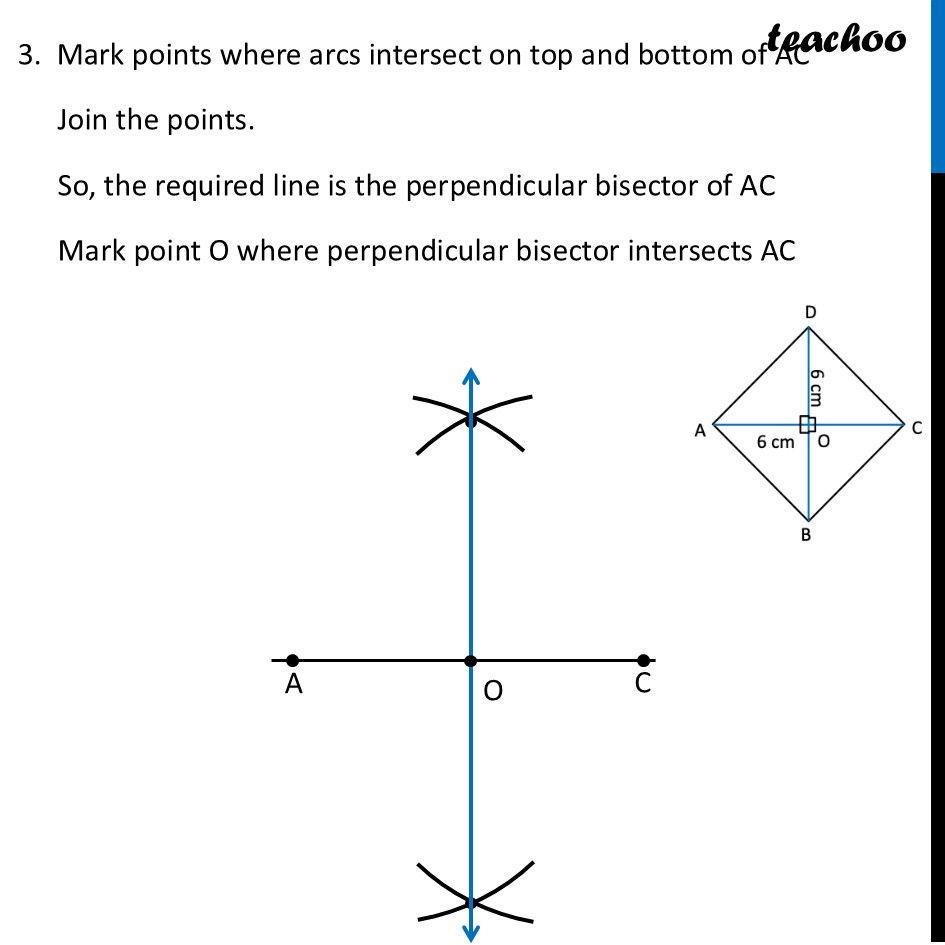
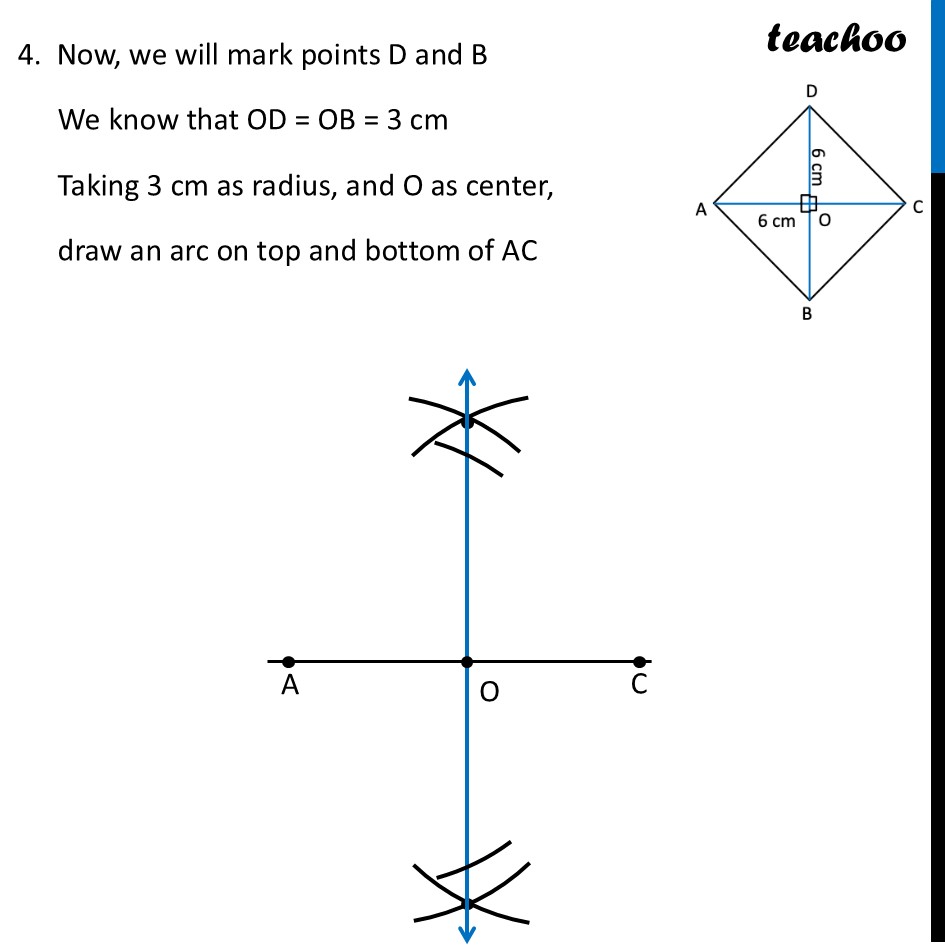
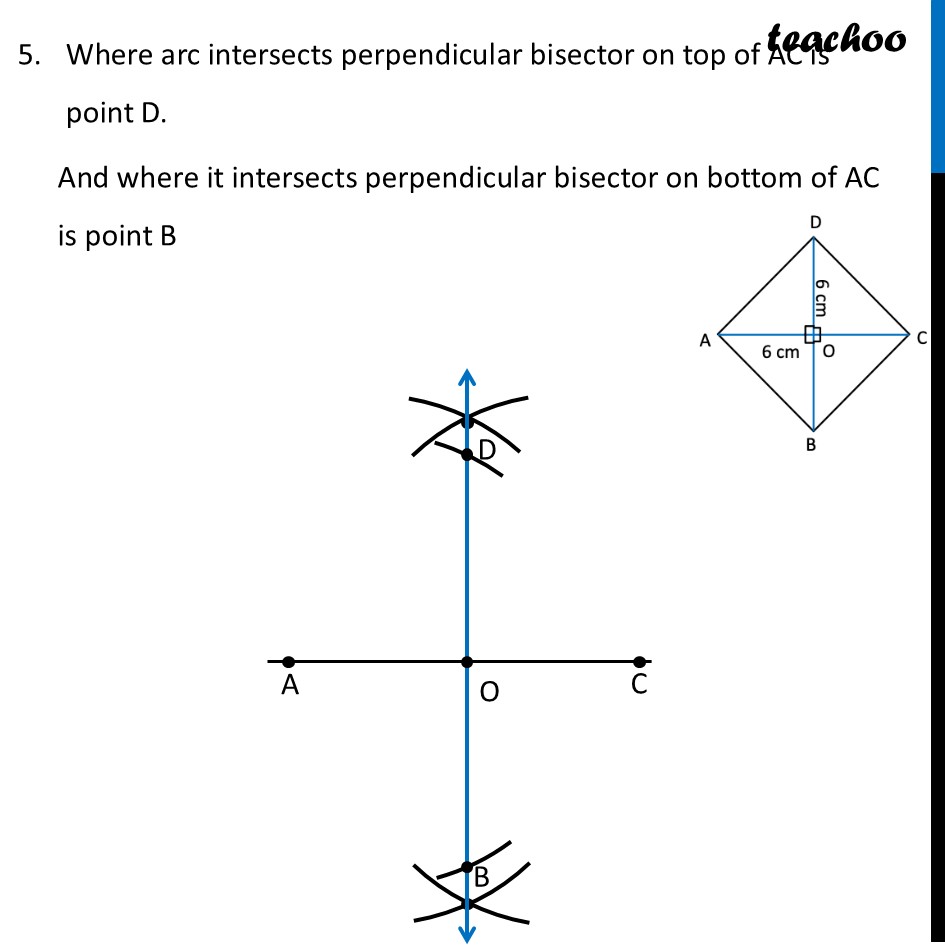
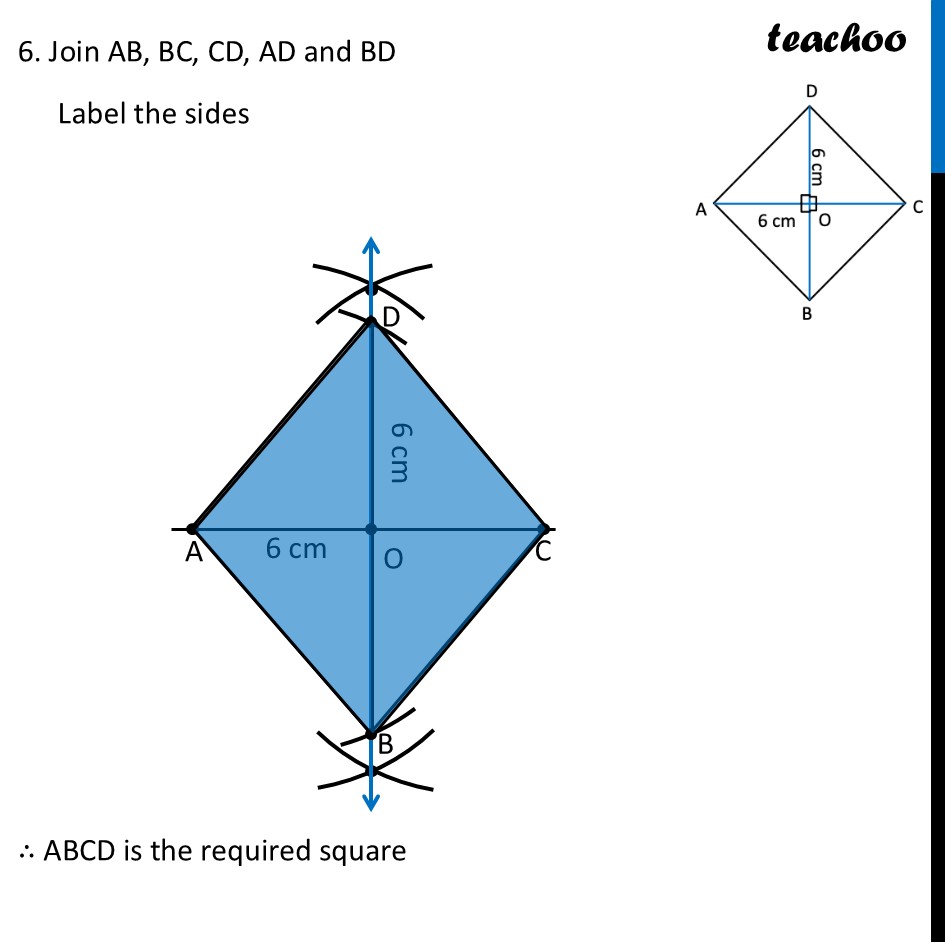
Question 6 Construct a square with diagonal 6 cm without using a protractor.For a square, both diagonals are equal Since diagonals are given, we make diagram such that diagonal is horizontal Now, In a square , Diagonals bisect each other at right angles ∴ OA = OC = 6/2 cm = 3 cm ∴ OD = OC = 6/2 cm = 3 cm To make AC ⊥ BD, we make a perpendicular bisector To construct it, we will first draw AC, then perpendicular bisector of AC Then, we will mark OD = 3 cm and OB = 3 cm on the perpendicular bisector. Let’s construct it step-by-step Steps of construction 1. Draw diagonal AC of length 6 cm 2. Drawing perpendicular bisector of AC With A as center, and radius more than half AC, draw an arc on top and bottom of AC Now with D as center, and same radius, draw an arc on top and bottom of AC 3. Mark points where arcs intersect on top and bottom of AC Join the points. So, the required line is the perpendicular bisector of AC Mark point O where perpendicular bisector intersects AC 4. Now, we will mark points D and B We know that OD = OB = 3 cm Taking 3 cm as radius, and O as center, draw an arc on top and bottom of AC Where arc intersects perpendicular bisector on top of AC is point D. And where it intersects perpendicular bisector on bottom of AC is point B 6. Join AB, BC, CD, AD and BD Label the sides ∴ ABCD is the required square