Constructing Regular Hexagon, Angle 60° and 6-pointed Star
Constructing Regular Hexagon, Angle 60° and 6-pointed Star
Last updated at February 6, 2026 by Teachoo









Transcript
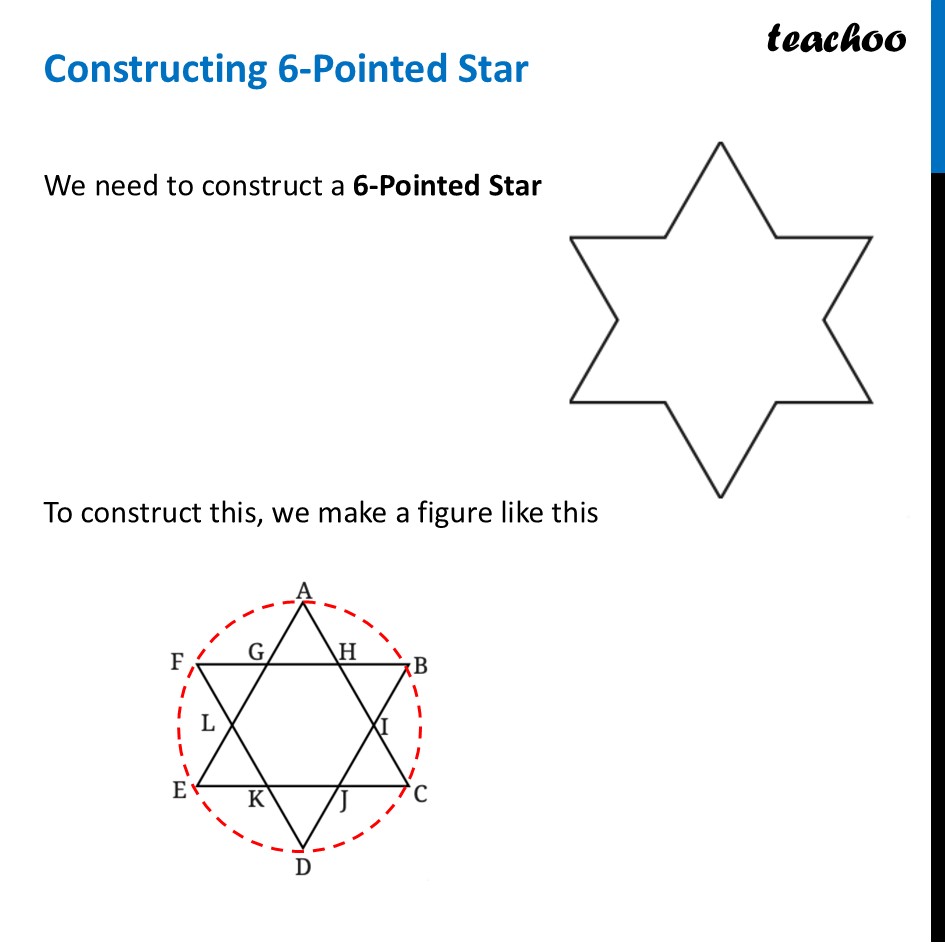
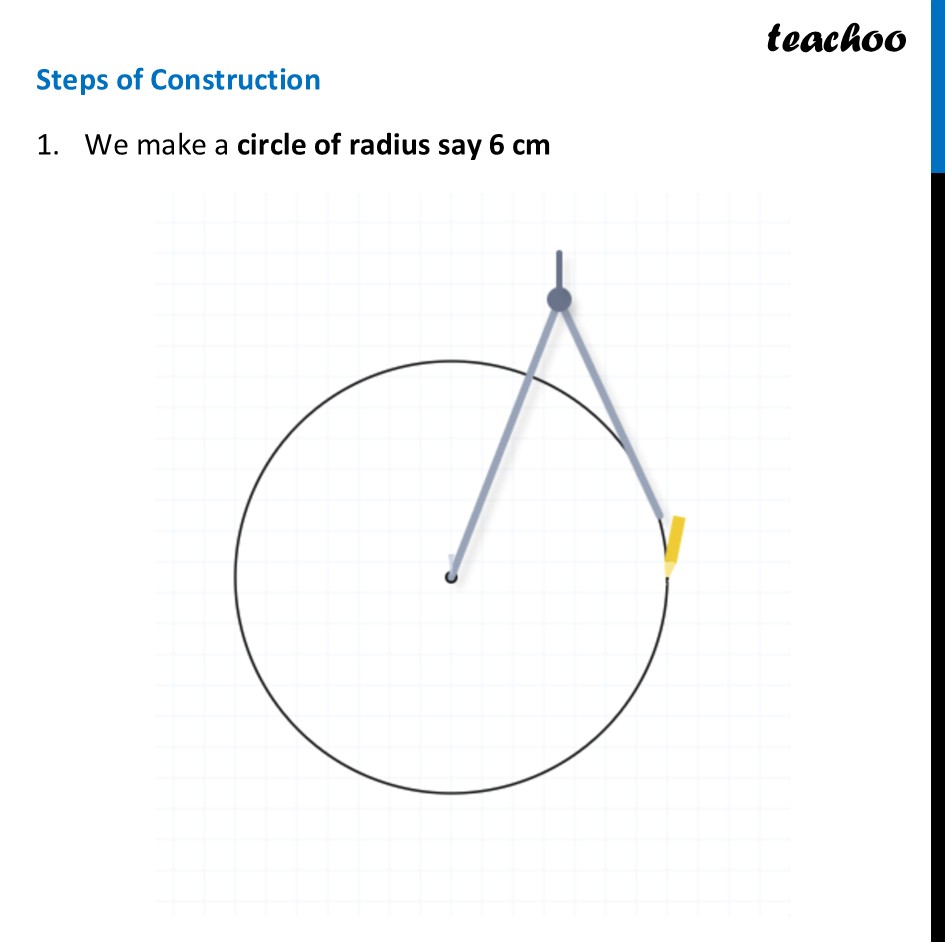
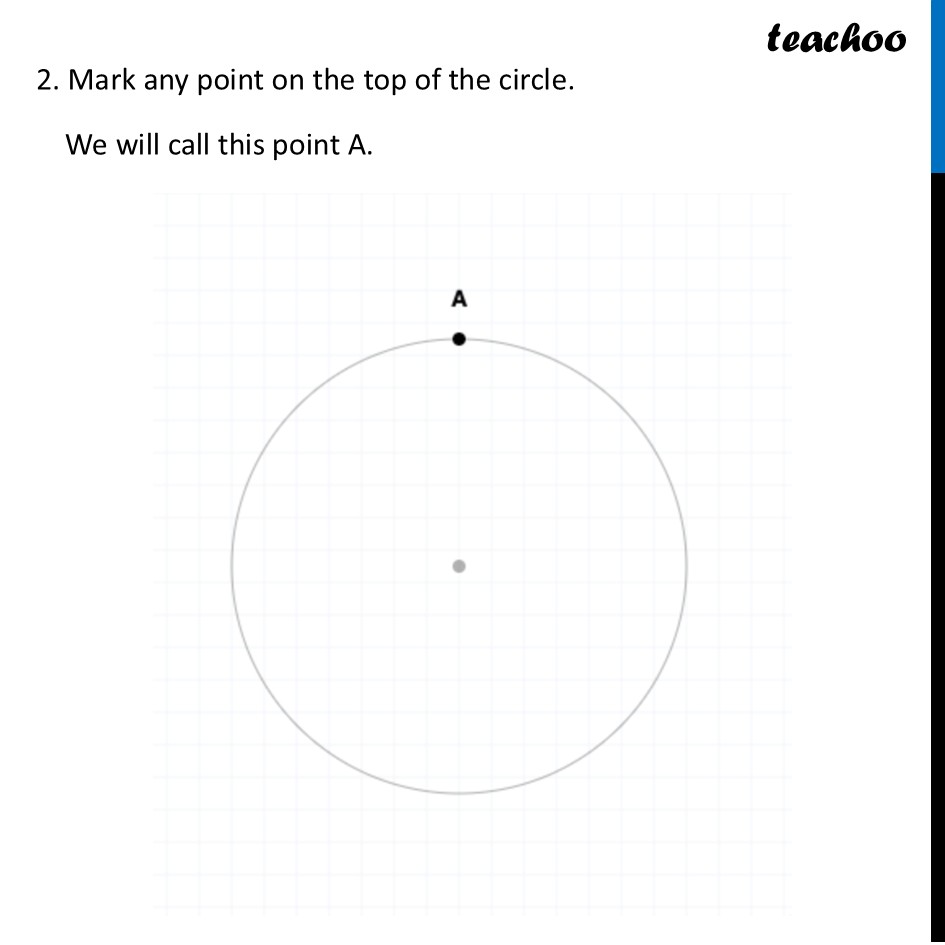
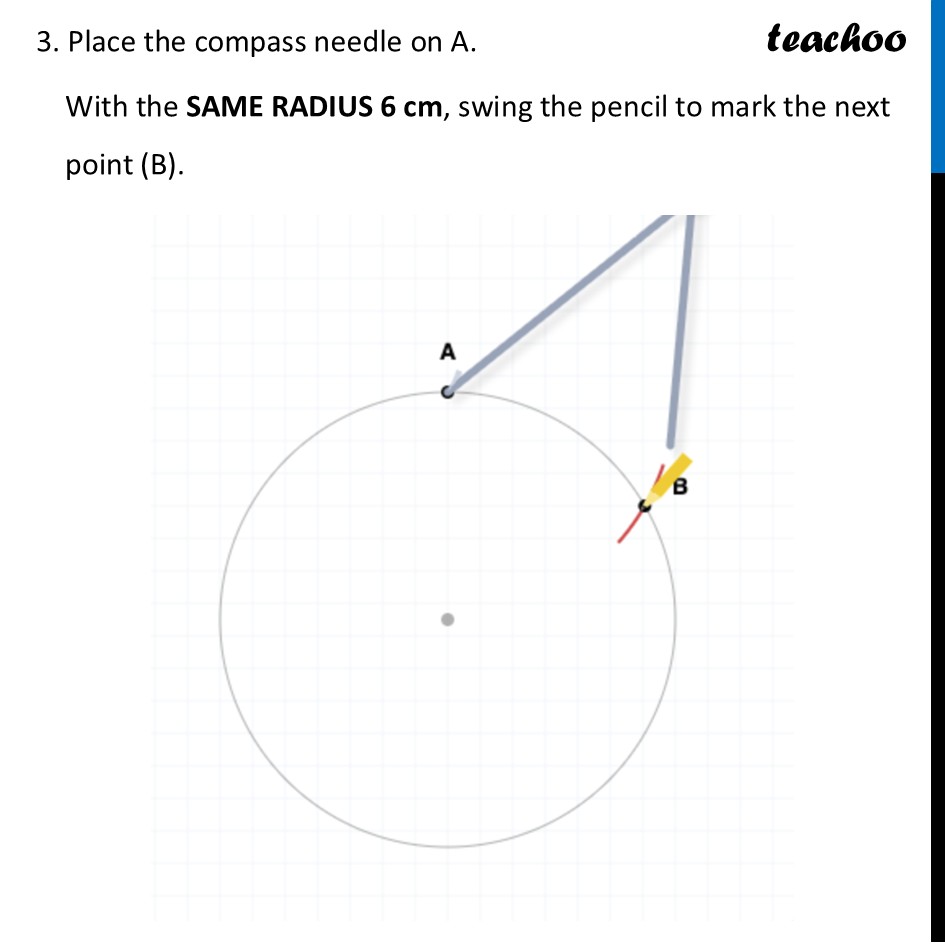
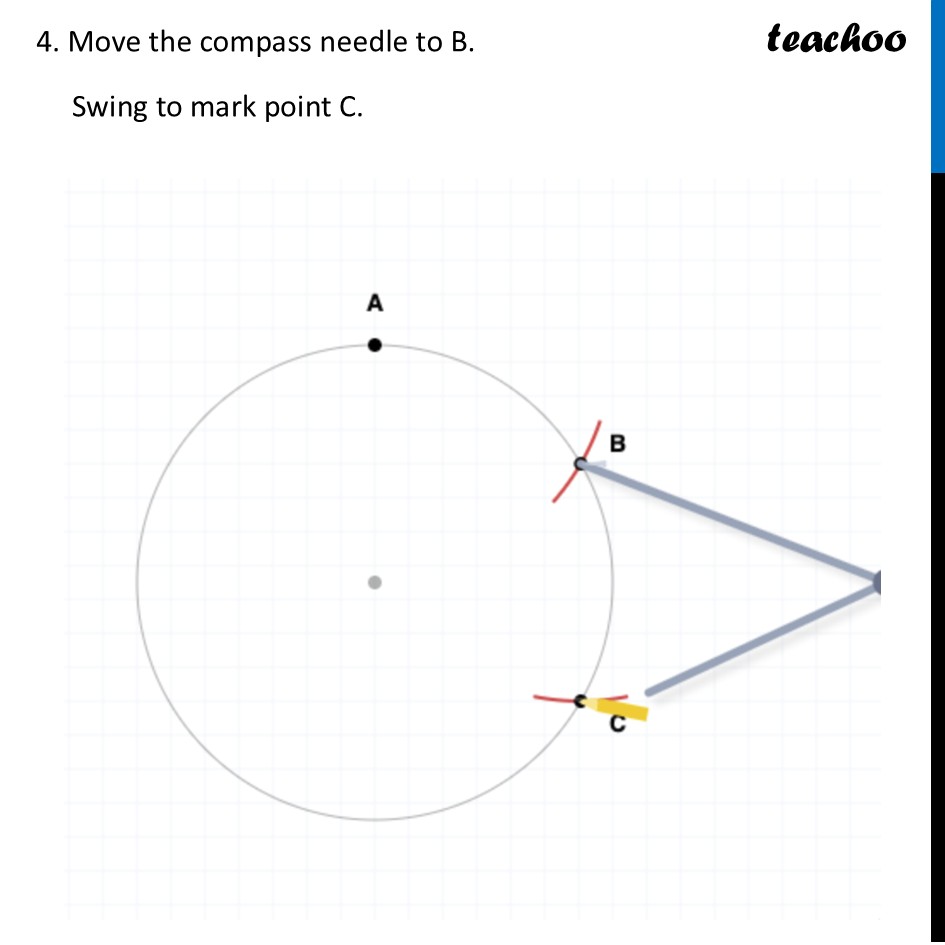
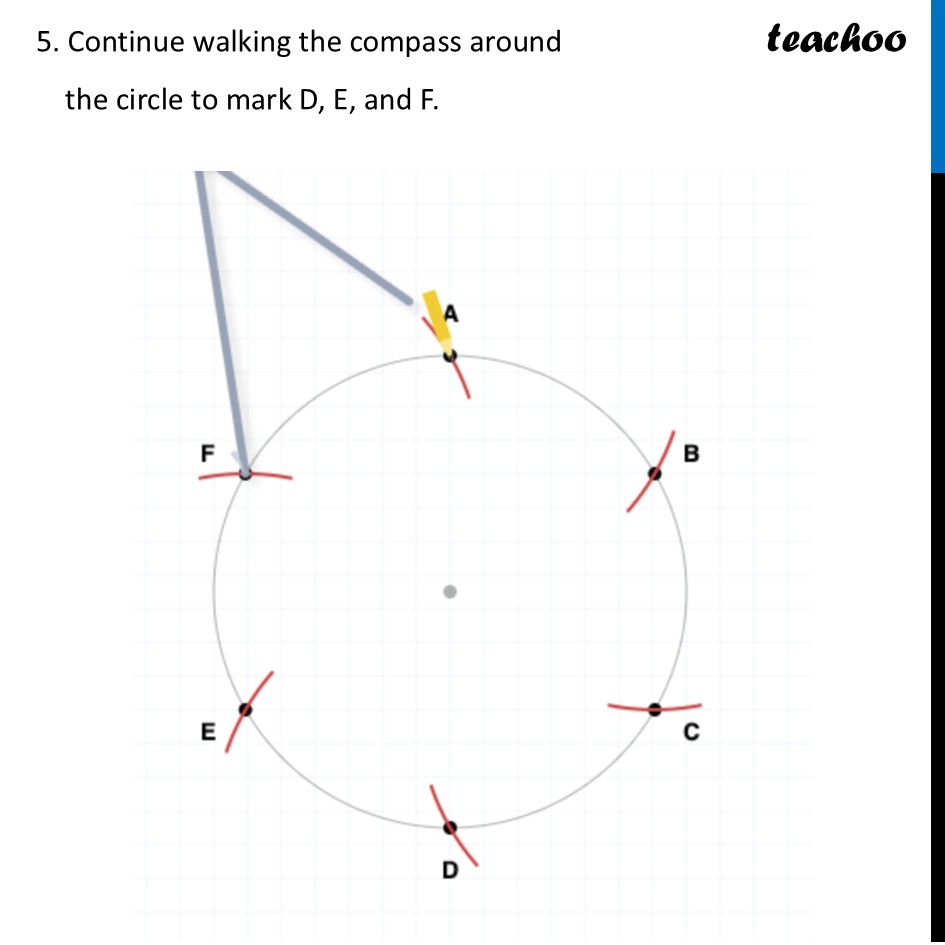
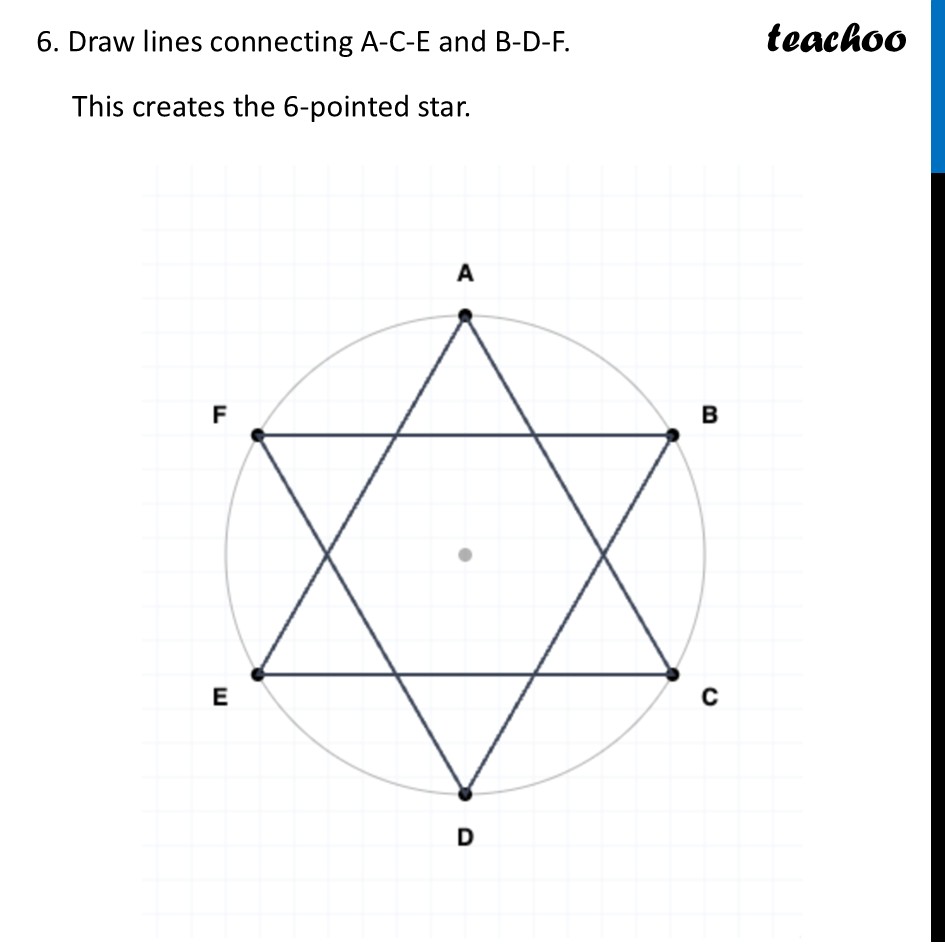
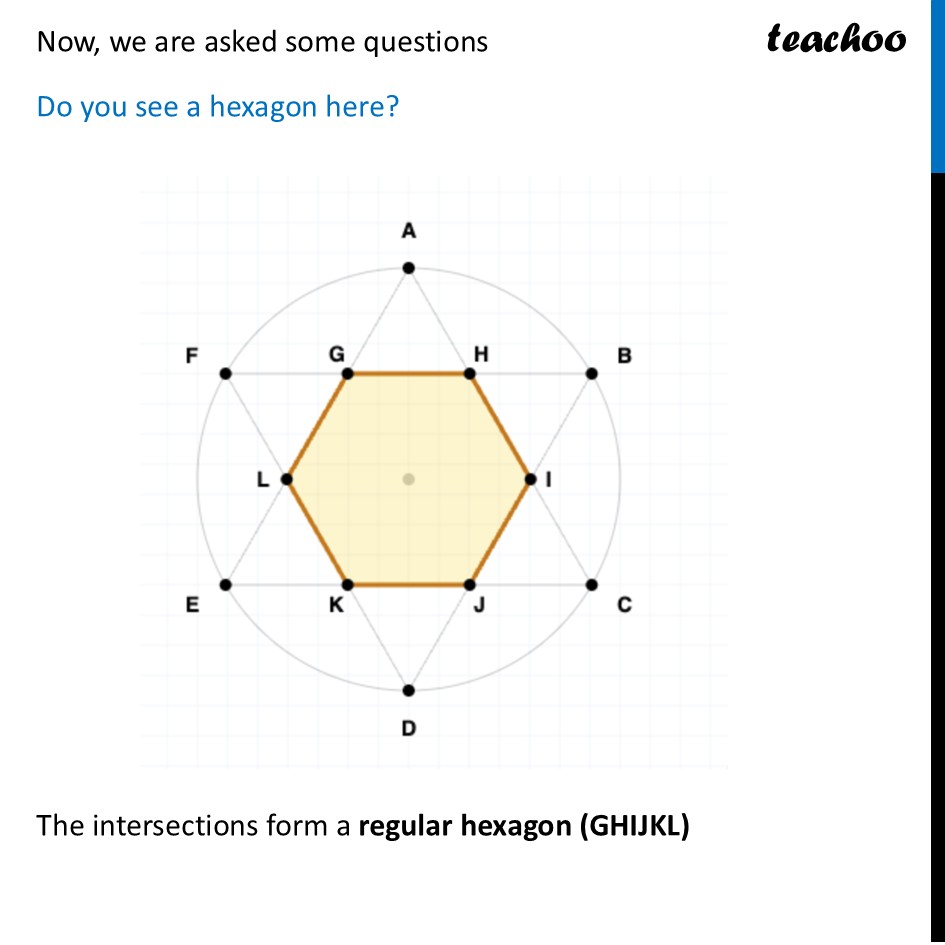
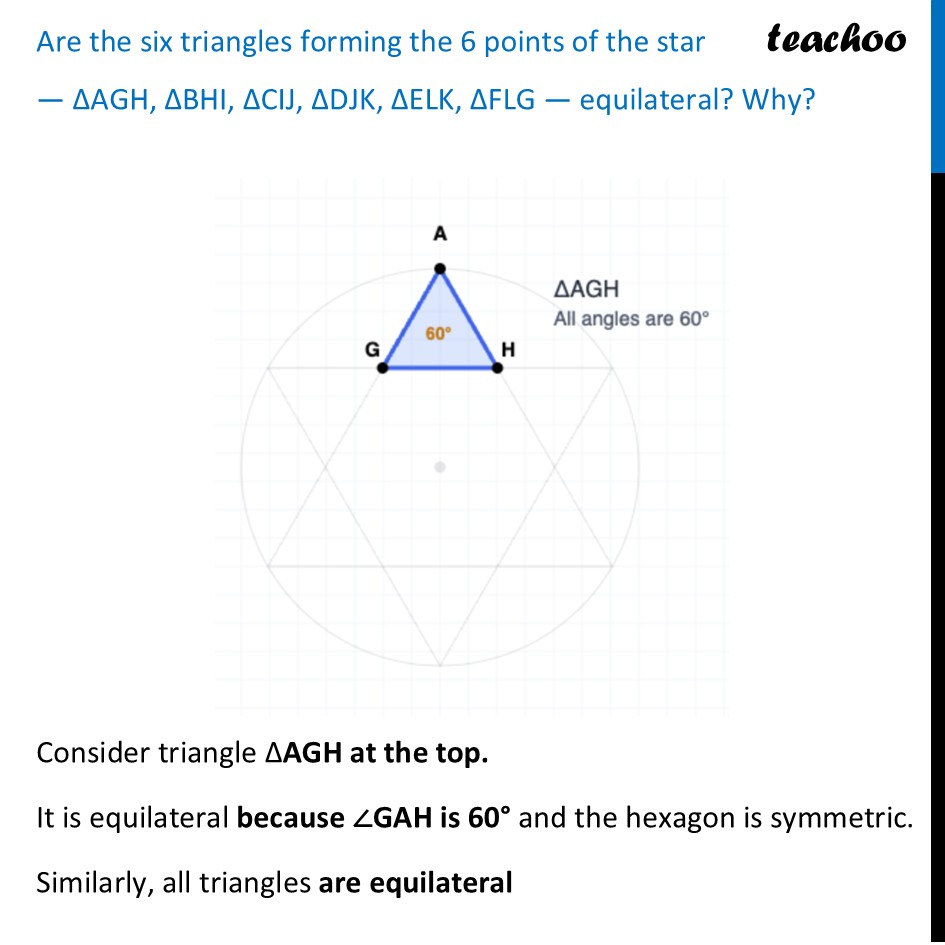
Constructing 6-Pointed StarWe need to construct a 6-Pointed Star To construct this, we make a figure like this Steps of Construction We make a circle of radius say 6 cm 2. Mark any point on the top of the circle. We will call this point A. 3. Place the compass needle on A. With the SAME RADIUS 6 cm, swing the pencil to mark the next point (B). 4. Move the compass needle to B. Swing to mark point C. 5. Continue walking the compass around the circle to mark D, E, and F. 6. Draw lines connecting A-C-E and B-D-F. This creates the 6-pointed star. Now, we are asked some questions Do you see a hexagon here? The intersections form a regular hexagon (GHIJKL) Are the six triangles forming the 6 points of the star — ∆AGH, ∆BHI, ∆CIJ, ∆DJK, ∆ELK, ∆FLG — equilateral? Why? Consider triangle ΔAGH at the top. It is equilateral because ∠GAH is 60° and the hexagon is symmetric. Similarly, all triangles are equilateral