Last updated at January 19, 2026 by Teachoo













Transcript
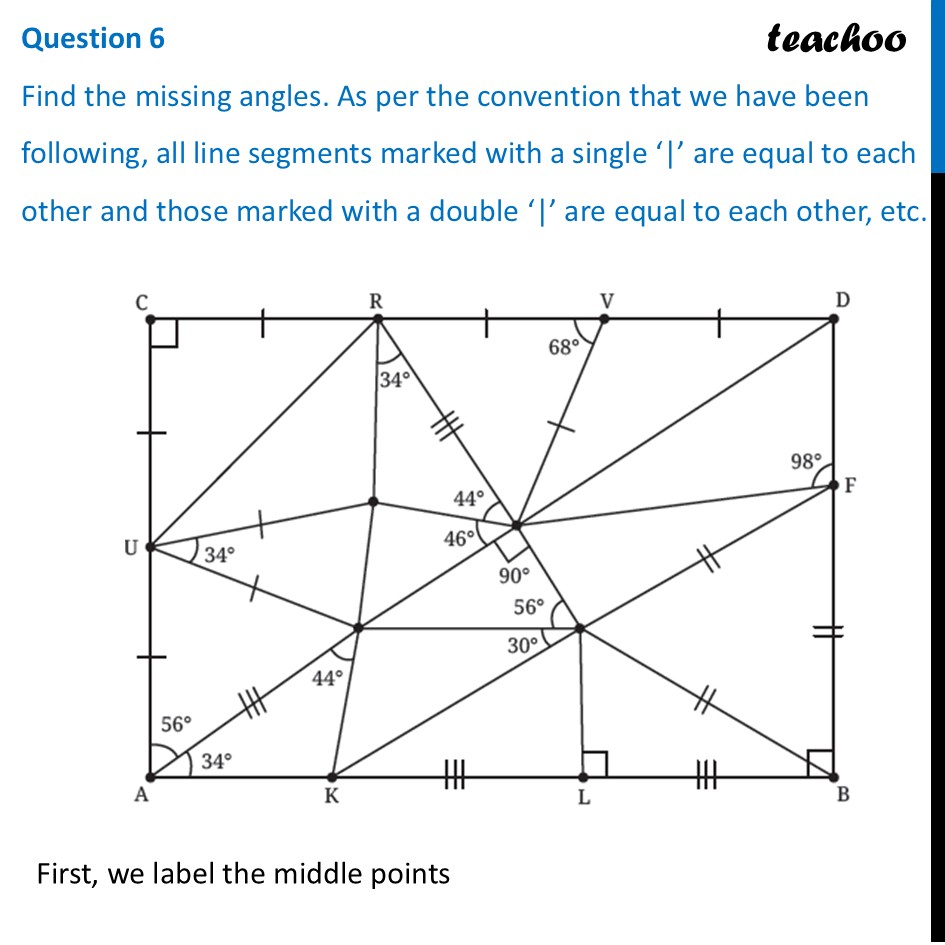
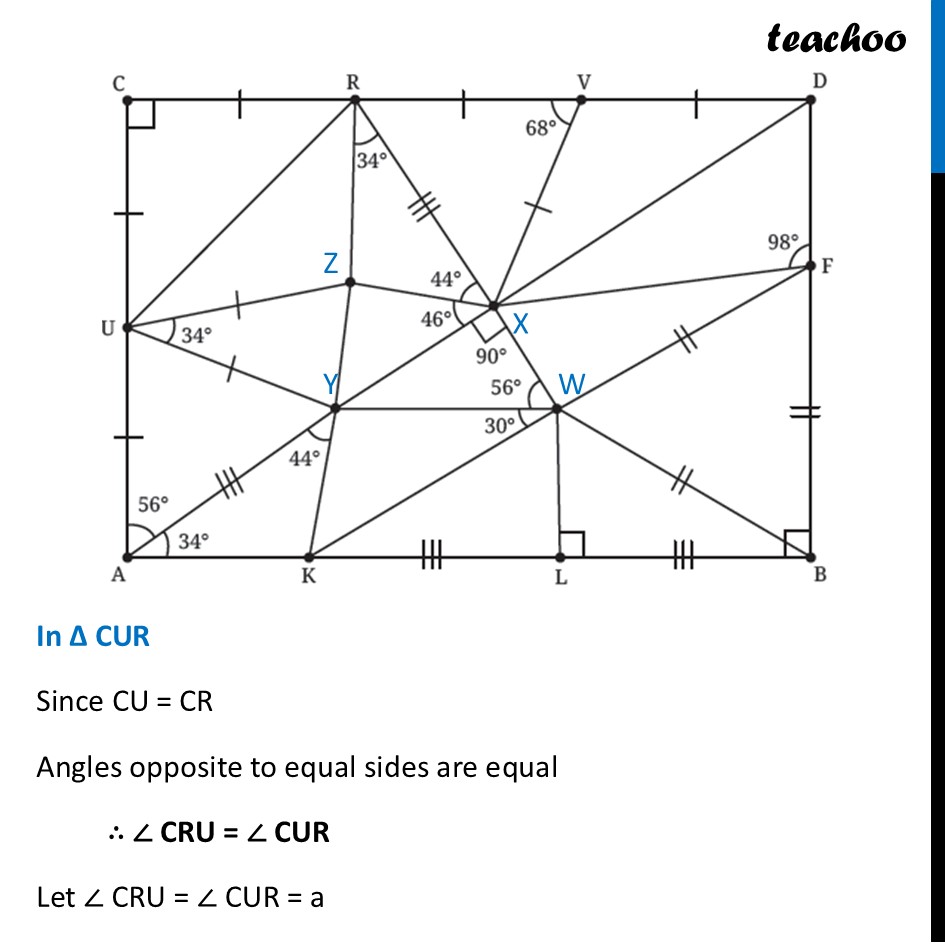
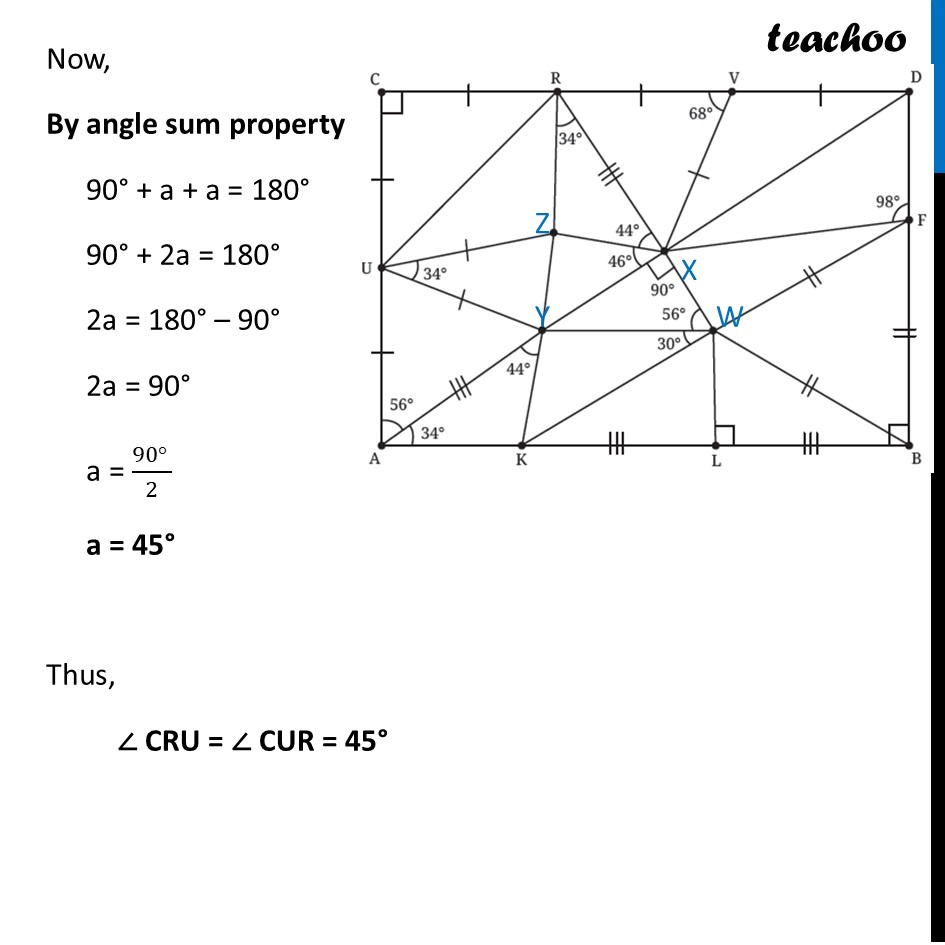
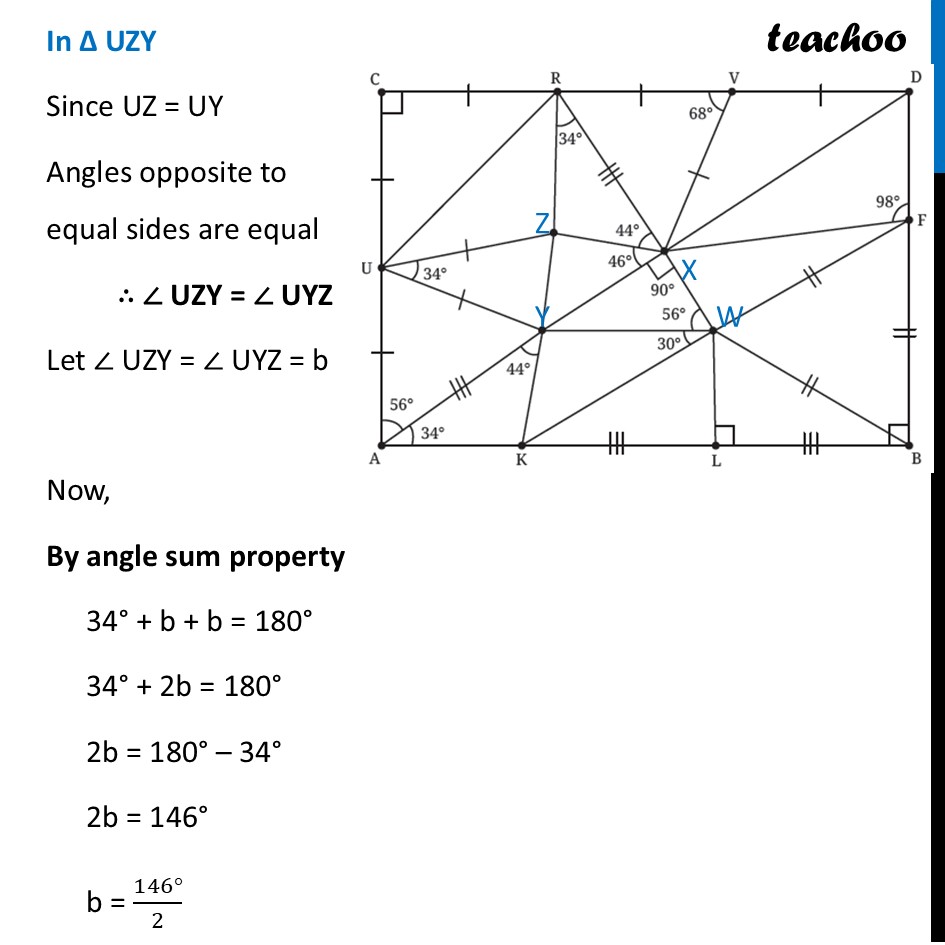
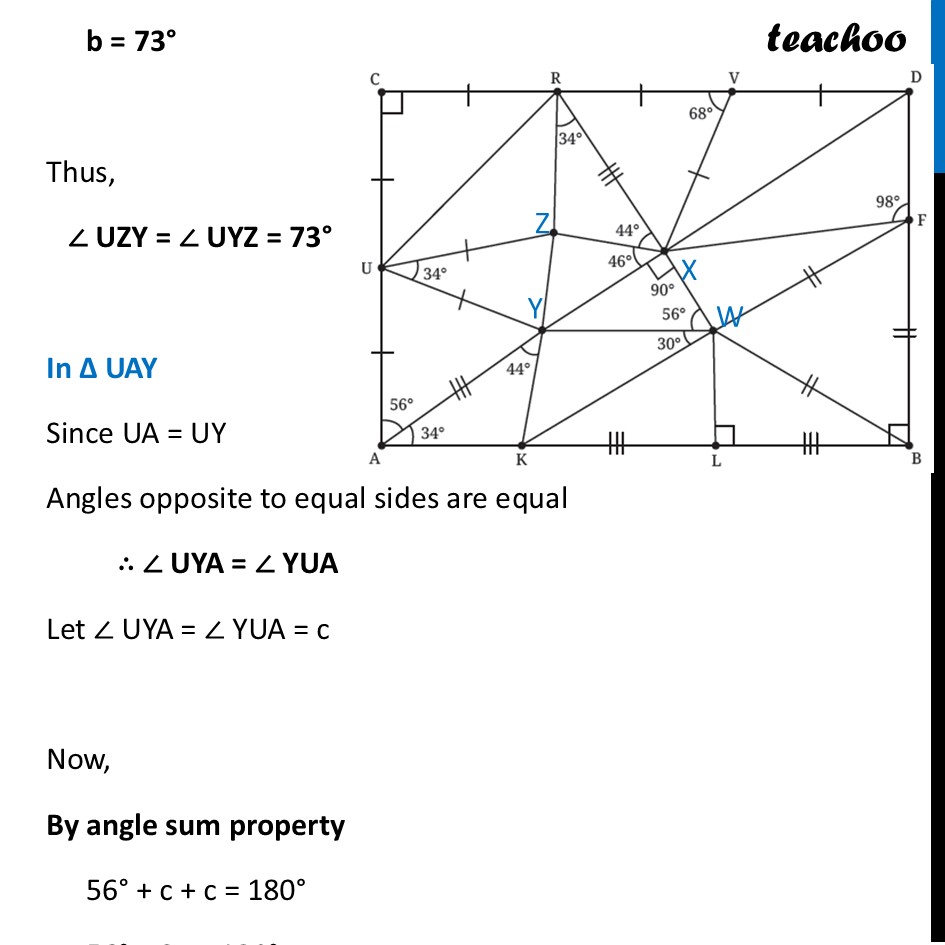
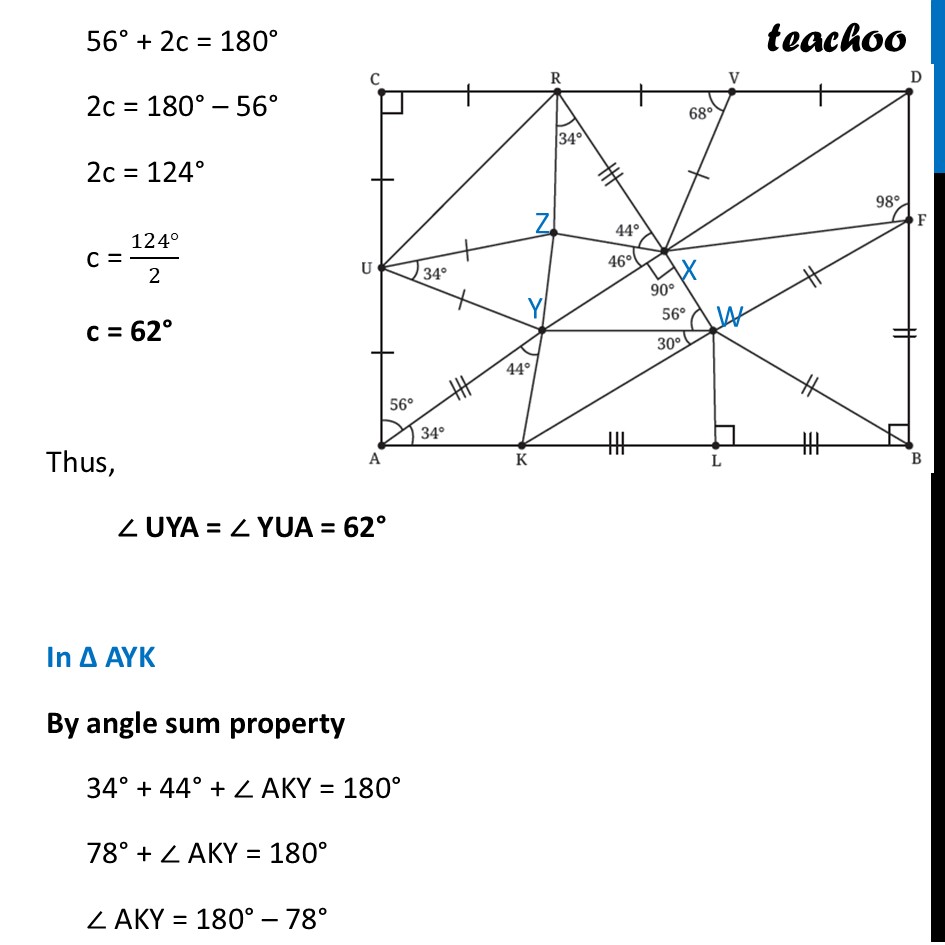
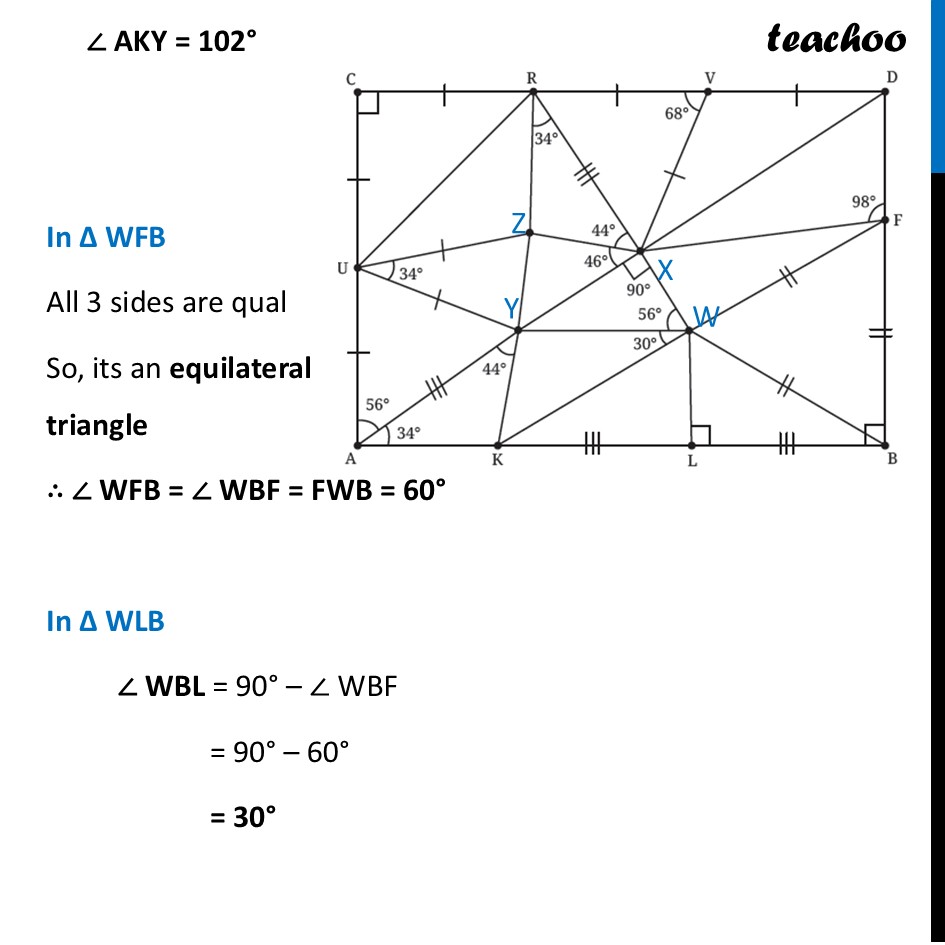
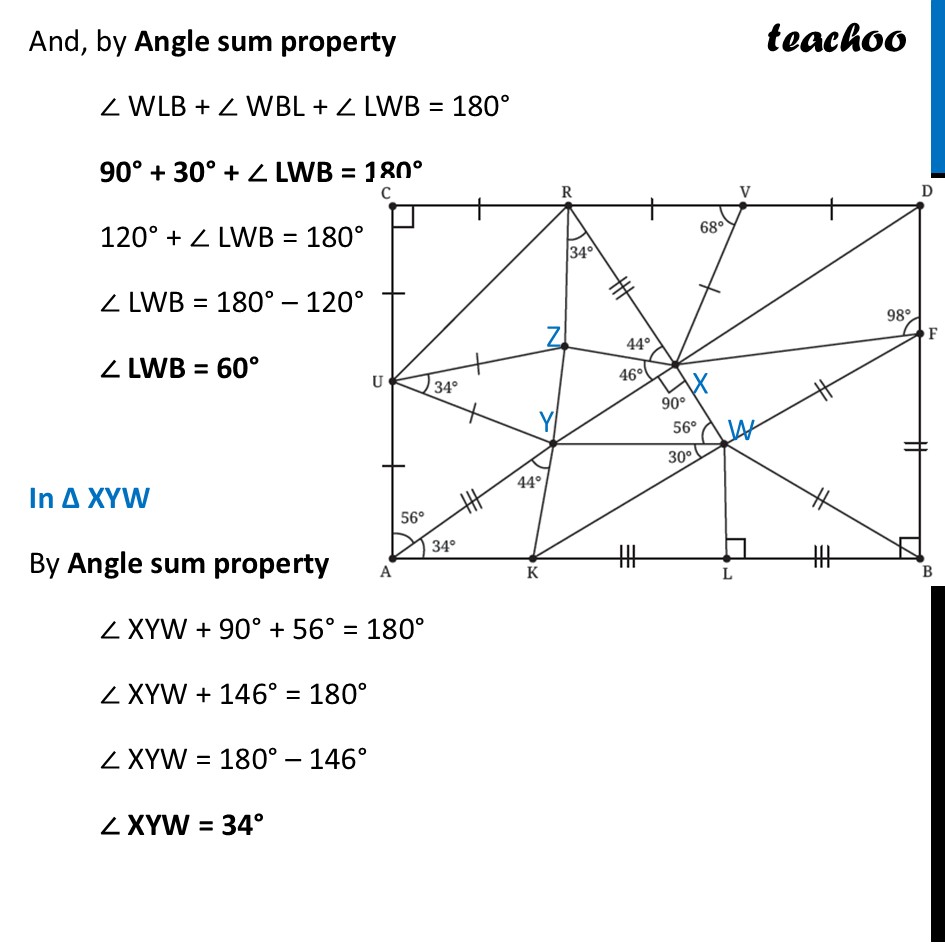
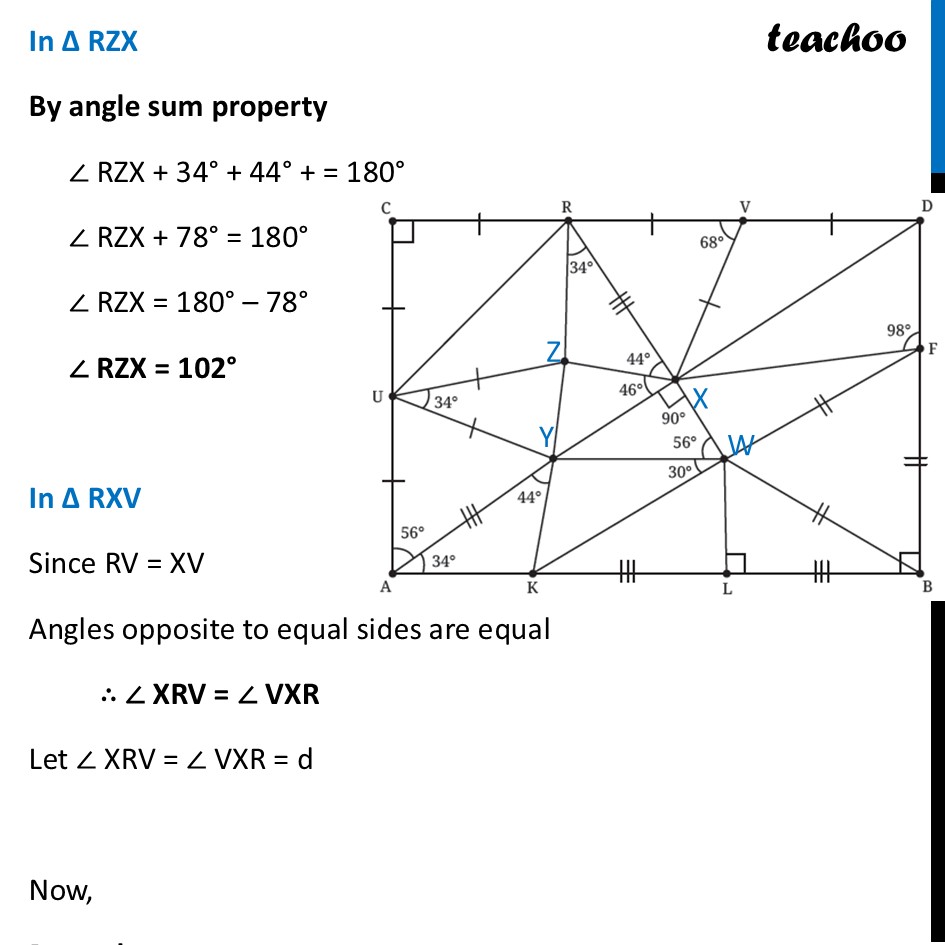
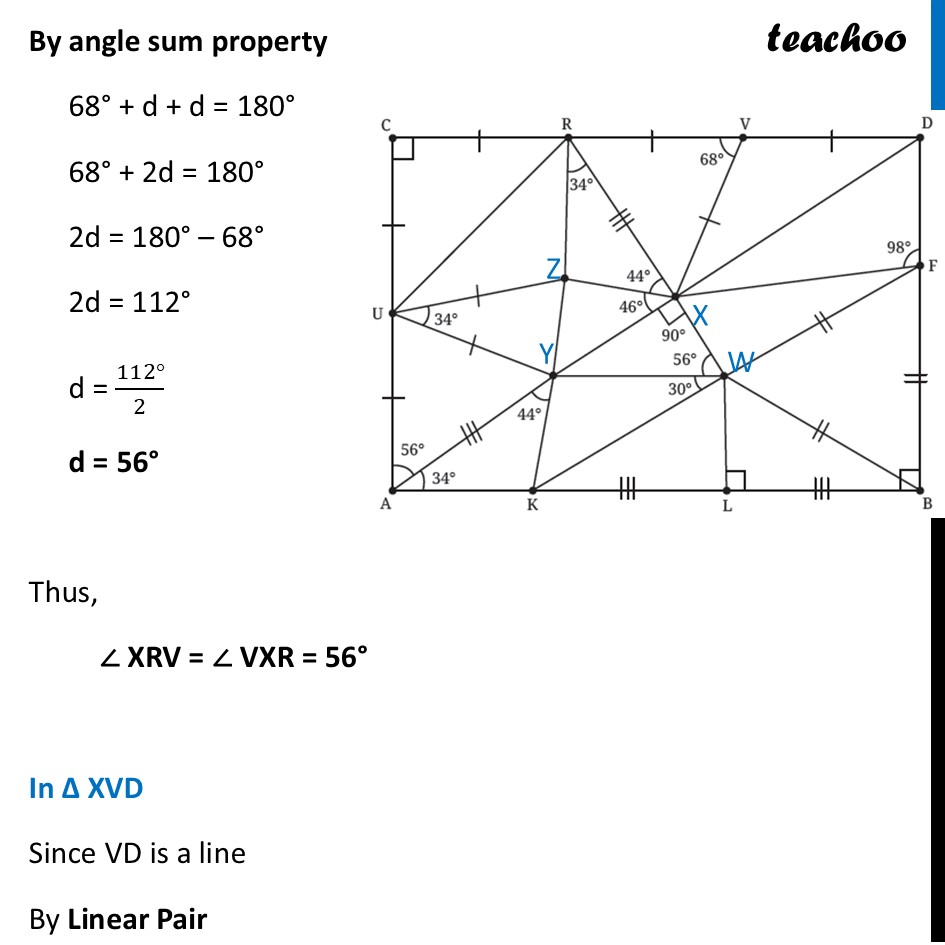
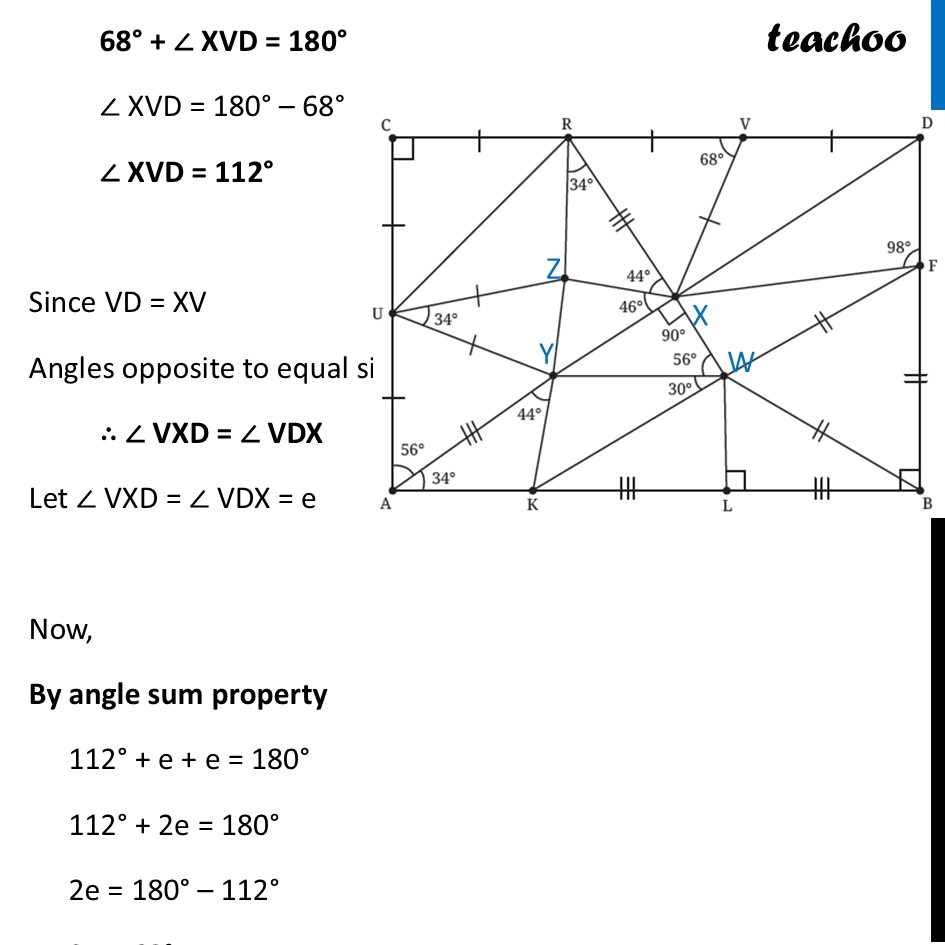
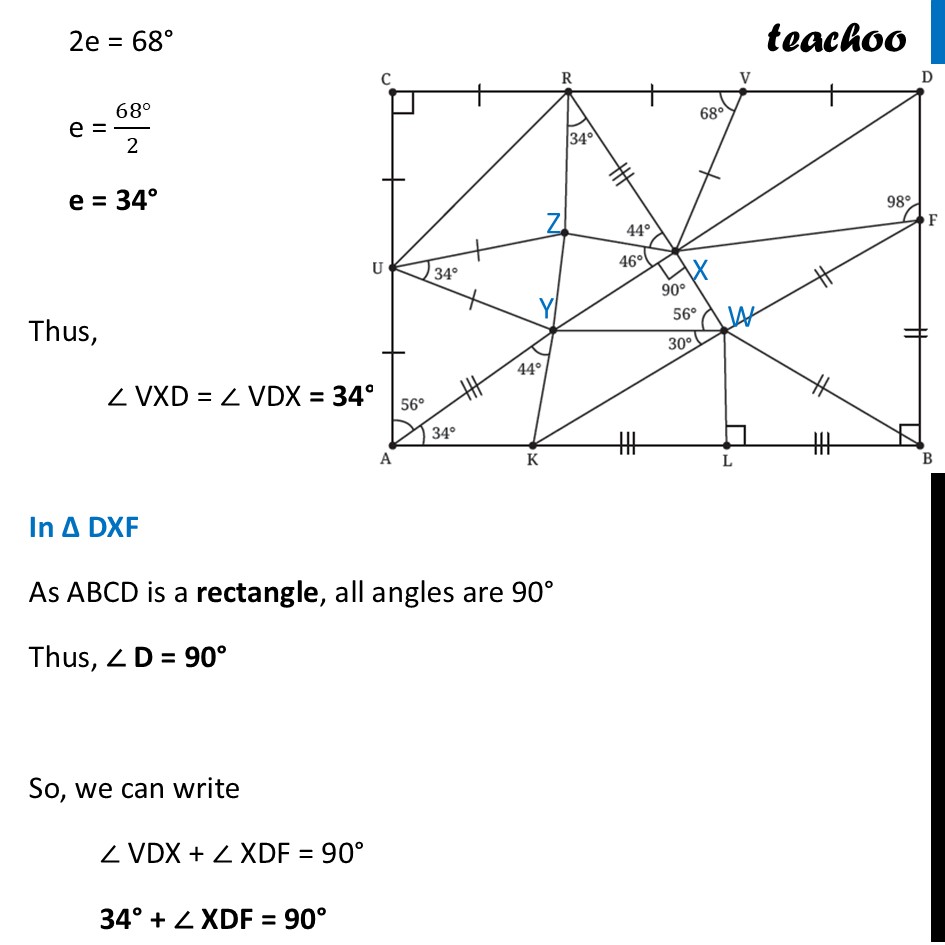
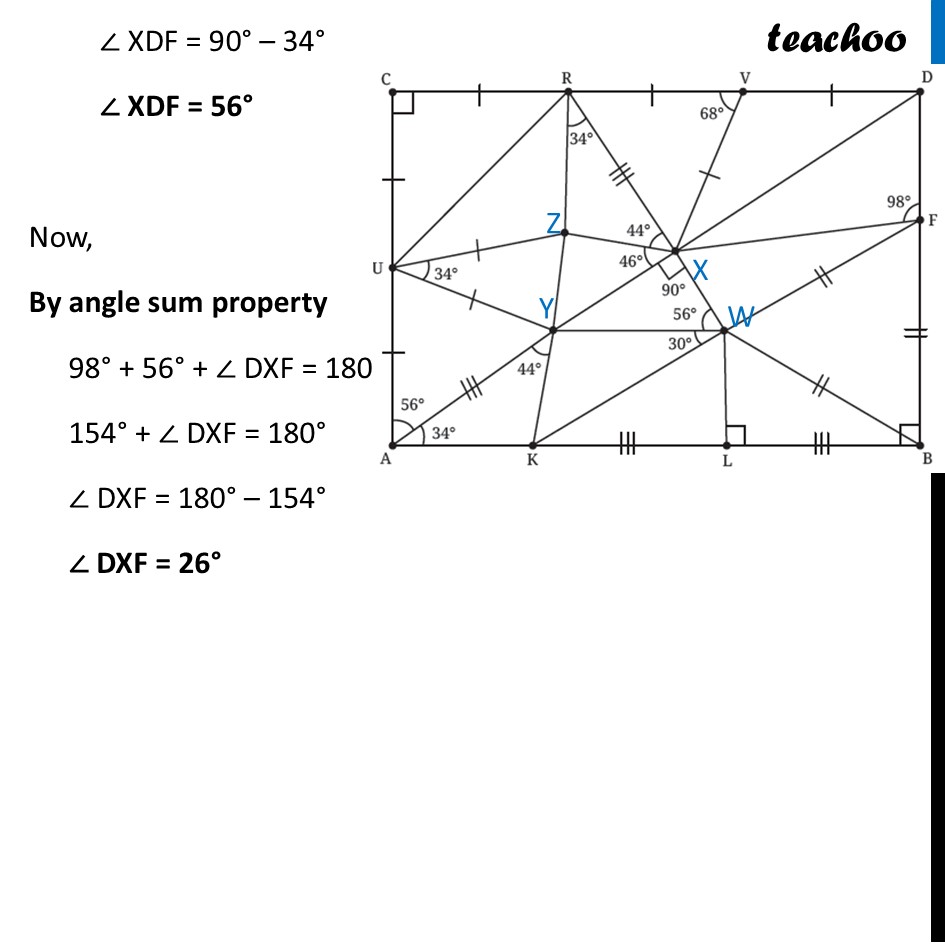
Question 6 Find the missing angles. As per the convention that we have been following, all line segments marked with a single ‘|’ are equal to each other and those marked with a double ‘|’ are equal to each other, etc.First, we label the middle points In ∆ CUR Since CU = CR Angles opposite to equal sides are equal ∴ ∠ CRU = ∠ CUR Let ∠ CRU = ∠ CUR = a Now, By angle sum property 90° + a + a = 180° 90° + 2a = 180° 2a = 180° – 90° 2a = 90° a = (90° )/2 a = 45° Thus, ∠ CRU = ∠ CUR = 45° In ∆ UZY Since UZ = UY Angles opposite to equal sides are equal ∴ ∠ UZY = ∠ UYZ Let ∠ UZY = ∠ UYZ = b Now, By angle sum property 34° + b + b = 180° 34° + 2b = 180° 2b = 180° – 34° 2b = 146° b = (146°)/2 b = 73° Thus, ∠ UZY = ∠ UYZ = 73° In ∆ UAY Since UA = UY Angles opposite to equal sides are equal ∴ ∠ UYA = ∠ YUA Let ∠ UYA = ∠ YUA = c Now, By angle sum property 56° + c + c = 180° 56° + 2c = 180° 2c = 180° – 56° 2c = 124° c = (124°)/2 c = 62° Thus, ∠ UYA = ∠ YUA = 62° In ∆ AYK By angle sum property 34° + 44° + ∠ AKY = 180° 78° + ∠ AKY = 180° ∠ AKY = 180° – 78° ∠ AKY = 102° ∠ AKY = 102° In ∆ WFB All 3 sides are qual So, its an equilateral triangle ∴ ∠ WFB = ∠ WBF = FWB = 60° In ∆ WLB ∠ WBL = 90° – ∠ WBF = 90° – 60° = 30° And, by Angle sum property ∠ WLB + ∠ WBL + ∠ LWB = 180° 90° + 30° + ∠ LWB = 180° 120° + ∠ LWB = 180° ∠ LWB = 180° – 120° ∠ LWB = 60° In ∆ XYW By Angle sum property ∠ XYW + 90° + 56° = 180° ∠ XYW + 146° = 180° ∠ XYW = 180° – 146° ∠ XYW = 34° In ∆ RZX By angle sum property ∠ RZX + 34° + 44° + = 180° ∠ RZX + 78° = 180° ∠ RZX = 180° – 78° ∠ RZX = 102° In ∆ RXV Since RV = XV Angles opposite to equal sides are equal ∴ ∠ XRV = ∠ VXR Let ∠ XRV = ∠ VXR = d Now, By angle sum property 68° + d + d = 180° 68° + 2d = 180° 2d = 180° – 68° 2d = 112° d = (112°)/2 d = 56° Thus, ∠ XRV = ∠ VXR = 56° In ∆ XVD Since VD is a line By Linear Pair 68° + ∠ XVD = 180° ∠ XVD = 180° – 68° ∠ XVD = 112° Since VD = XV Angles opposite to equal sides are equal ∴ ∠ VXD = ∠ VDX Let ∠ VXD = ∠ VDX = e Now, By angle sum property 112° + e + e = 180° 112° + 2e = 180° 2e = 180° – 112° 2e = 68° e = (68°)/2 e = 34° In ∆ DXF As ABCD is a rectangle, all angles are 90° Thus, ∠ D = 90° So, we can write ∠ VDX + ∠ XDF = 90° 34° + ∠ XDF = 90° ∠ XDF = 90° – 34° ∠ XDF = 56° Now, By angle sum property 98° + 56° + ∠ DXF = 180° 154° + ∠ DXF = 180° ∠ DXF = 180° – 154° ∠ DXF = 26°