Last updated at January 19, 2026 by Teachoo





Transcript
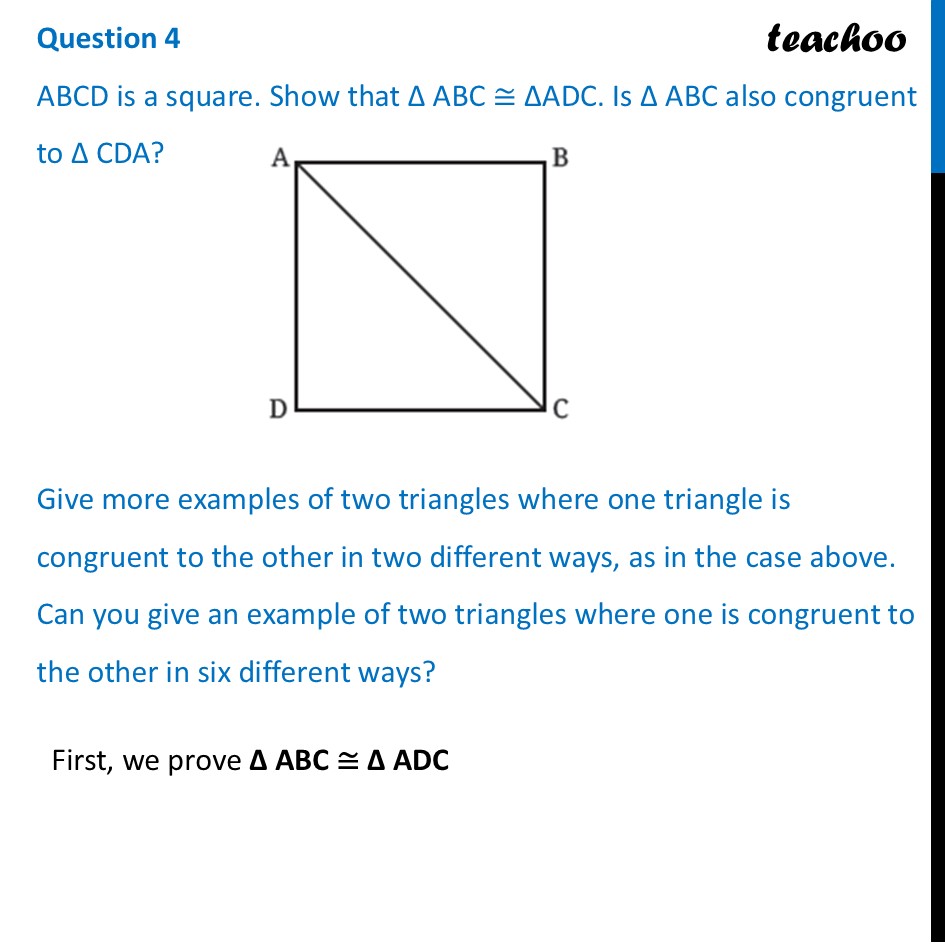
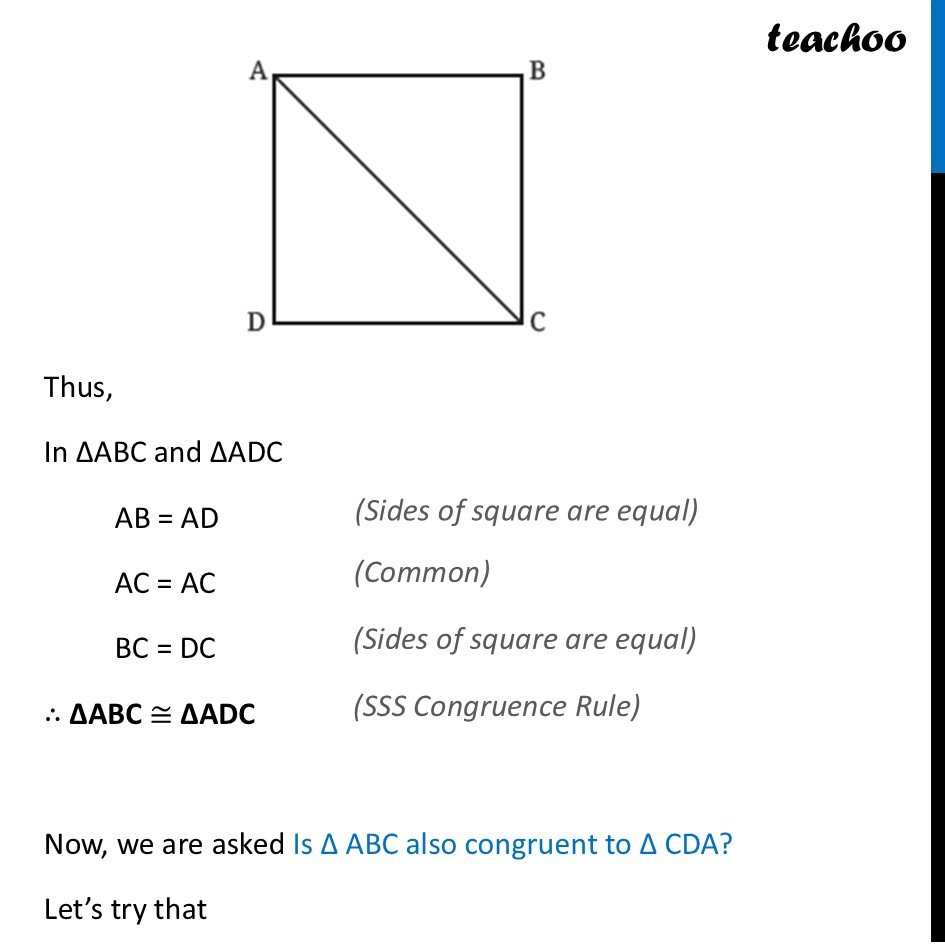
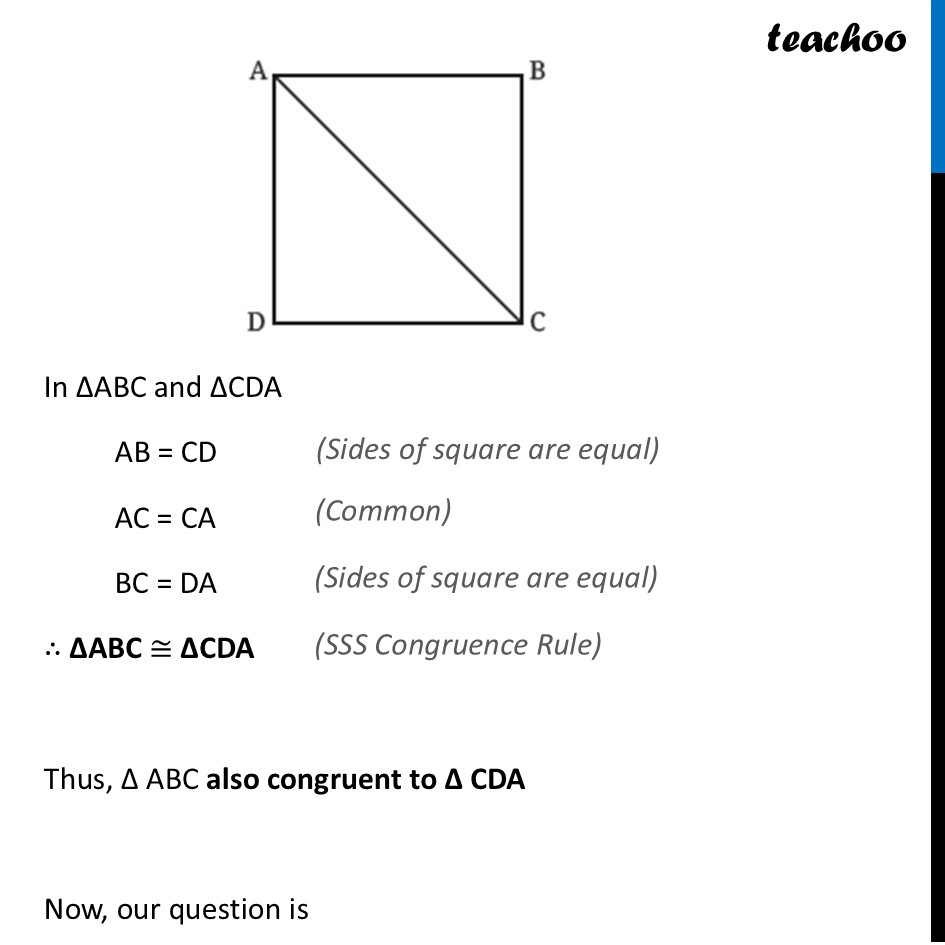
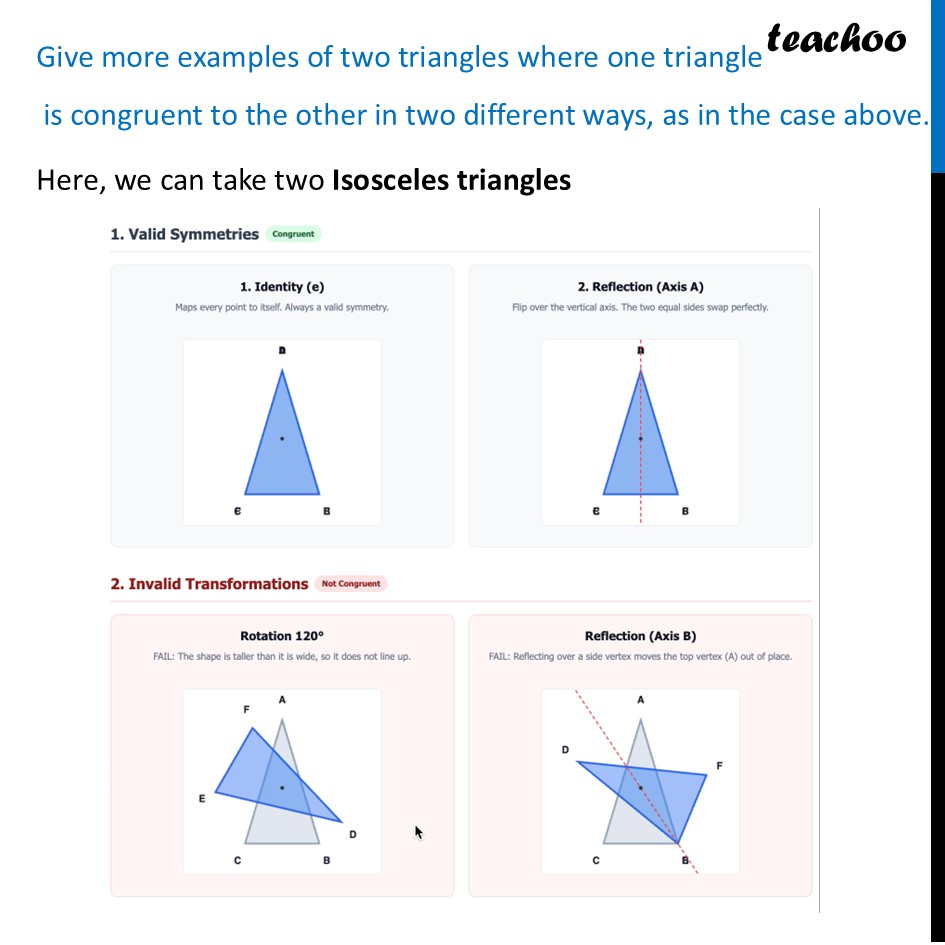
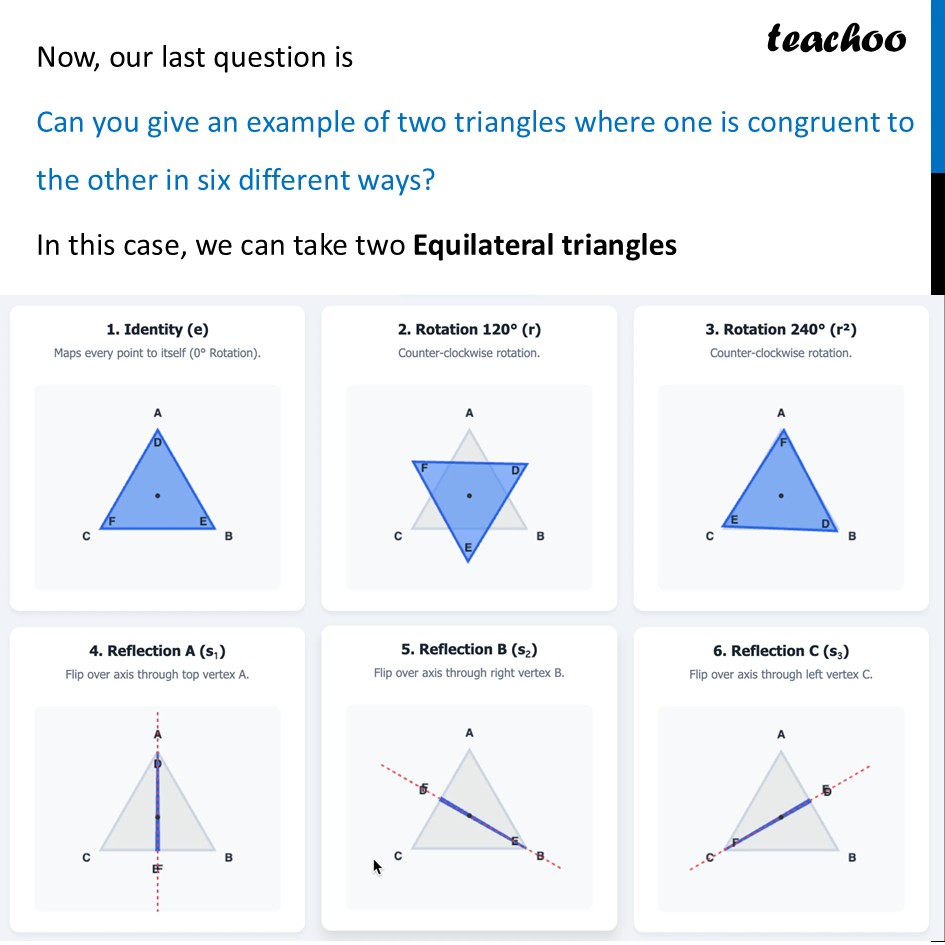
Question 4 ABCD is a square. Show that Δ ABC ≅ ΔADC. Is Δ ABC also congruent to Δ CDA? Give more examples of two triangles where one triangle is congruent to the other in two different ways, as in the case above. Can you give an example of two triangles where one is congruent to the other in six different ways?First, we prove ∆ ABC ≅ ∆ ADC Thus, In ∆ABC and ∆ADC AB = AD AC = AC BC = DC ∴ ∆ABC ≅ ∆ADC Now, we are asked Is Δ ABC also congruent to Δ CDA? Let’s try that In ∆ABC and ∆CDA AB = CD AC = CA BC = DA ∴ ∆ABC ≅ ∆CDA Thus, Δ ABC also congruent to Δ CDA Now, our question is Give more examples of two triangles where one triangle is congruent to the other in two different ways, as in the case above. Here, we can take two Isosceles triangles Valid Symmetries Congruent Identity (e) Maps every point to itself. Always a vald symmetry. 2. Invalid Transformations Nat Congruent 2. Reflection (Axis A) Filp over the vertical aus. The two equal sides smap perlectly. Rotation 120* FAIL: The shape is taller than it is wide, so it does not line up. Reflection (Axis B) FAIL: Raflecting over a side verter moves the top vertos (A) out of place.Now, our last question is Can you give an example of two triangles where one is congruent to the other in six different ways? In this case, we can take two Equilateral triangles Identity (e) Maps every point to itself ( Rotation). 4. Reflection Flip over axis through top vertex A. 2. Rotation (r) Counter-clockwise rotation. 5. Reflection B ( ) Flip over axis through right vertex B. 3. Rotation ( ) Counter-clockwise rotation. 6. Reflection Flip over axis through left vertex C .