![[Maths] AAS Congruency (Measuring Two Angles and a Non-Included Side) - Other Congruencies](https://cdn.teachoo.com/3e9d43ef-ae27-418c-8867-267ca492e85d/slide90.jpg)


Last updated at January 19, 2026 by Teachoo
![[Maths] AAS Congruency (Measuring Two Angles and a Non-Included Side) - Other Congruencies](https://cdn.teachoo.com/3e9d43ef-ae27-418c-8867-267ca492e85d/slide90.jpg)



Transcript
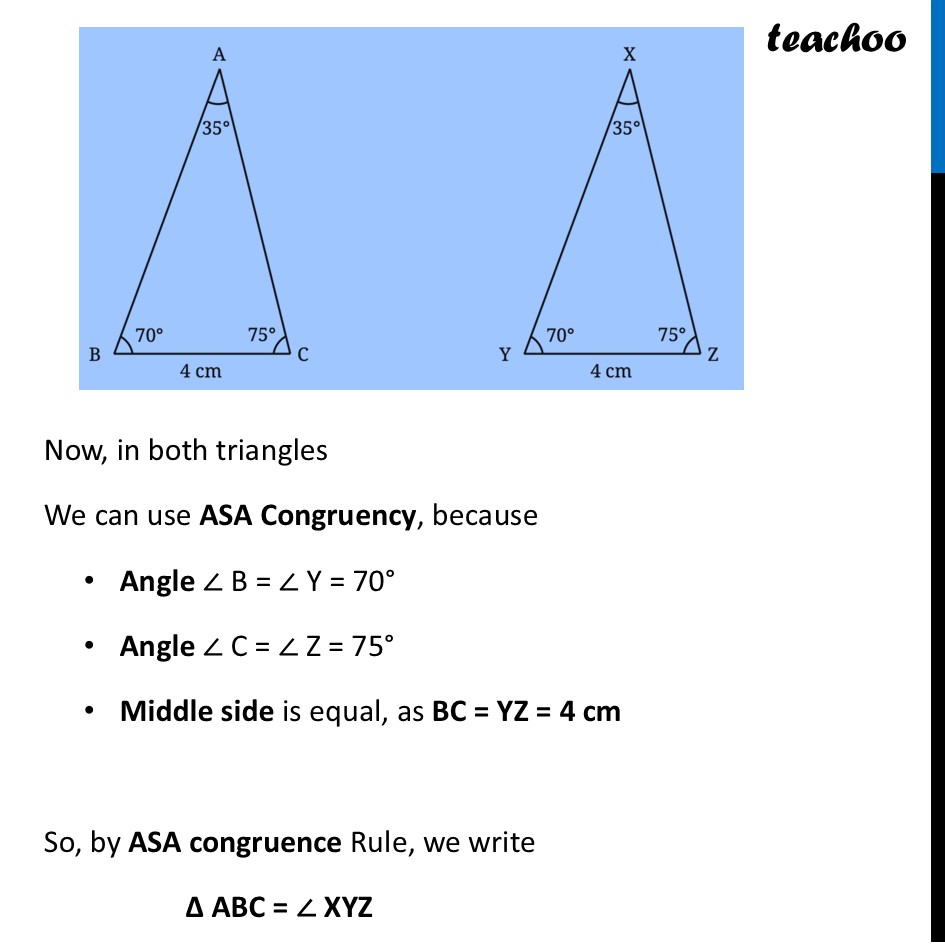
AAS Congruency (Measuring Two Angles and a Non-Included Side)We try triangles where two angles and a non-included side are equal. Our situation now is The following triangles ΔABC and ΔXYZ are such that ∠A = ∠X = 35°, ∠C = ∠Z = 75°, and BC = YZ = 4 cm. Are the triangles congruent? Give a reason. Let’s first draw the diagram We use Angle sum property to find the 3rd angle in each case We know that Sum of Angles in a triangle is 180° So, our figures now become In ∆ ABC ∠ A + ∠ B + ∠ C = 180° Putting values 35° + ∠ B + 75° = 180° ∠ B + (75° + 35°) = 180° ∠ B + 110° = 180° ∠ B = 180° – 110° ∠ B = 70° In ∆ XYZ ∠ X + ∠ Y + ∠ Z = 180° Putting values 35° + ∠ Y + 75° = 180° ∠ Y + (75° + 35°) = 180° ∠ Y + 110° = 180° ∠ Y = 180° – 110° ∠ Y = 70° Now, in both triangles We can use ASA Congruency, because Angle ∠ B = ∠ Y = 70° Angle ∠ C = ∠ Z = 75° Middle side is equal, as BC = YZ = 4 cm So, by ASA congruence Rule, we write ∆ ABC = ∠ XYZ So, all triangles with these measurements are congruent Thus, we can conclude When two angles and the non-included side of two triangles are equal, the two triangles are congruent. This is referred to as the AAS (Angle Angle Side) condition for congruence.