

Miscellaneous
Misc 1 (ii)
Misc 1 (iii) Important
Misc 2 (i)
Misc 2 (ii) Important
Misc 2 (iii)
Misc 2 (iv) Important
Misc 3 Important
Misc 4
Misc 5 Important You are here
Misc 6
Misc 7 Important
Misc 8 Important
Misc 9
Misc 10 Important
Misc 11
Misc 12 Important
Misc 13 (MCQ)
Misc 14 (MCQ) Important
Misc 15 (MCQ)
Question 1 Deleted for CBSE Board 2024 Exams
Question 2 Important Deleted for CBSE Board 2024 Exams
Question 3 Important Deleted for CBSE Board 2024 Exams
Last updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo




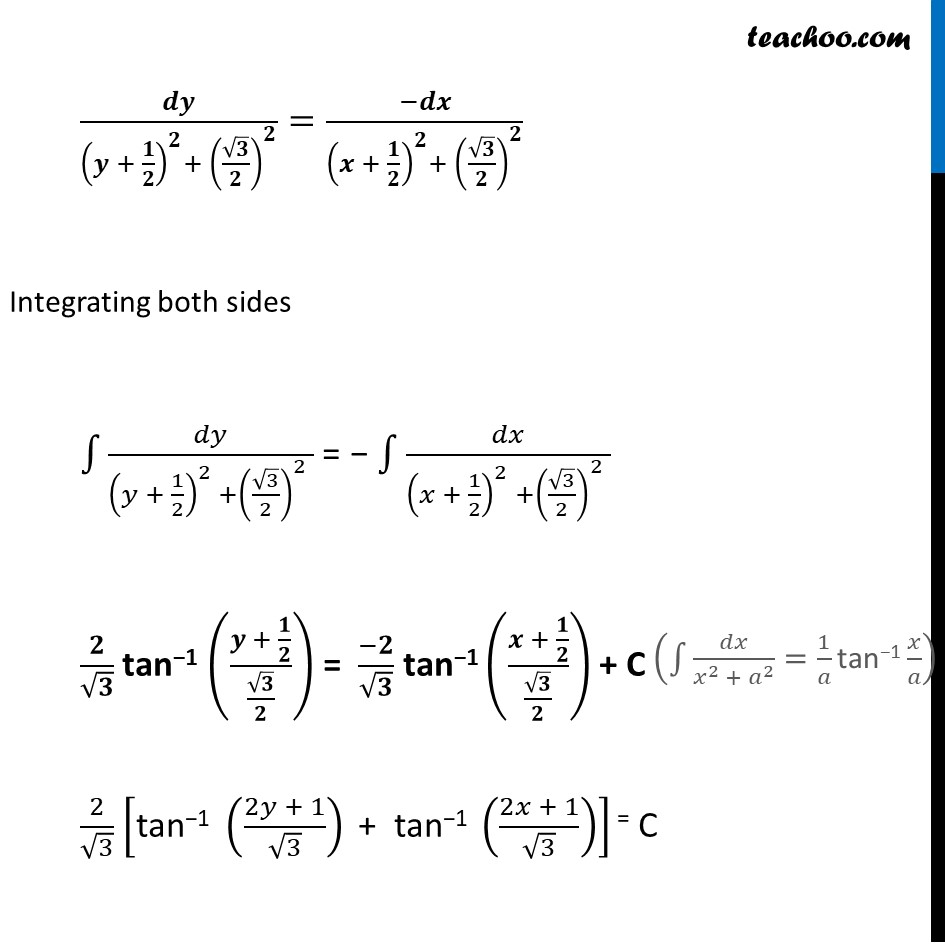
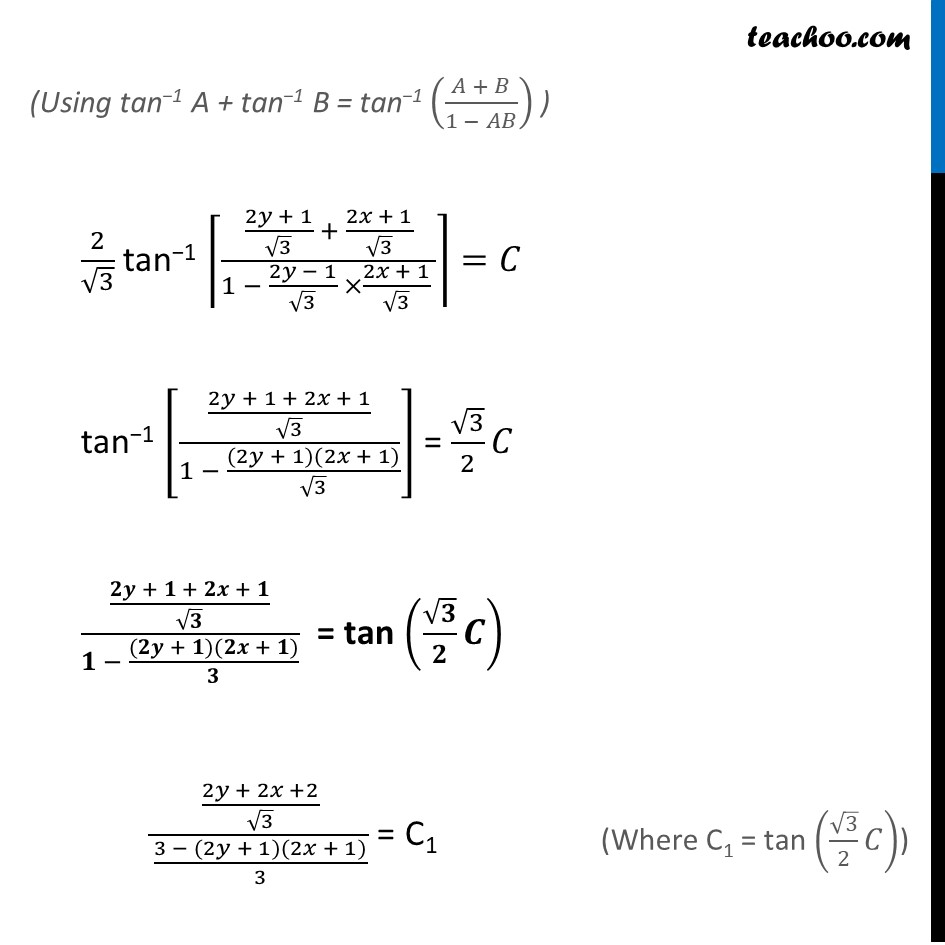
Misc 5 Show that the general solution of the differential equation 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥+(𝑦^2+𝑦+1)/(𝑥^2+𝑥+1)=0 is given by (𝑥+𝑦+1)=A(1−𝑥−𝑦−2𝑥𝑦), where A is parameter. 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥+(𝑦^2 + 𝑦 + 1)/(𝑥^2 + 𝑥 + 1) = 0 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=(−(𝑦^2 + 𝑦 + 1))/(𝑥^2 + 𝑥 + 1) 𝒅𝒚/(𝒚^𝟐 + 𝒚 + 𝟏)=(−𝒅𝒙)/(𝒙^𝟐 + 𝒙 + 𝟏) 𝑑𝑦/(𝑦^2 +2(1/2)𝑦 + (1/2)^2− (1/2)^2+ 1)=(−𝑑𝑥)/(𝑥^2 + 2(1/2)𝑥 + (1/2)^2− (1/2)^2+ 1) 𝑑𝑦/((𝑦 + 1/2)^2+ 3/4)=(−𝑑𝑥)/((𝑥 + 1/2)^2+ 3/4) 𝒅𝒚/((𝒚 + 𝟏/𝟐)^𝟐+ (√𝟑/𝟐)^𝟐 )=(−𝒅𝒙)/((𝒙 + 𝟏/𝟐)^𝟐+ (√𝟑/𝟐)^𝟐 ) Integrating both sides ∫1▒𝑑𝑦/((𝑦 + 1/2)^2 +(√3/2)^2 ) = − ∫1▒𝑑𝑥/((𝑥 + 1/2)^2 +(√3/2)^2 ) 𝟐/√𝟑 tan−1 ((𝒚 + 𝟏/𝟐)/(√𝟑/𝟐)) = (−𝟐)/√𝟑 tan−1 ((𝒙 + 𝟏/𝟐)/(√𝟑/𝟐)) + C 2/√3 ["tan−1 " ((2𝑦 + 1)/√3)" + tan−1 " ((2𝑥 + 1)/√3)] = C (Using tan−1 A + tan−1 B = tan−1 ((𝐴 + 𝐵)/(1 − 𝐴𝐵)) ) 2/√3 "tan−1" ⌈((2𝑦 + 1)/√3 + (2𝑥 + 1)/√3)/(1 − (2𝑦 − 1)/√3 ×(2𝑥 + 1)/√3 )⌉=𝐶 "tan−1" [((2𝑦 + 1 + 2𝑥 + 1)/√3)/(1 − ((2𝑦 + 1)(2𝑥 + 1))/√3)] = √3/2 𝐶 ((𝟐𝒚 + 𝟏 + 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟏)/√𝟑)/(𝟏 − ((𝟐𝒚 + 𝟏)(𝟐𝒙 + 𝟏))/𝟑) = tan (√𝟑/𝟐 𝑪) ((2𝑦 + 2𝑥 +2)/√3)/((3 − (2𝑦 + 1)(2𝑥 + 1))/3) = C1 (√3(2𝑦 + 2𝑥 + 2))/(3 − (4𝑥𝑦 + 2𝑦 + 2𝑥 + 1) ) = C 2√𝟑 (x + y + 1) = C1 (𝟑−𝟒𝒙𝒚−𝟐𝒙−𝟐𝒚−𝟏) 2√3 (x + y + 1) = C1 (2−4𝑥𝑦−2𝑥−2𝑦) 2√3 (x + y + 1) = C1 × 2 (1−𝑥−𝑦−𝑥𝑦) √𝟑 (x + y + 1) = C1 (1 − x − y − 2xy) is the required general solution