Examples
Example 2
Example 3 (i) Important
Example 3 (ii)
Example 4 Important
Example 5 Important
Example 6 Important
Question 1 Deleted for CBSE Board 2024 Exams
Question 2 Deleted for CBSE Board 2024 Exams You are here
Question 3 Deleted for CBSE Board 2024 Exams
Question 4 Important Deleted for CBSE Board 2024 Exams
Question 5 Important Deleted for CBSE Board 2024 Exams
Question 6 Important Deleted for CBSE Board 2024 Exams
Question 7 Important Deleted for CBSE Board 2024 Exams
Last updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo


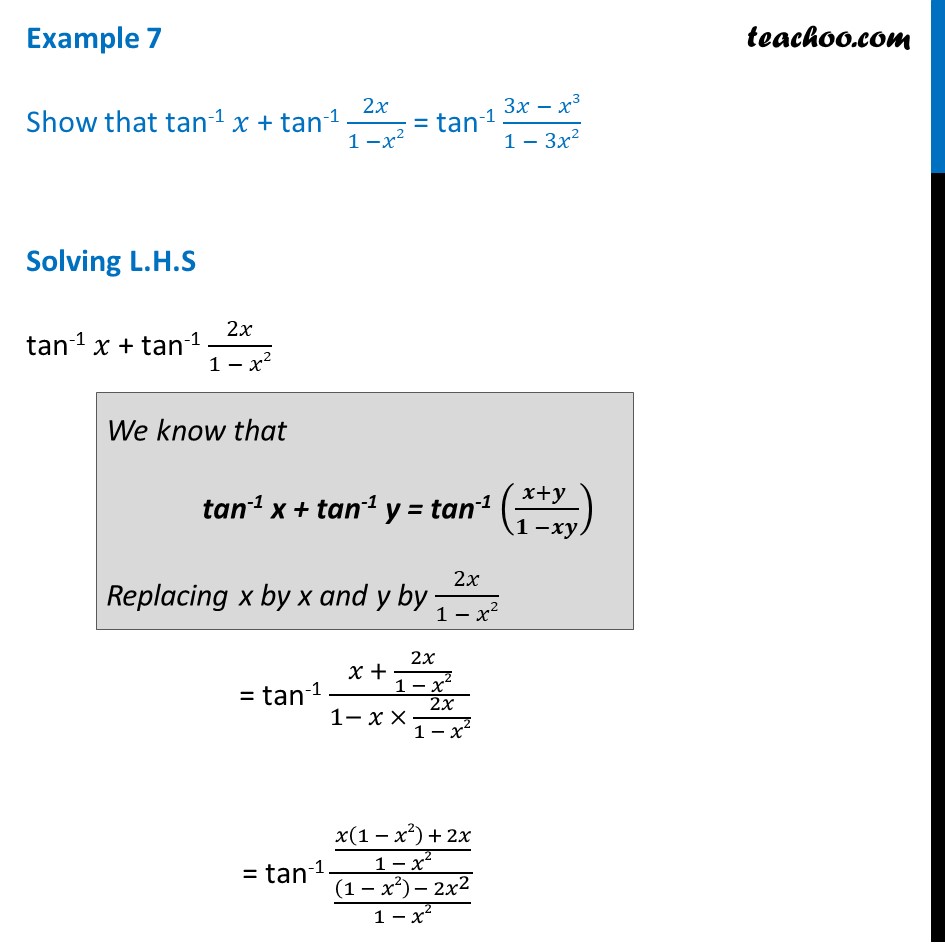
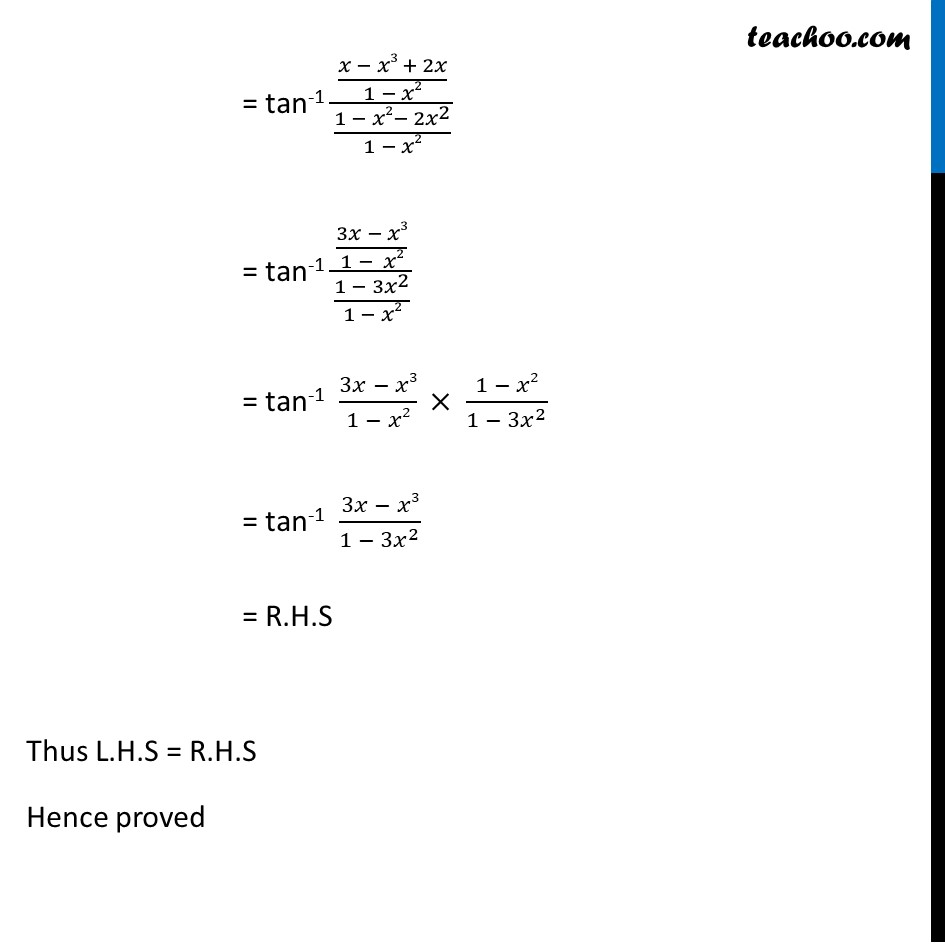
Question 2 Show that tan-1 𝑥 + tan-1 2𝑥/(1 −𝑥2) = tan-1 (3𝑥 − 𝑥3)/(1 − 3𝑥2) Solving L.H.S tan-1 𝑥 + tan-1 2𝑥/(1 − 𝑥2) = tan-1 (𝑥 + 2𝑥/(1 − 𝑥2))/(1− 𝑥 × 2𝑥/(1 − 𝑥2)) = tan-1 ((𝑥(1 − 𝑥2) + 2𝑥)/(1 − 𝑥2))/(〖(1 − 𝑥2) − 2𝑥〗^2/(1 − 𝑥2)) We know that tan-1 x + tan-1 y = tan-1 ((𝒙+𝒚 )/(𝟏 −𝒙𝒚)) Replacing x by x and y by 2𝑥/(1 − 𝑥2) = tan-1 ((𝑥 − 𝑥3 + 2𝑥)/(1 − 𝑥2))/(〖1 − 𝑥2− 2𝑥〗^2/(1 − 𝑥2)) = tan-1 ((3𝑥 − 𝑥3)/(1 − 𝑥2))/(〖1 − 3𝑥〗^2/(1 − 𝑥2)) = tan-1 (3𝑥 − 𝑥3)/(1 − 𝑥2) × (1 − 𝑥2)/〖1 − 3𝑥〗^2 = tan-1 (3𝑥 − 𝑥3)/〖1 − 3𝑥〗^2 = R.H.S Thus L.H.S = R.H.S Hence proved